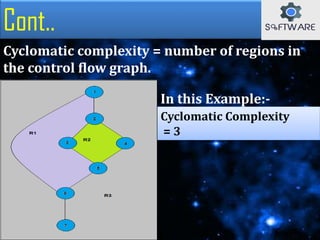
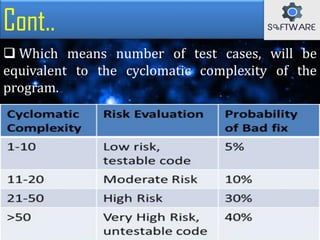
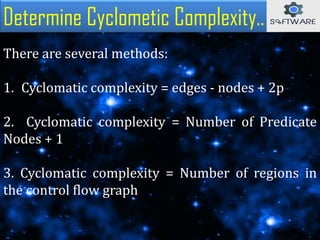
The document discusses cyclomatic complexity, a software metric developed by McCabe in 1976, which measures the number of linearly independent paths in a program and helps assess its complexity. It outlines various methods to calculate cyclomatic complexity, emphasizes its importance in software testing, and suggests that a complexity score above ten can increase the likelihood of errors and maintenance challenges. Cyclomatic complexity aids developers and testers by ensuring all paths are executed during testing and by evaluating program risks.








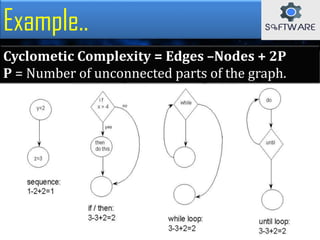
![Another Example..
[1—2—6]
[1—2—3—5—2—6]
[1—2—3—4—5—2—6]
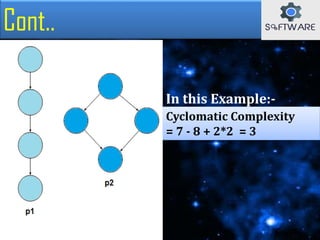
Cyclomatic Complexity
= 7 - 6 + 2*1 = 3
In this Example:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cyclometiccomplexity-180412151659/85/Cyclomatic-complexity-11-320.jpg)