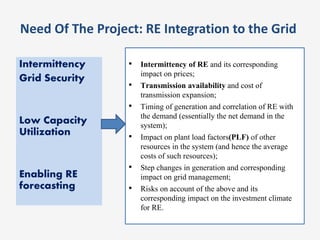
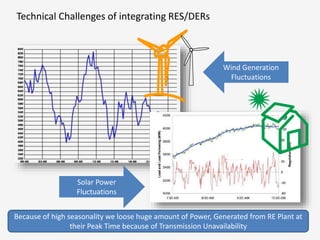
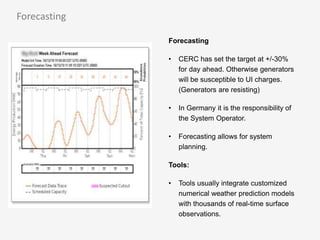
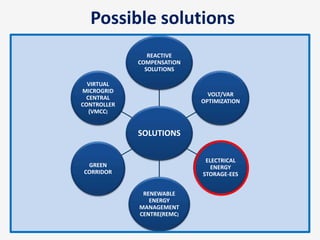
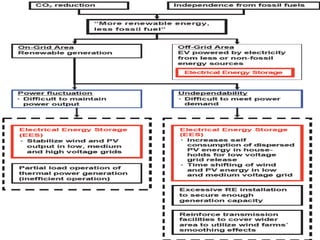
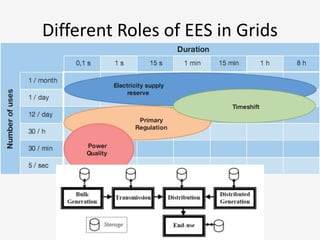
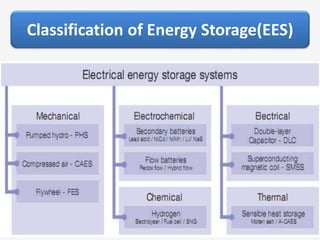
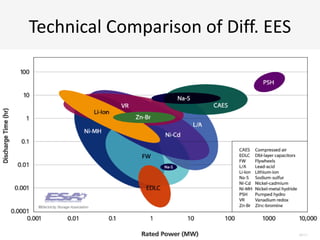
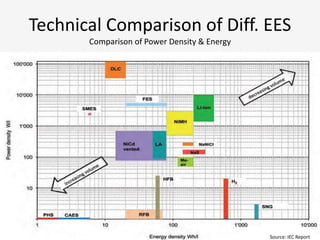
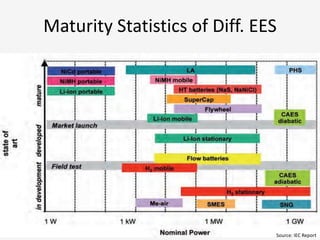
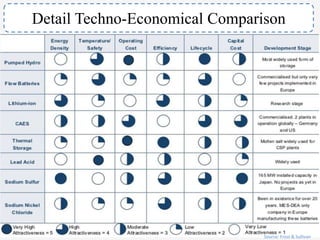
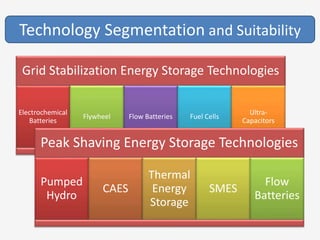
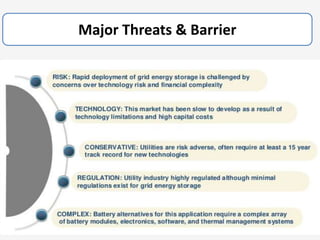
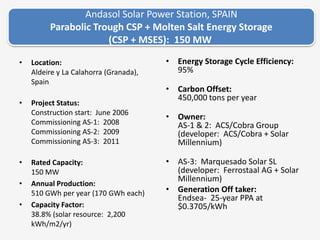
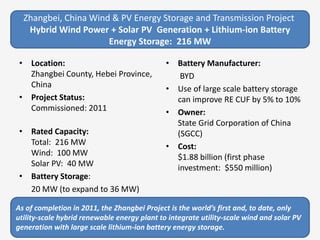
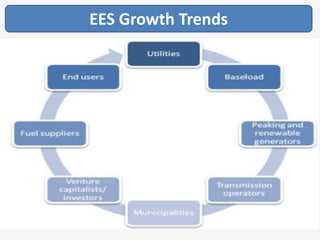
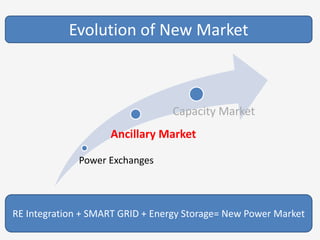
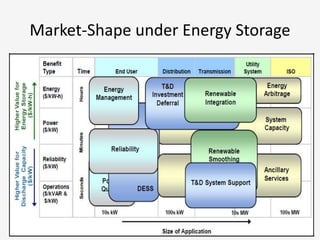
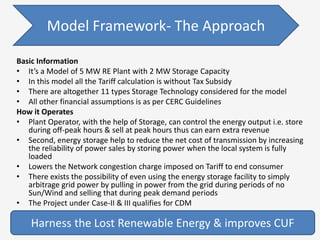
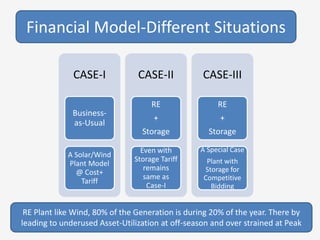
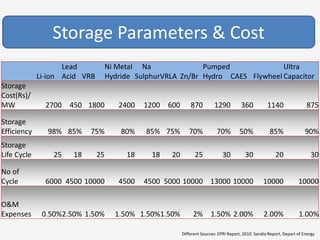
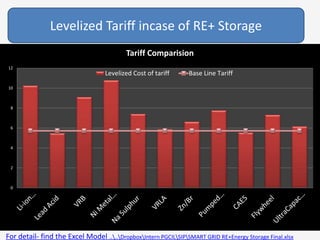
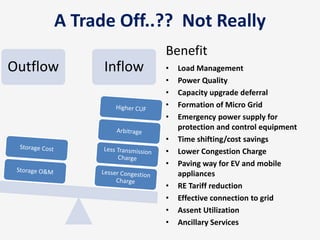
The document discusses a roadmap for integrating renewable energy through large-scale energy storage in Puducherry's smart grid pilot project. It provides background on India's renewable energy targets and challenges of integrating intermittent renewables. The objectives are to develop a techno-commercial model to guide decisions on energy storage and set up India's first 5MW grid-integrated energy storage pilot project. Different energy storage technologies are compared and international case studies presented, including a wind/solar plus storage project in China. The document models how energy storage could improve a renewable energy plant's capacity utilization factor and revenue by storing excess power for sale during peak periods.