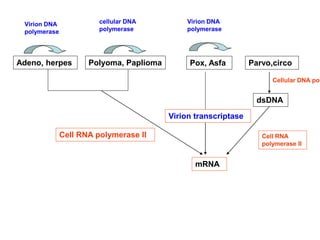
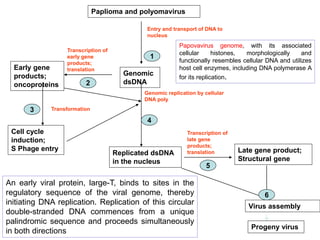
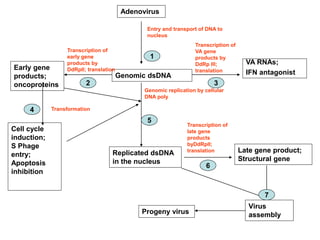
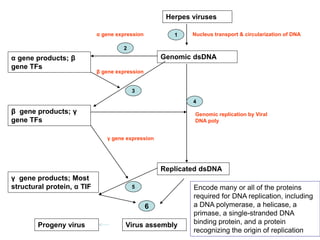
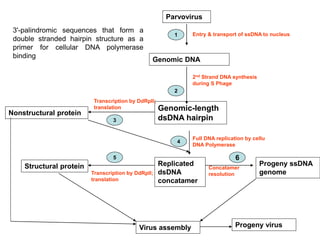
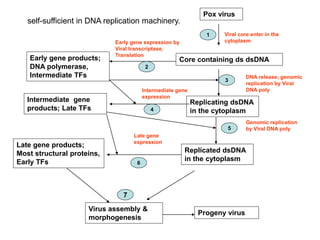
The document discusses the replication processes of various DNA viruses, including parvovirus, polyomavirus, adenovirus, herpes viruses, and poxvirus. It outlines the necessary viral and cellular enzymes involved in these processes, emphasizing the role of DNA polymerases, helicases, and various gene products in viral DNA synthesis, assembly, and gene expression. Each virus showcases unique characteristics regarding their DNA structure and replication mechanisms within host cells.