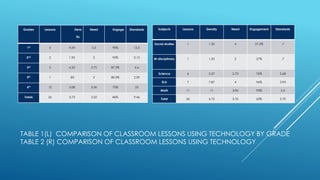
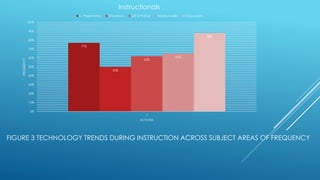
Teachers are integrating various technologies in the classroom to facilitate instruction, engage students, and meet standards according to a study of 26 lessons across four elementary schools. Computer programs, document cameras, interactive whiteboards, and other technologies were commonly used by teachers and students. Patterns showed a correlation between grade level, learning activities, and technology engagement. The study concluded that student-centered, creative and communication-focused technology instruction can help meet standards, but more equal analysis across subjects and grades would strengthen the findings.