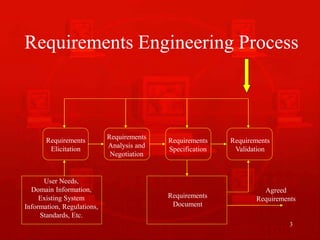
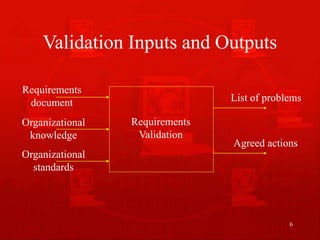
1. Requirements validation ensures the requirements document accurately describes the system by checking for completeness, consistency, conformance to standards, and resolving any conflicts or ambiguities.
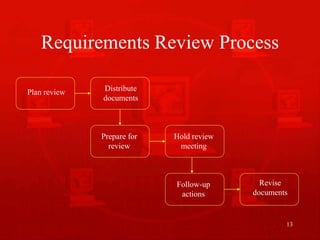
2. The validation process involves reviewing the final requirements document, then producing a list of any problems found and agreed actions to address them.
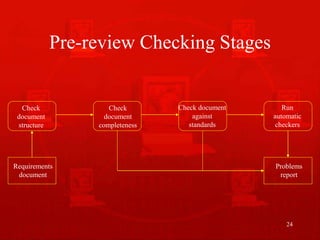
3. Reviews are carried out by a group analyzing the requirements in detail, and pre-review checking can reduce costs by identifying basic issues beforehand.