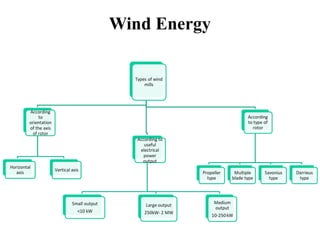
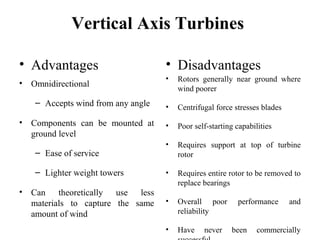
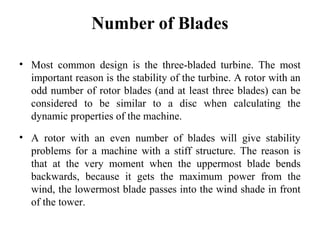
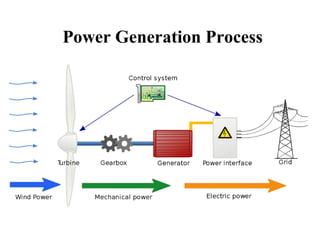
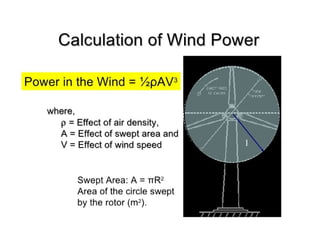
Wind energy is derived from the sun's power, with wind being the result of atmospheric motion. Wind turbines convert wind's kinetic energy into electricity, influenced by wind speed and air density, with vertical axis turbines having advantages and disadvantages in design and performance. Despite high initial costs and noise, wind power is increasingly viable due to its availability and lack of carbon emissions.