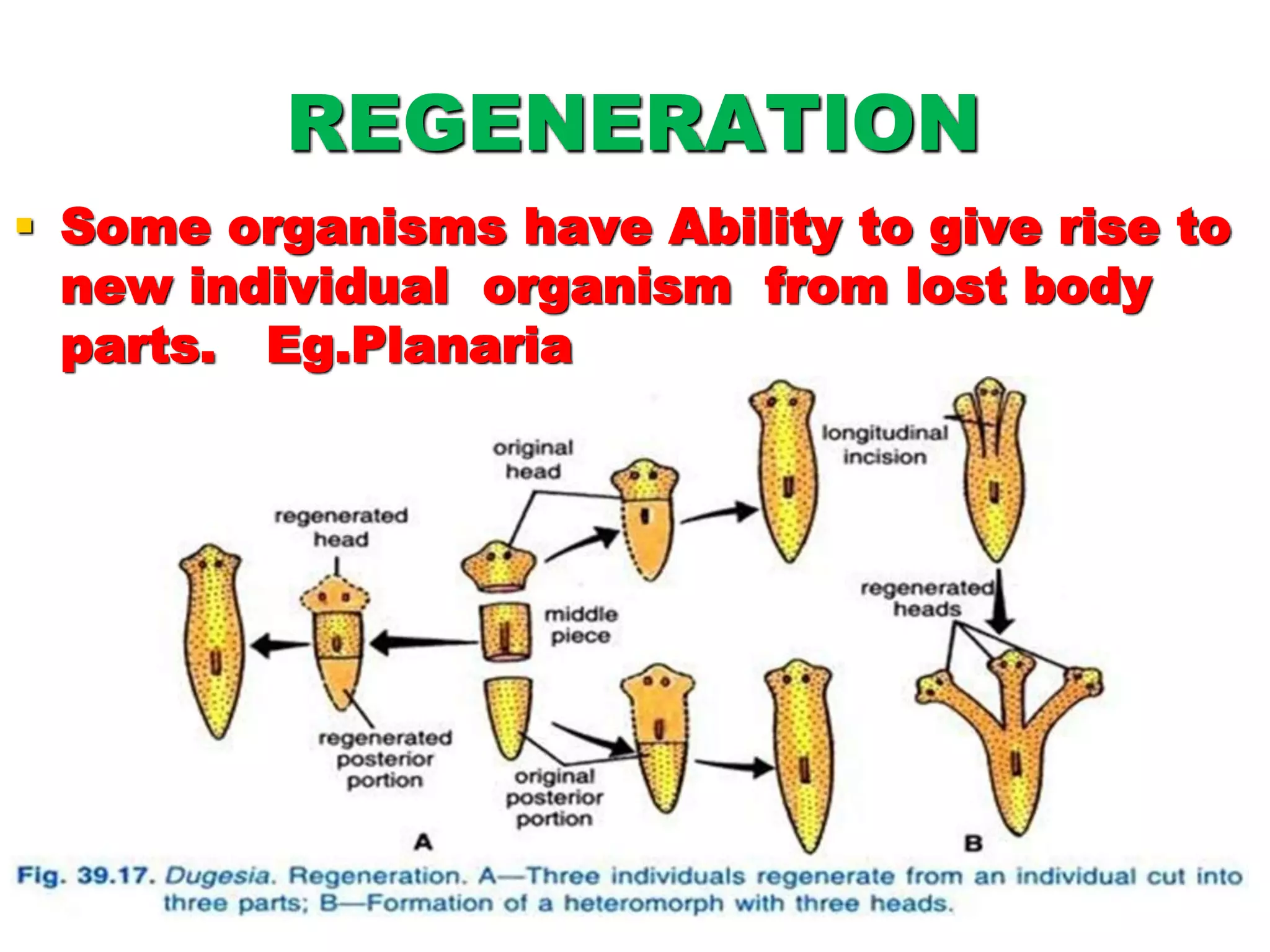
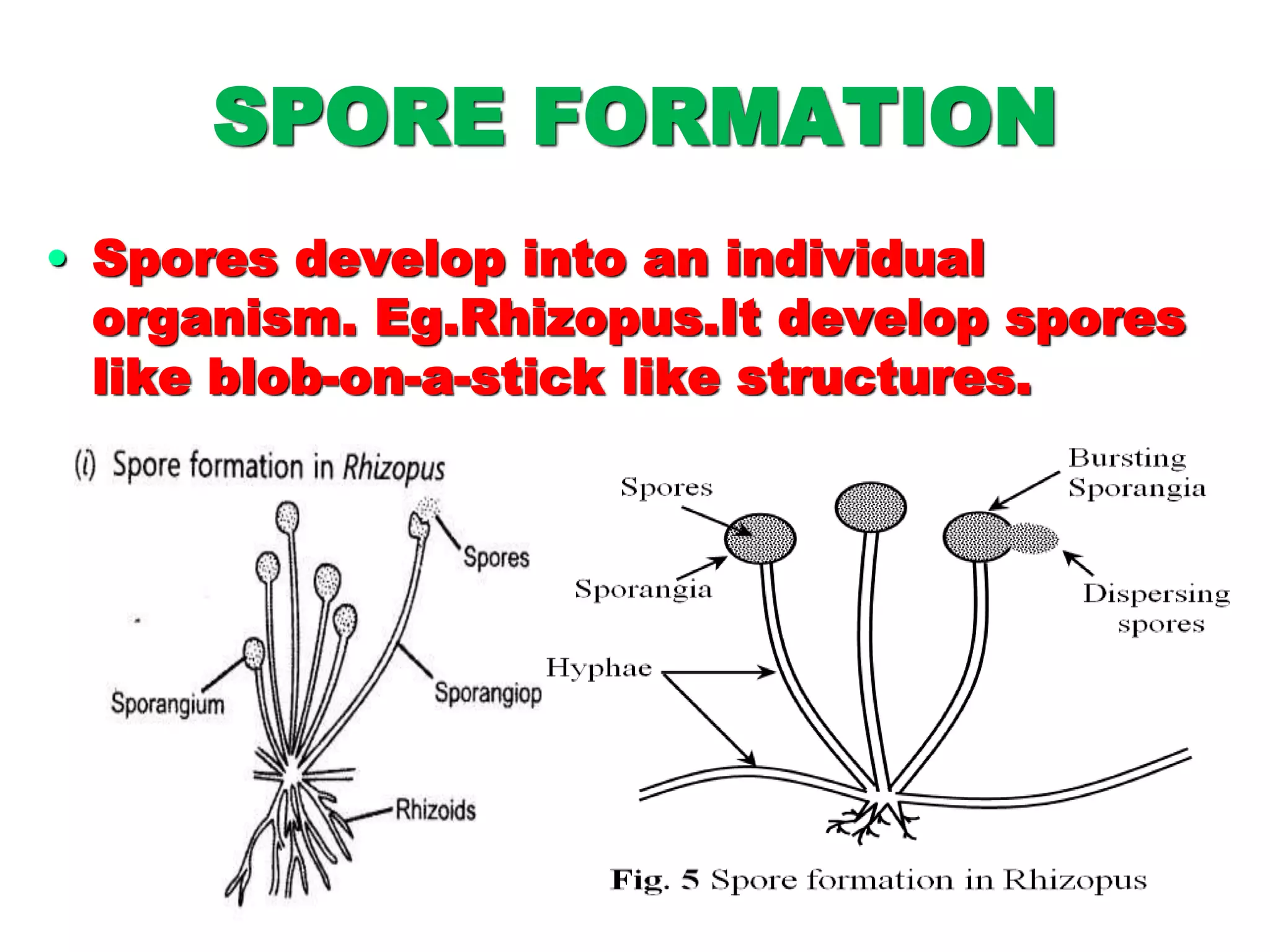
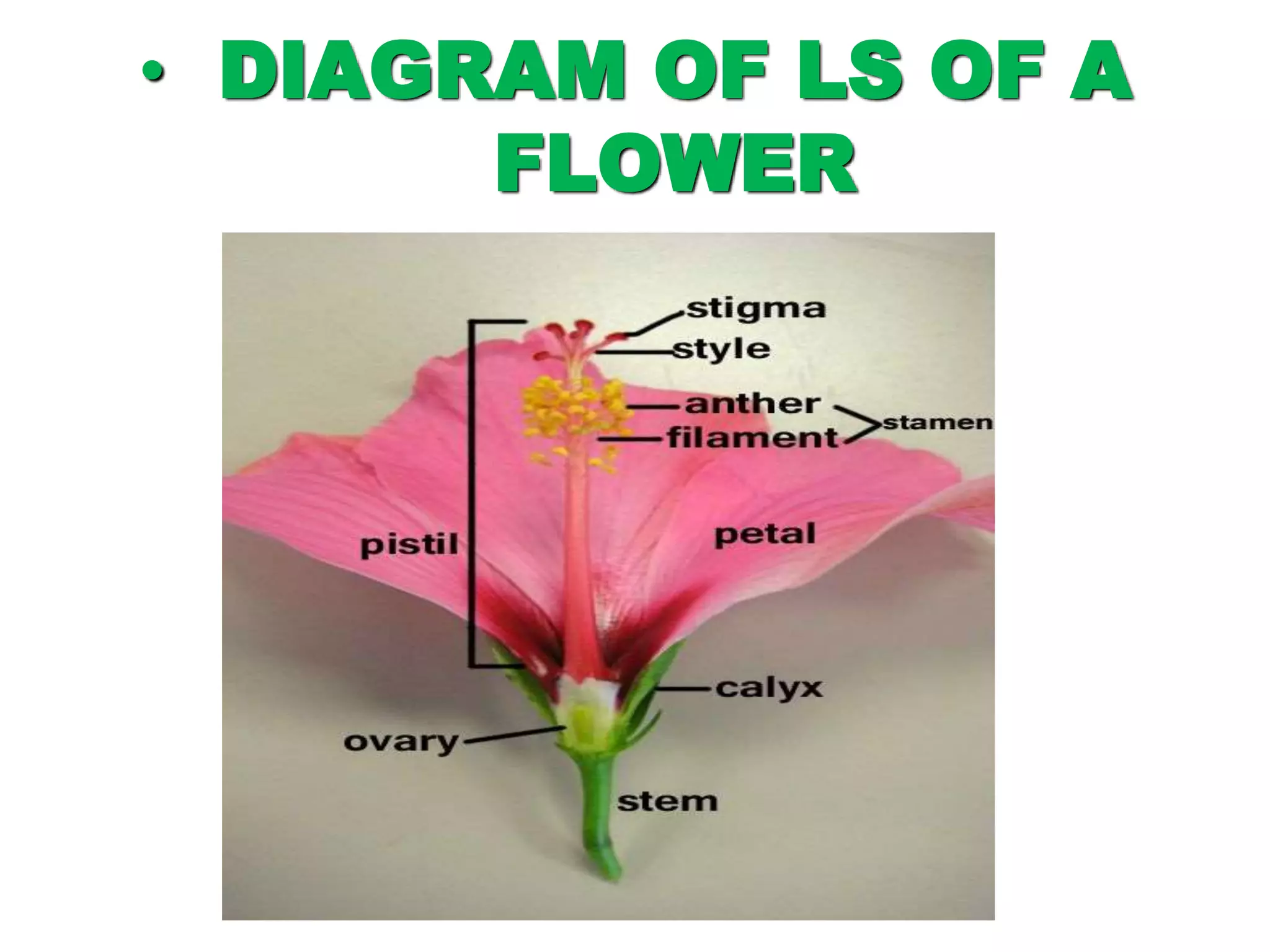
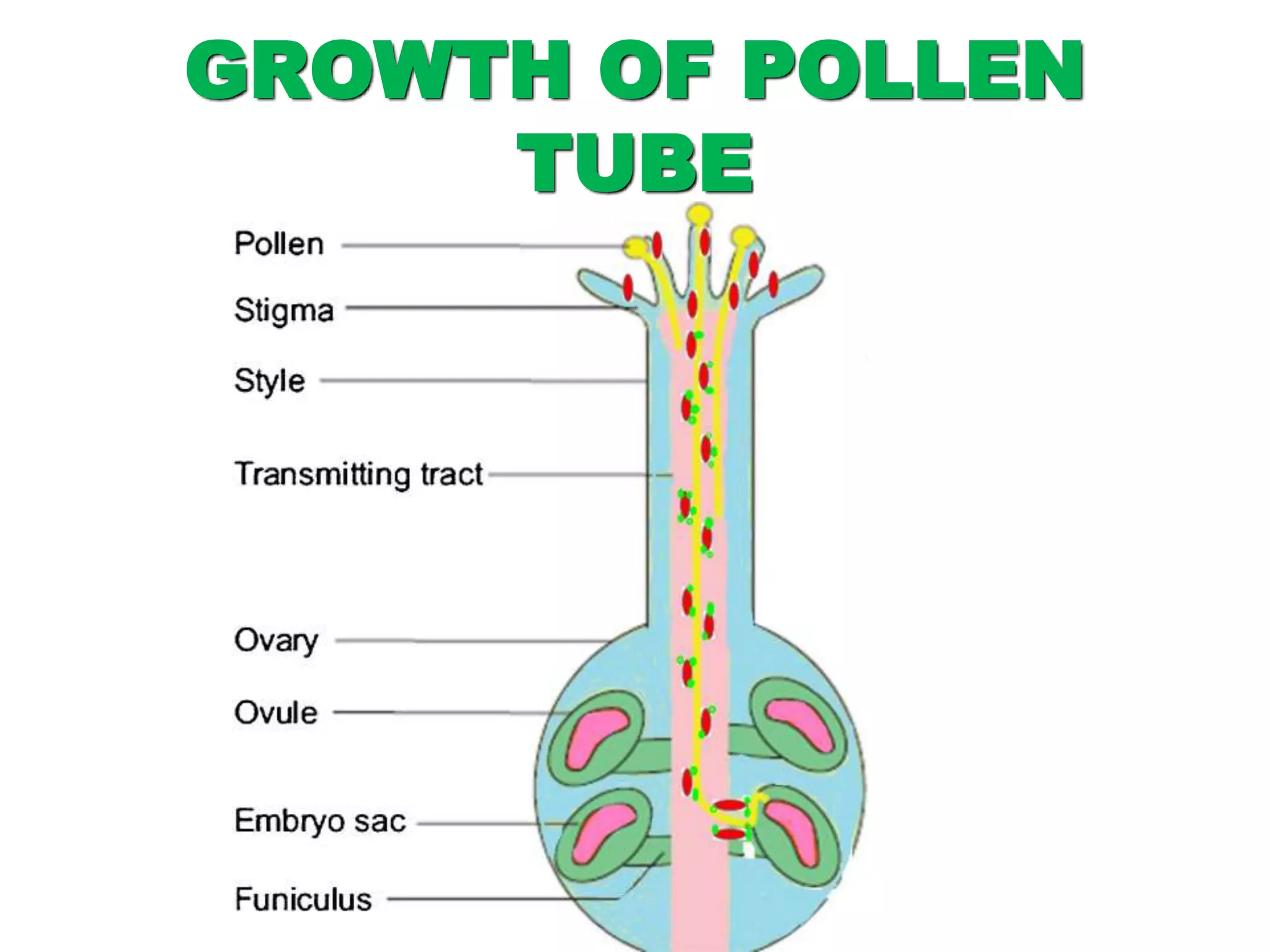
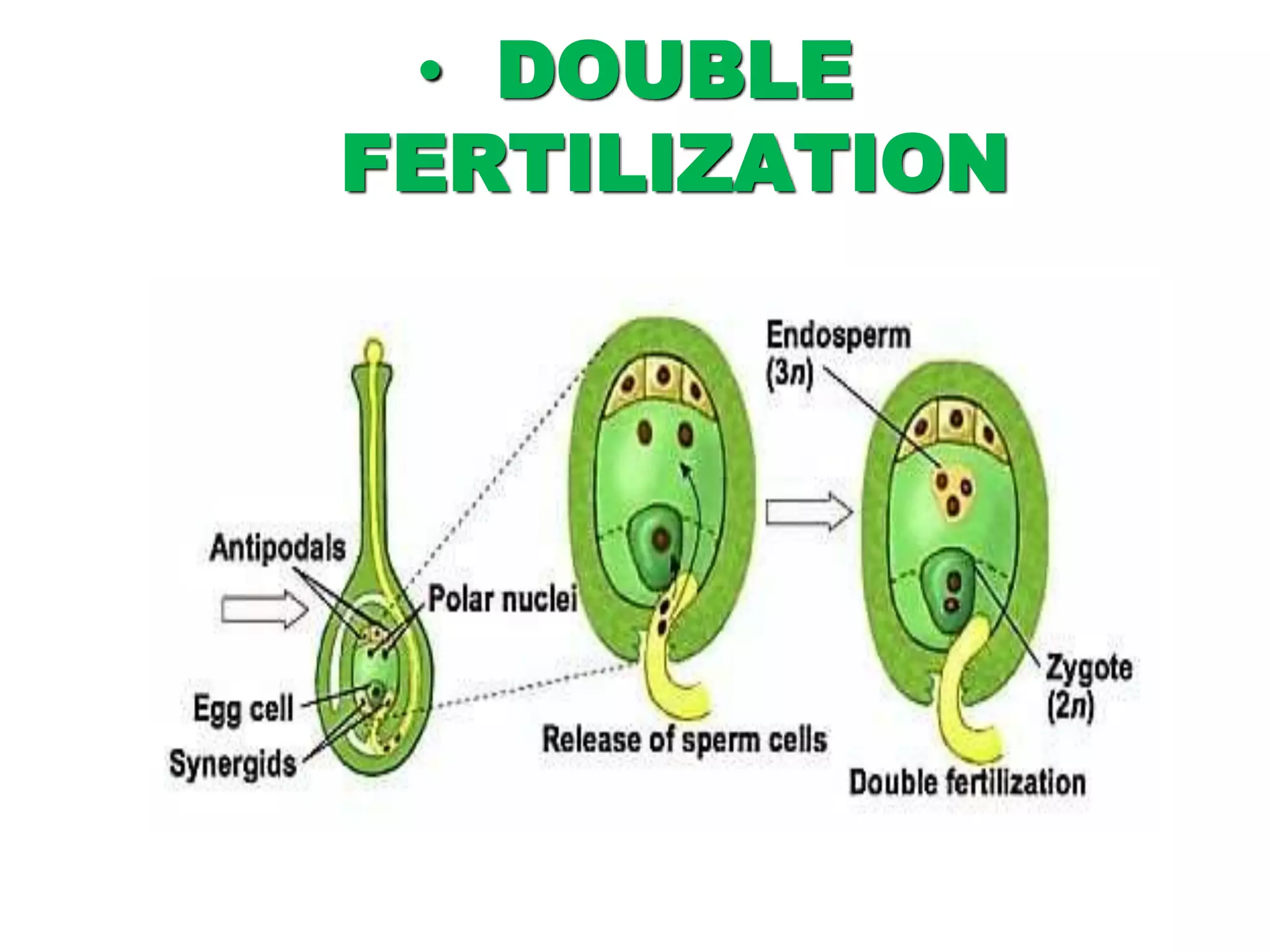
This document discusses different types of reproduction in organisms. It describes asexual reproduction, which involves a single parent and can occur through fission, fragmentation, budding, regeneration, or vegetative propagation. It also explains sexual reproduction in flowering plants, including the parts of the flower, pollination, double fertilization where the male gametes fuse with the egg cell and central cell, and the formation of the embryo and seed. Various examples of different modes of asexual reproduction like binary fission in amoeba and multiple fission in Plasmodium are provided.