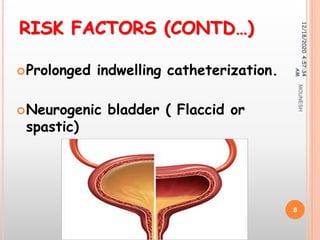
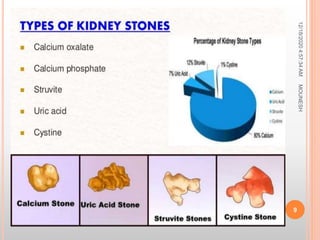
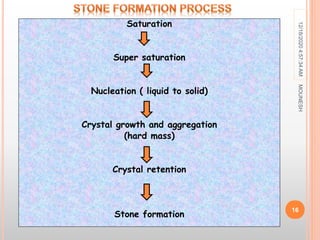
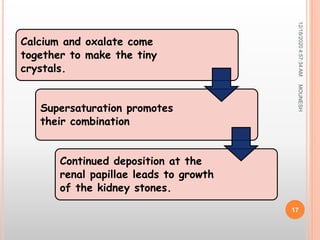
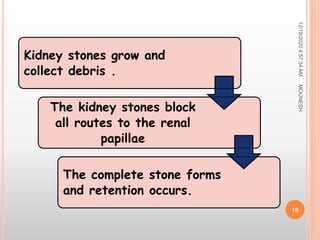
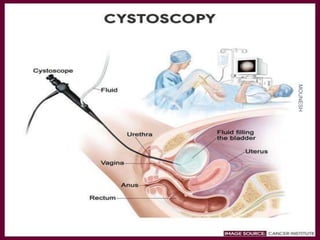
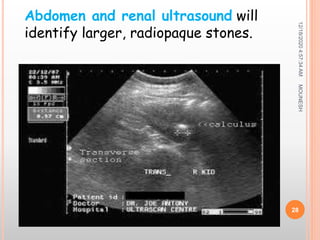
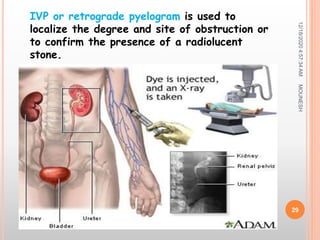
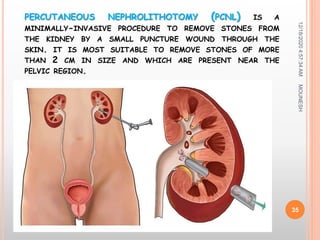
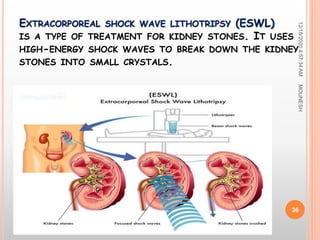
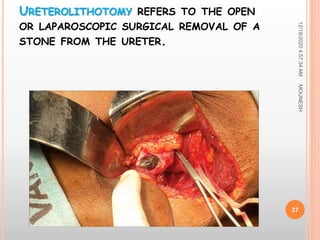
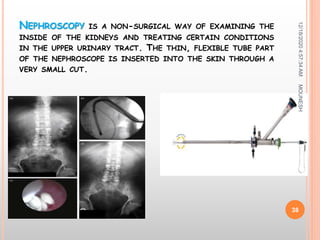
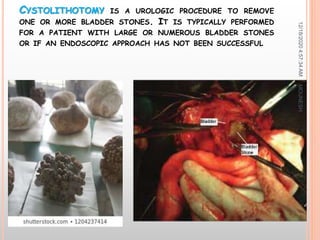
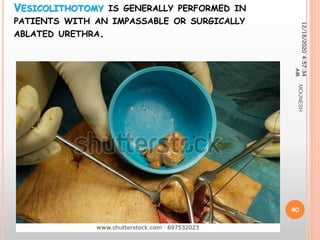
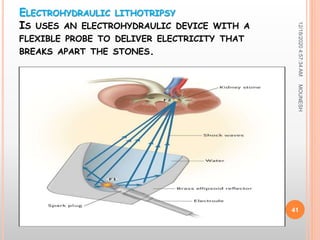
This document discusses renal calculi (kidney stones). It defines renal calculi as solid pieces of material that form in the urinary tract. It then discusses the etiology, risk factors, types, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic studies, medical management, and surgical management of kidney stones. The key points are that kidney stones are usually caused by crystallization of substances in the urine, like calcium oxalate, and can cause pain, infection, and potentially kidney damage if not treated properly through measures like increased fluid intake, medications to dissolve stones, or surgical procedures like lithotripsy to break up stones.