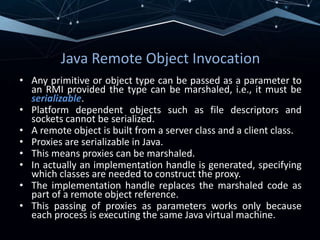
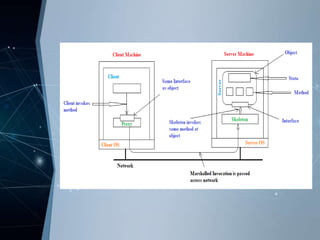
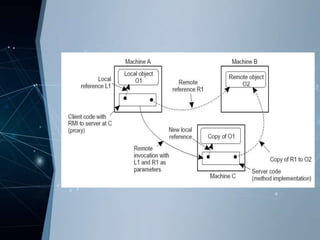
RMI allows objects in one Java virtual machine to invoke methods on objects residing in another JVM. It uses distributed objects, where a client proxy marshals method invocations into messages and unmarshals reply messages. A server skeleton unmarshals invocations and forwards replies. RMI supports both static and dynamic invocation. Examples of RMI include DCE remote objects, which extend RPCs to support remote method invocation, and Java RMI, which integrates distributed objects into Java for high distribution transparency.
























![Java Distributed-Object Model
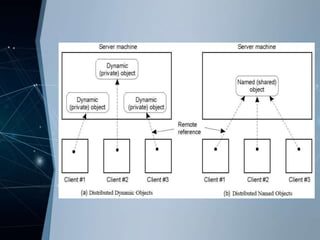
• Java adopts remote objects as the only form of distributed
objects. [i.e., objects whose state only resides on a
single machine]
• Java allows each object to be constructed as a monitor by
declaring a method to be synchronized.
• However there are problems with distributed synchronization.
• Thus, Java RMI restricts blocking on remote objects only to
the proxies.
• This means remote objects cannot be protected against
simultaneous access from processes operating on different
proxies by using synchronization methods.
• Explicit distributed locking techniques must be used.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/42sabiha-210419185912/85/Remote-Method-Invocation-28-320.jpg)