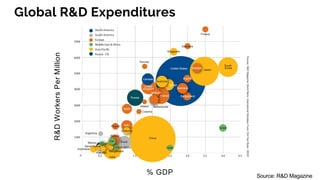
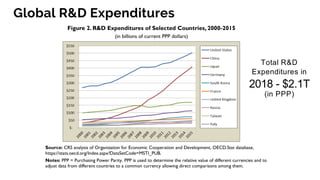
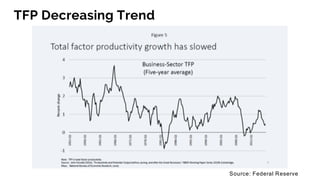
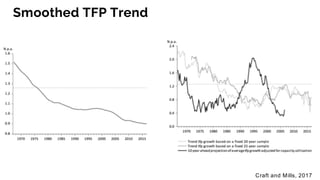
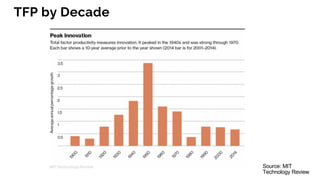
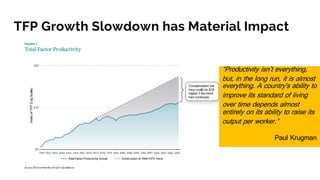
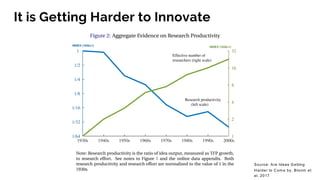
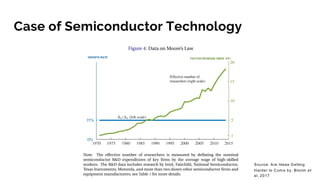
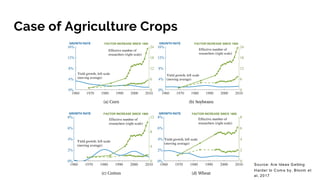
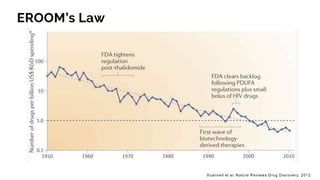
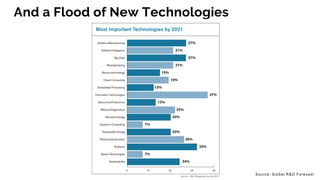
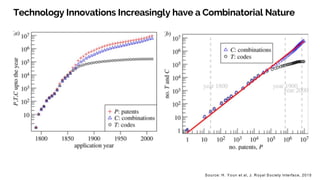
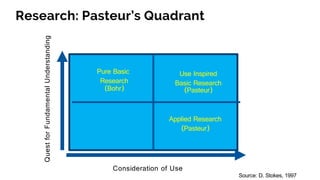
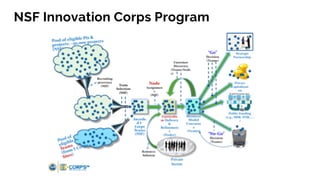
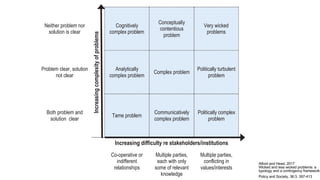
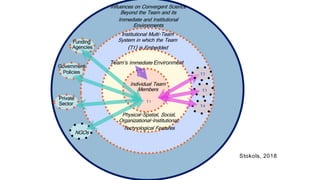
The document discusses the evolution of research to innovation in systems and control, emphasizing the importance of interconnected feedback loops between research and commercialization, as opposed to a linear model. It highlights recent trends, challenges, and the need for interdisciplinary collaboration to address complex 'wicked problems' in various sectors such as healthcare, environmental issues, and advanced manufacturing. The paper concludes by advocating for a balanced ecosystem that fosters both deep disciplinary and transdisciplinary research to enhance innovation and societal impact.