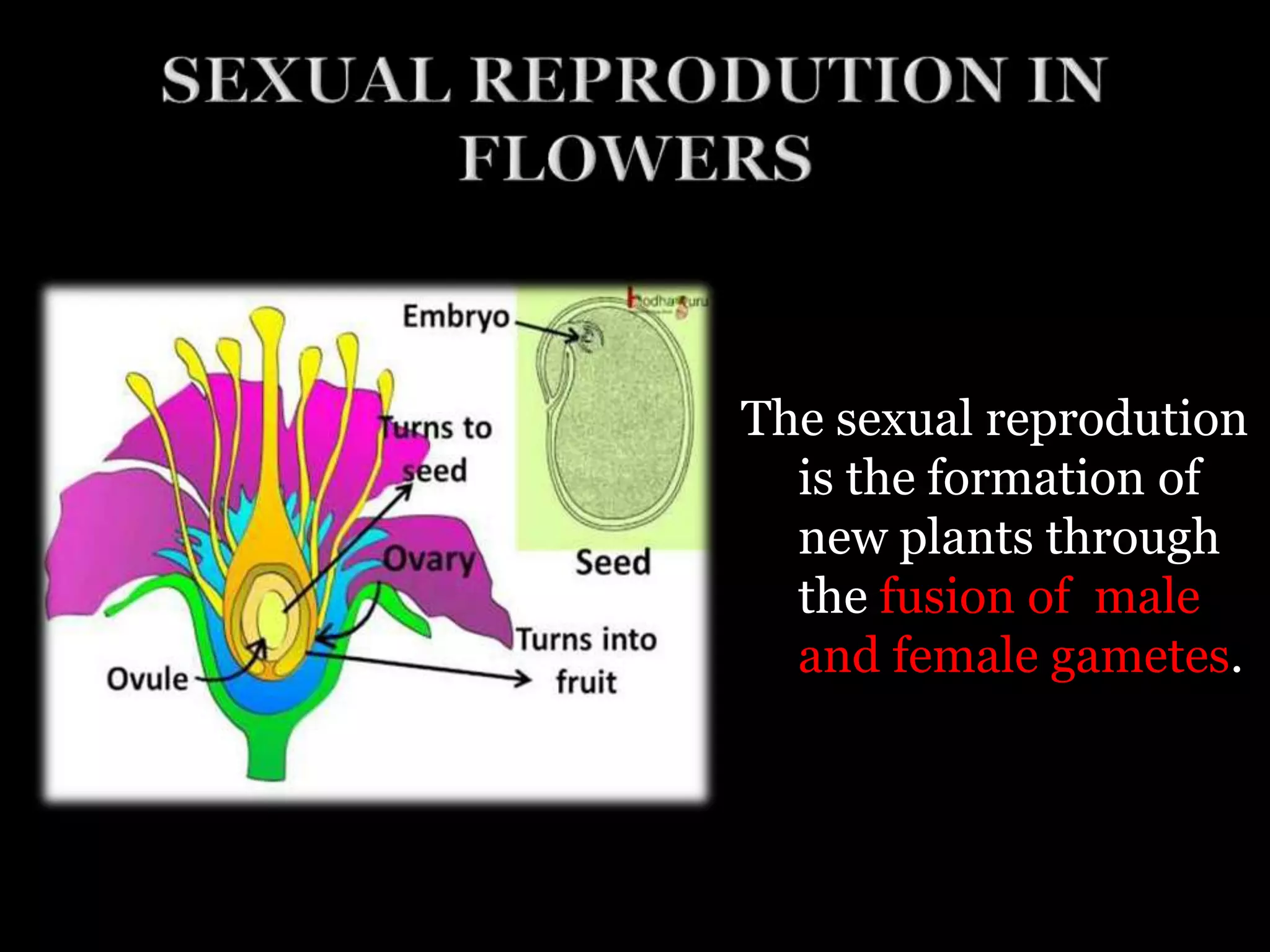
This document discusses different modes of reproduction in organisms. It explains that bacteria reproduce asexually through binary fission, fungi through spore formation, and hydra through budding. Sexual reproduction in plants involves the fusion of male and female gametes, where the male reproductive organ is the stamen that contains pollen grains, and the female is the pistil containing the ovary. Pollination is when pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma, and can involve insects or other animals as pollinators. After pollination, the pollen tube grows and the male gametes fuse with the egg and polar nuclei to form a zygote and endosperm that develop into an embryo.