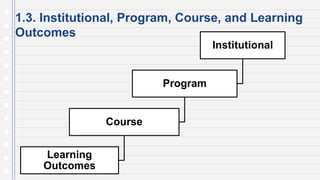
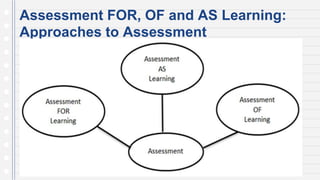
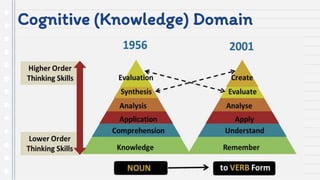
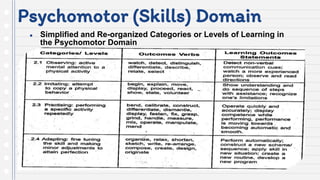
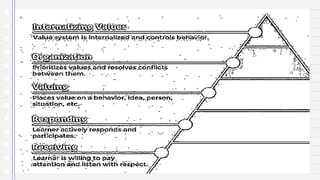
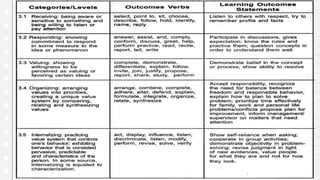
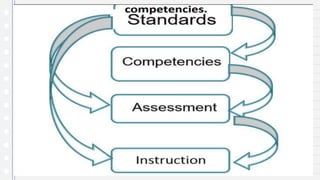
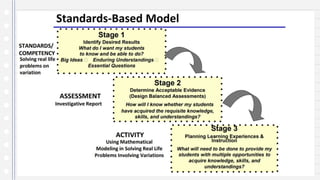
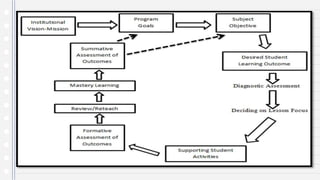
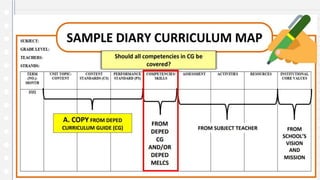
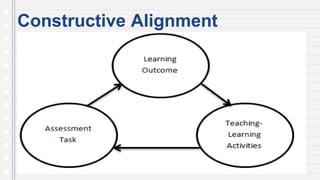
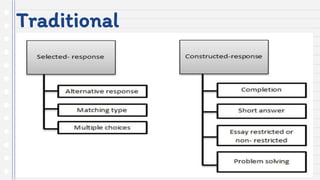
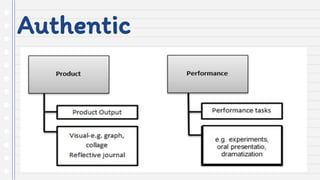
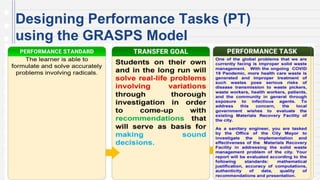
This document discusses key concepts in assessing student learning outcomes. It explains that outcome assessment is used to determine if a program is achieving desired learning results. There are various assessment methods, including traditional tests as well as authentic assessments like portfolios and performance tasks. Scoring rubrics are used to evaluate student work objectively according to established criteria. Assessment should account for student multiple intelligences and allow diverse ways for demonstrating knowledge. The goal is to obtain a full picture of what students have learned through various assessment practices.