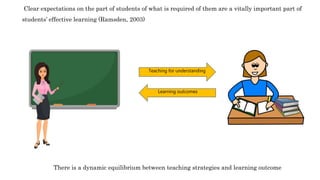
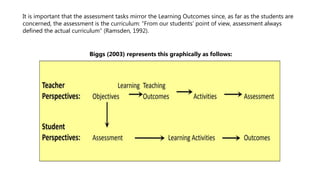
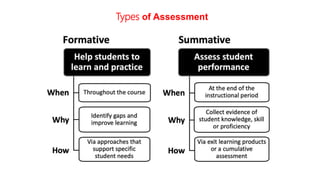
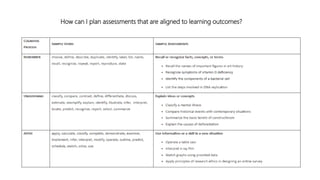
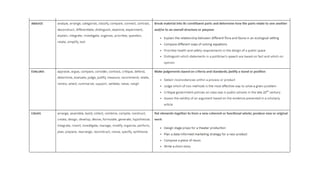
The document discusses aligning learning outcomes, teaching strategies, and assessments. It defines learning outcomes as statements of what students should know and be able to do after learning. Learning activities involve students solving tasks to learn. There are three types of assessment: assessment for learning uses formative feedback, assessment as learning involves student self-reflection, and assessment of learning makes summative judgments on achievement. Proper alignment involves defining outcomes, choosing teaching methods to achieve them, and assessing if they were achieved.