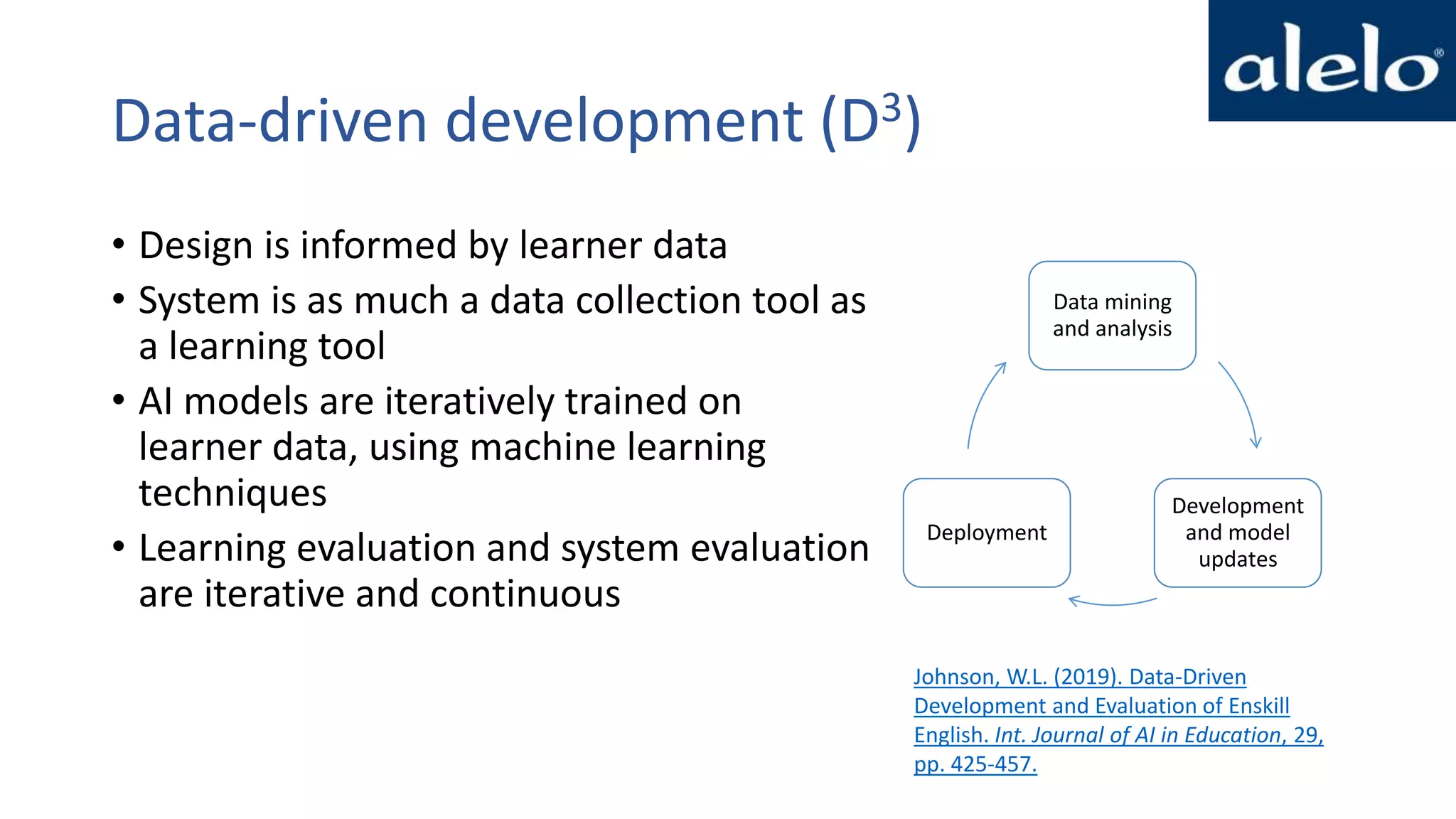
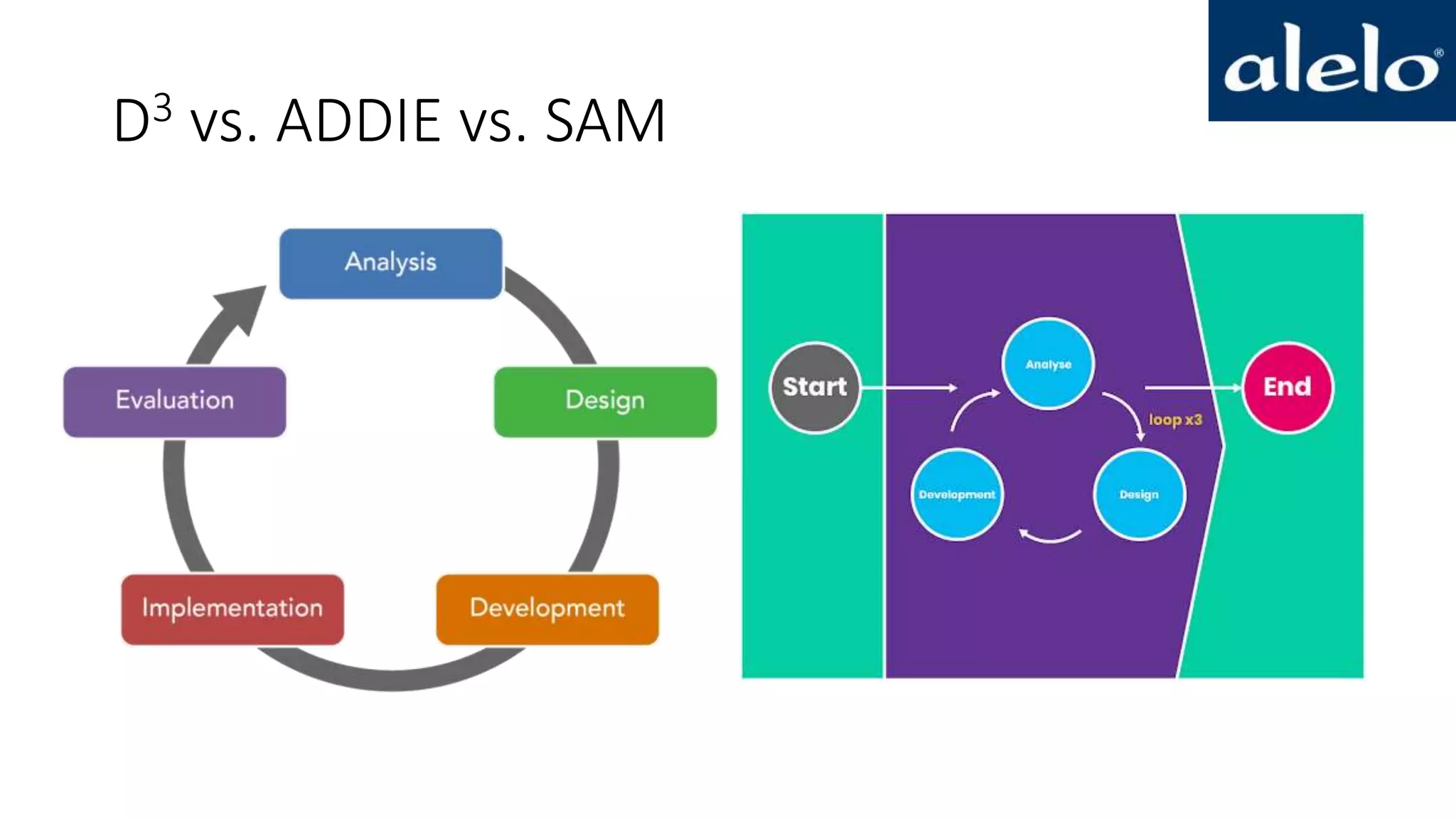
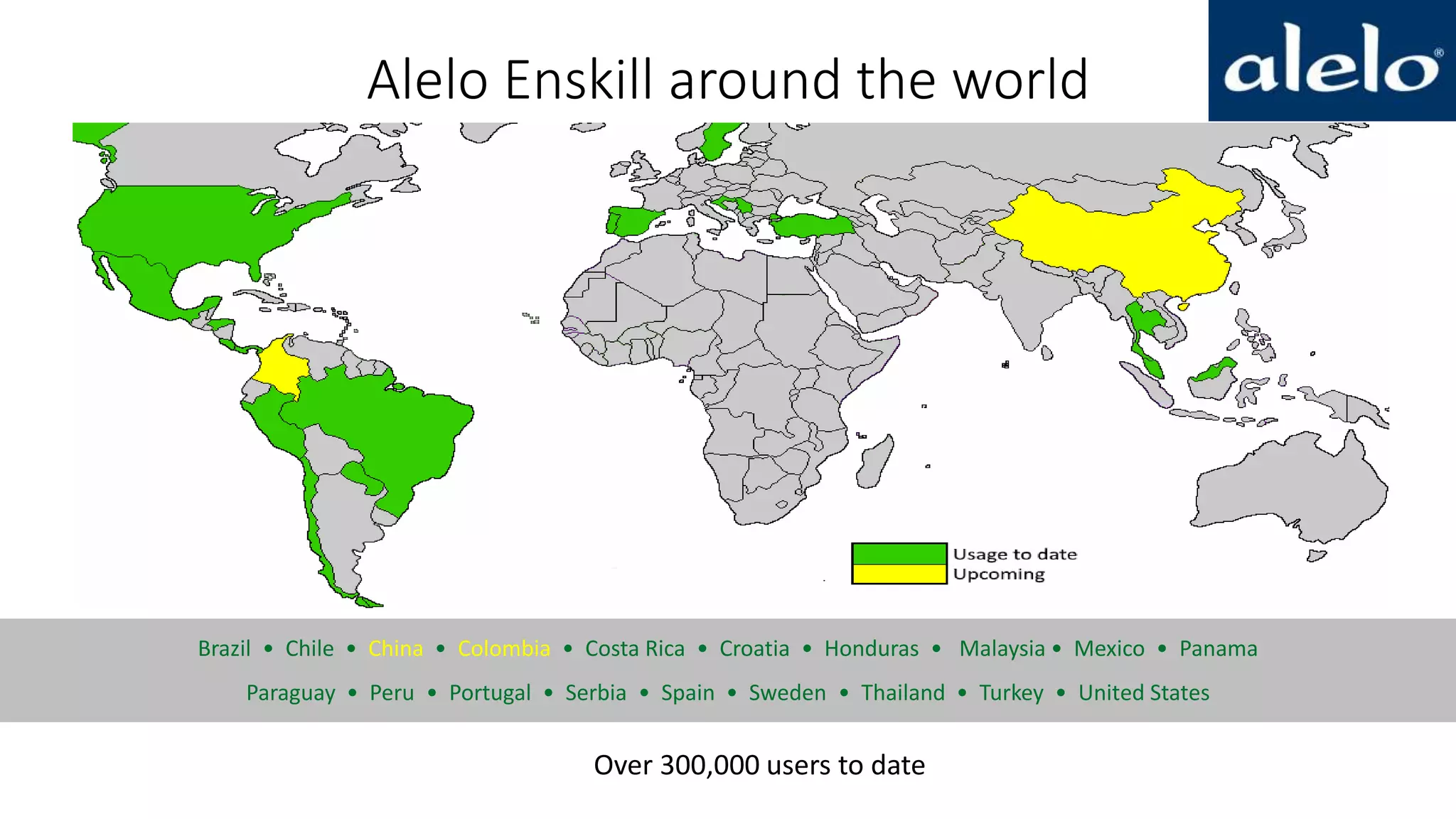
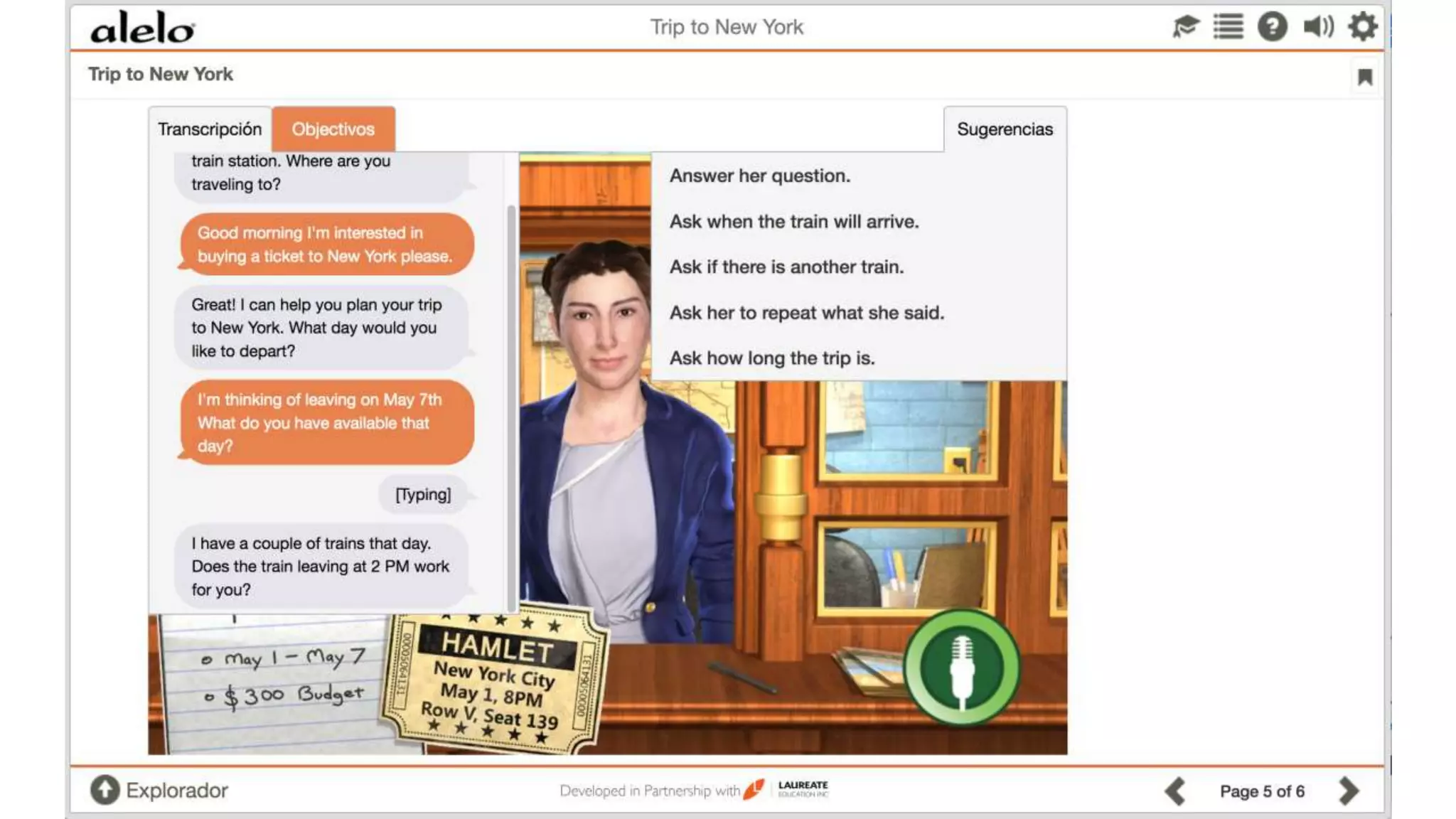
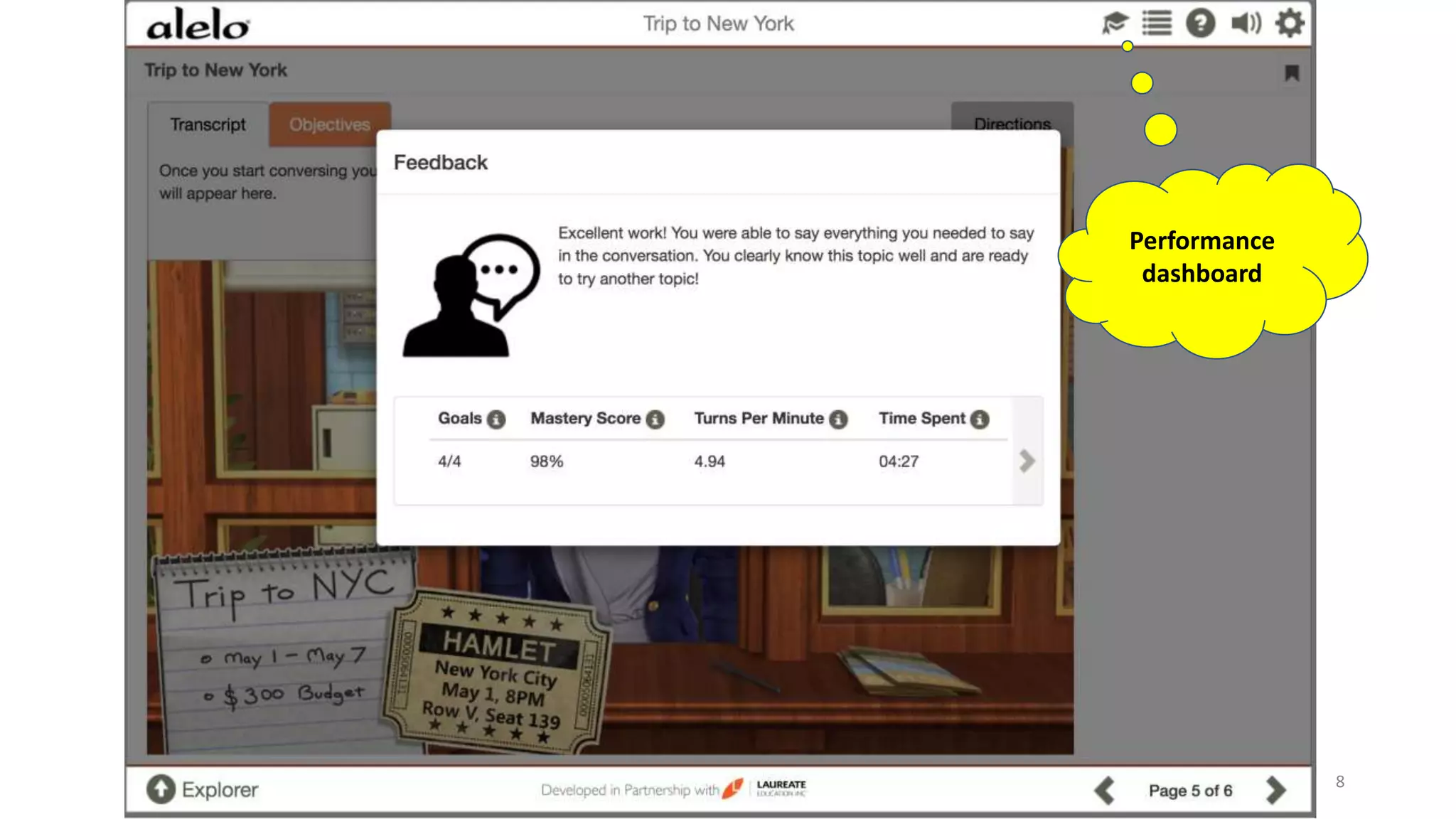
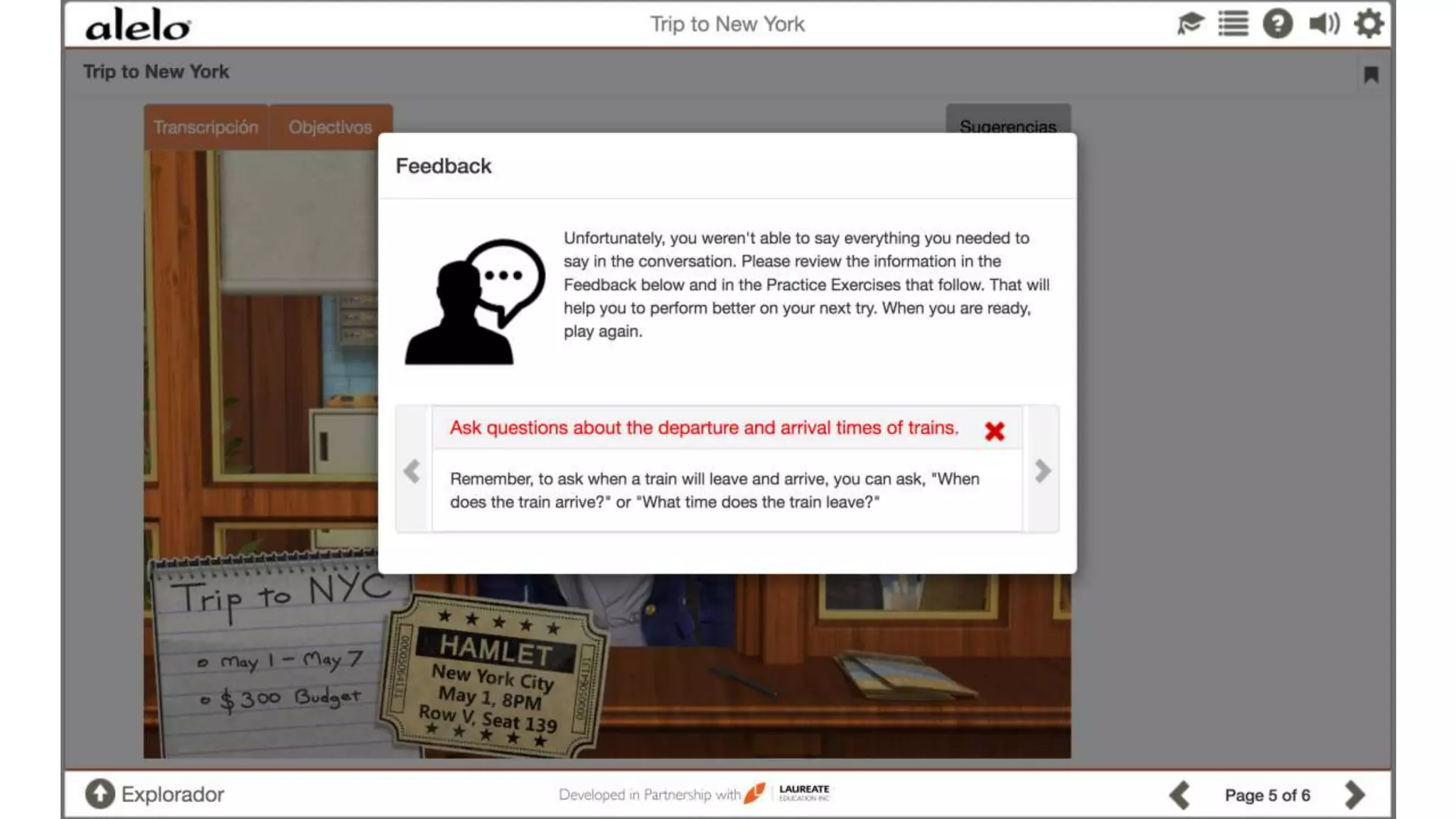
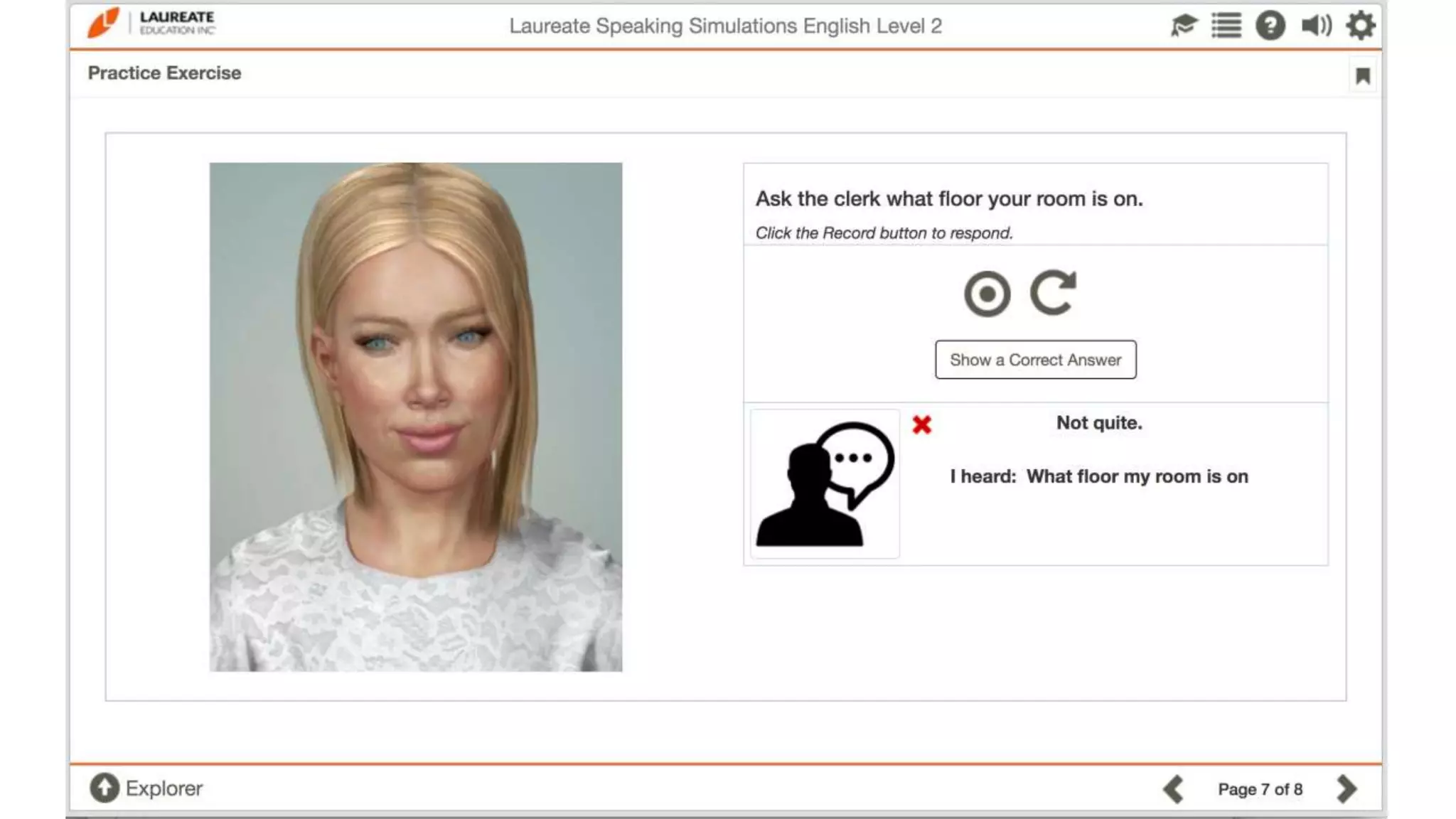
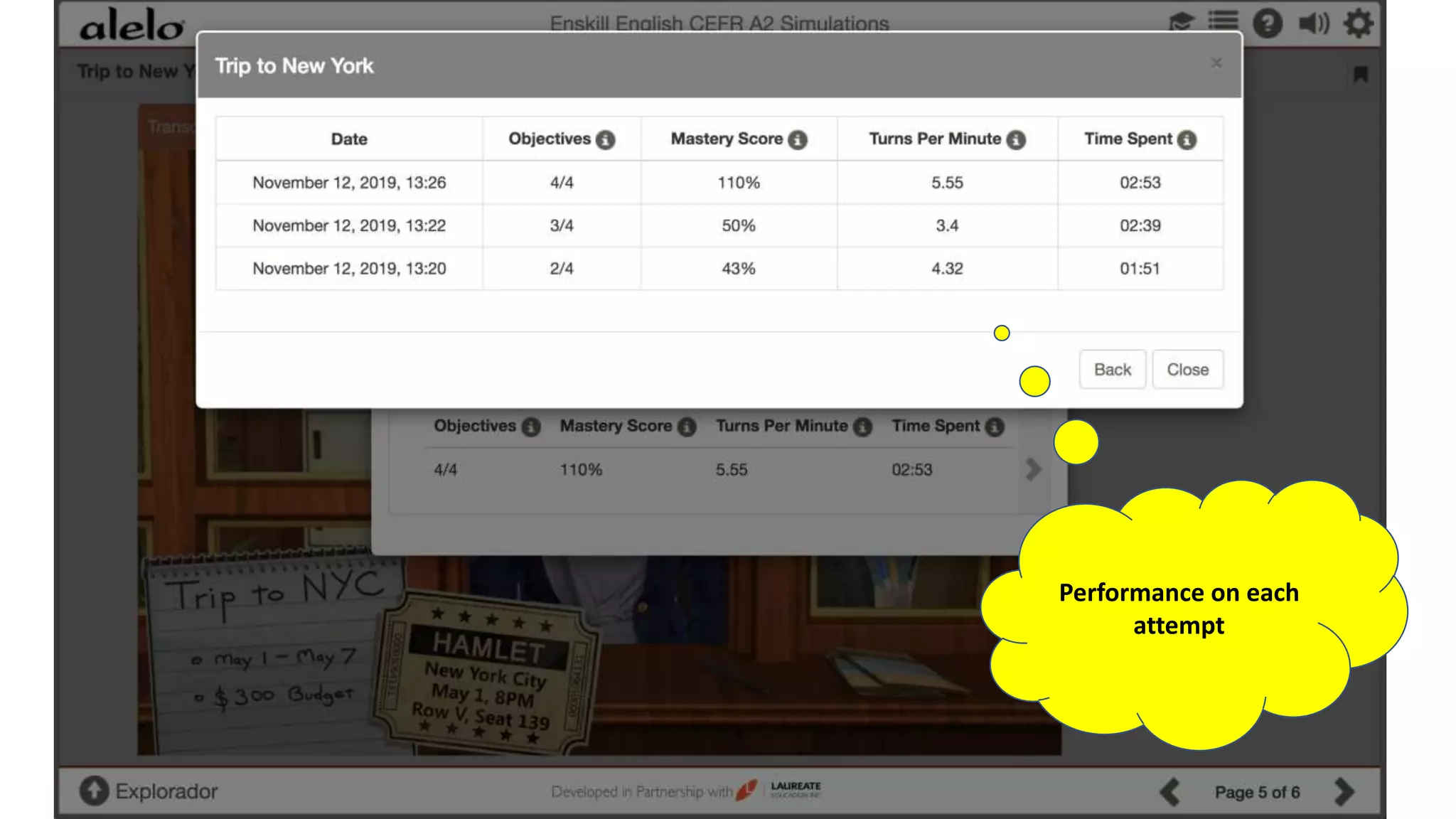
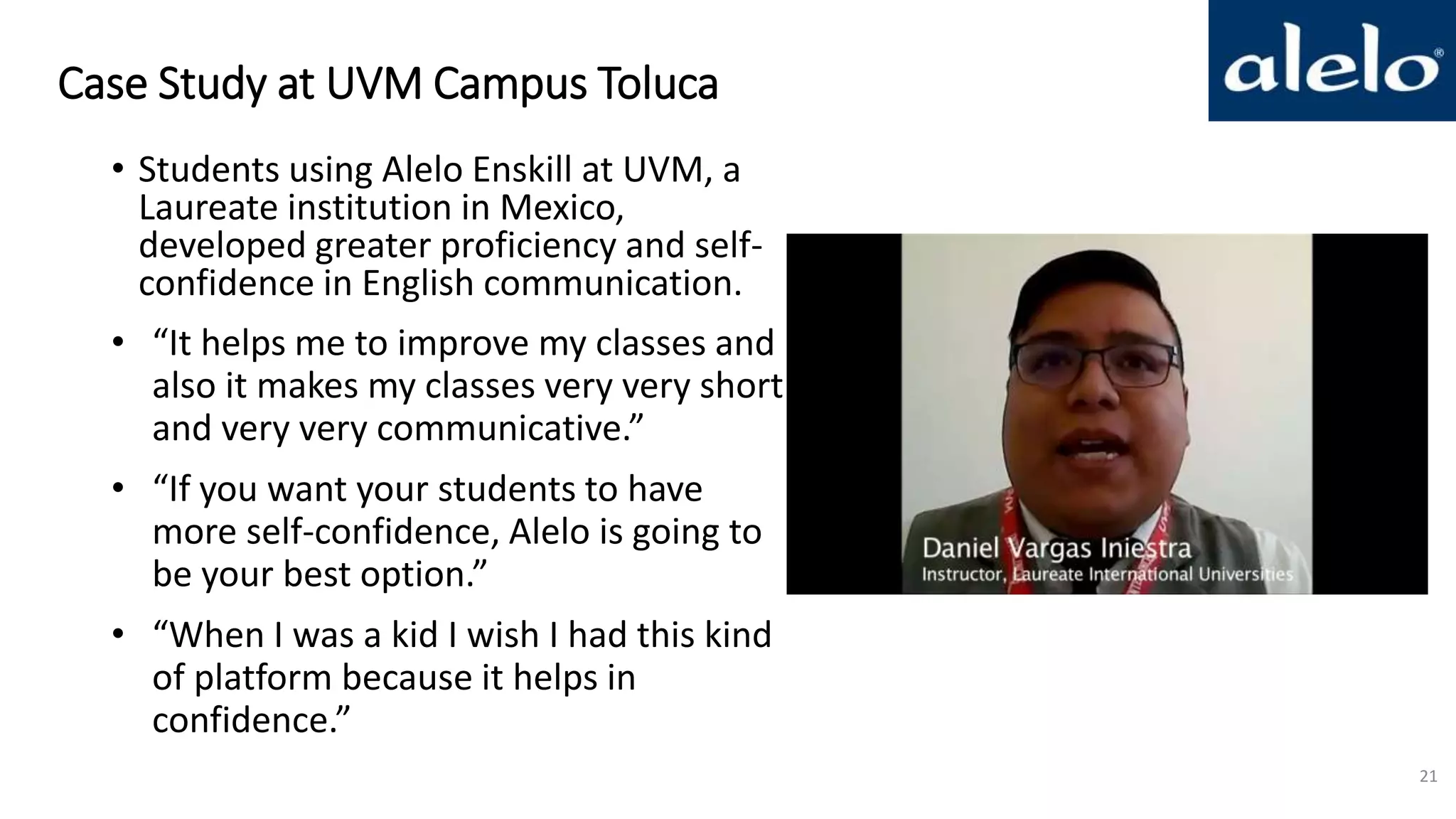
The document discusses the data-driven development and evaluation of Alelo's Enskill English program, emphasizing the integration of learner data and AI models to enhance learning experiences. It highlights various evaluations conducted in different educational contexts, showcasing improvements in learner performance and engagement through the use of simulations. The findings support the effectiveness of agile and iterative evaluation methods in educational AI development.