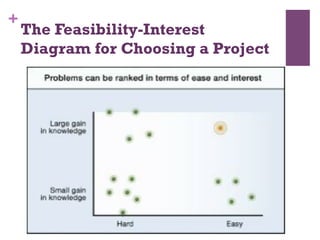
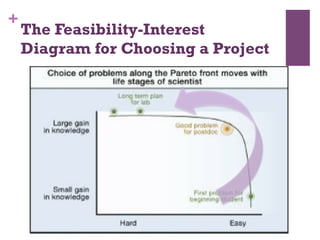
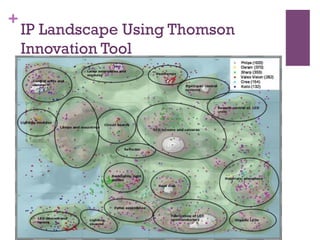
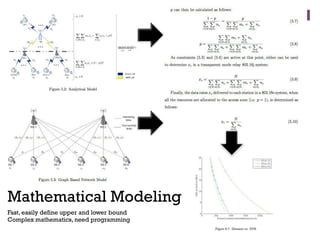
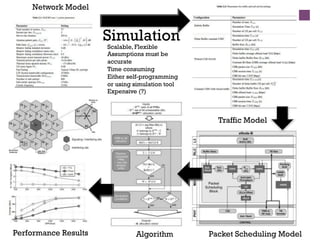
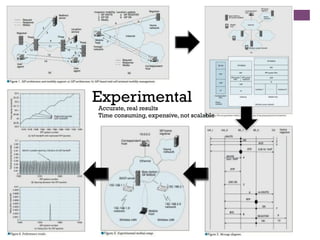
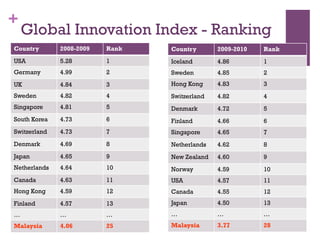
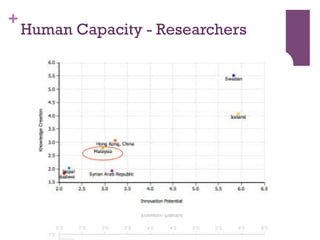
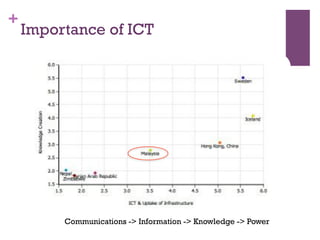
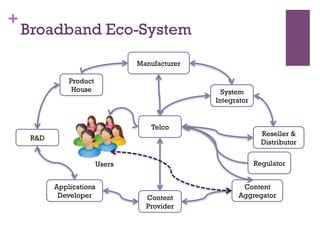
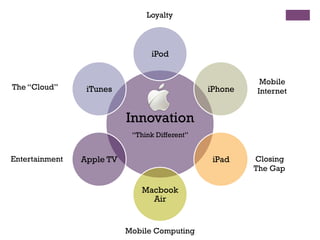
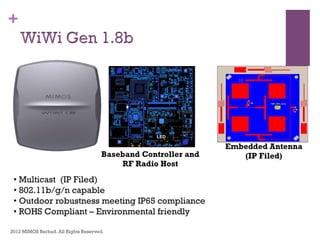
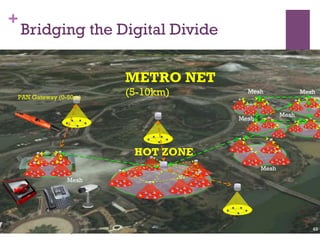
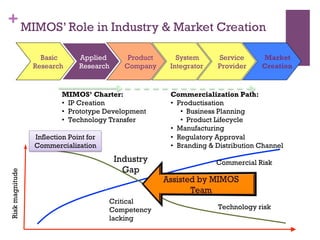
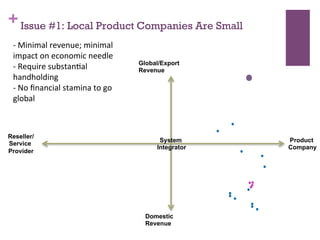
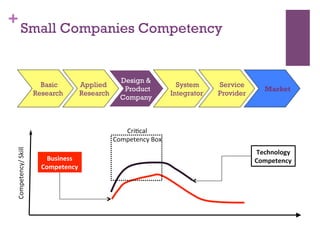
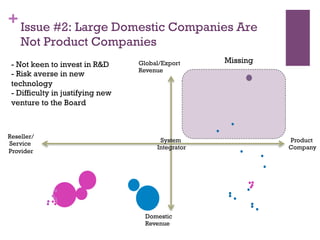
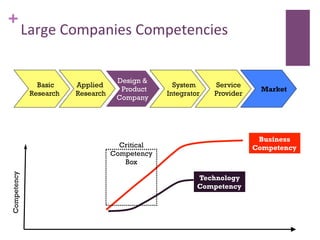
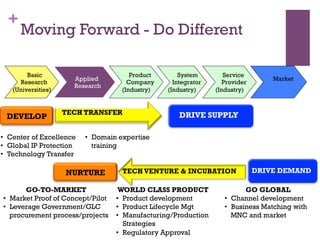
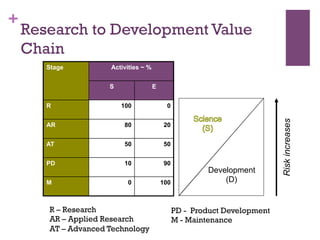
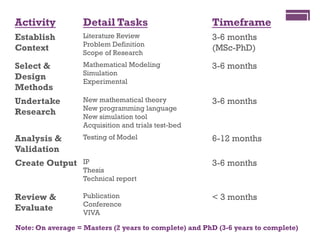
The document discusses research challenges and commercialization challenges. It provides definitions of basic research and applied research. It explains the differences between research and development approaches. It outlines typical activity details and timeframes for research processes like establishing context, selecting and designing methods, undertaking research, analysis and validation, and review and evaluation. It also discusses managing researchers, choosing good scientific problems, and MIMOS' role in supporting industry and market creation through technology creation, research, and commercialization.






![How To Choose a Good
Scientific Problem?
[Excerpts from the Article “How To Choose a Good Scientific Problem” by Uri Alon]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/researchandcommercializationchallenges-130830044436-phpapp02/85/Research-and-Commercialisation-Challenges-8-320.jpg)