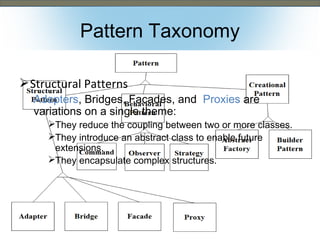
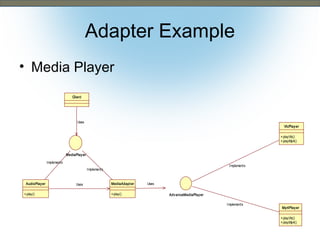
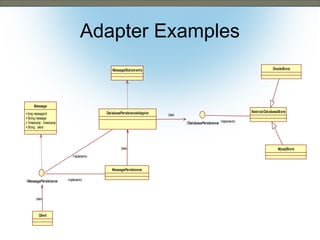
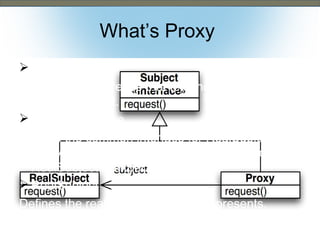
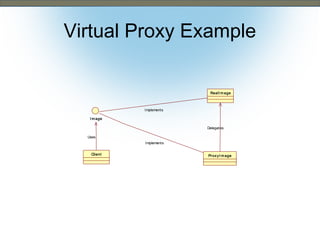
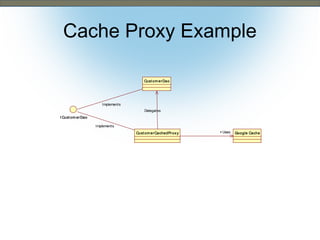
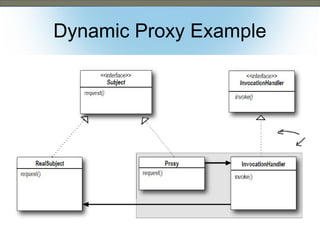
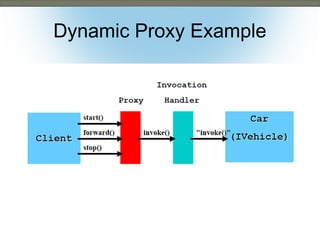
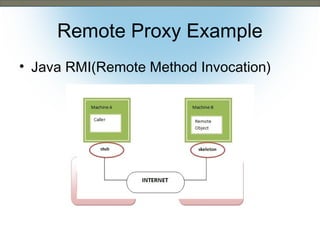
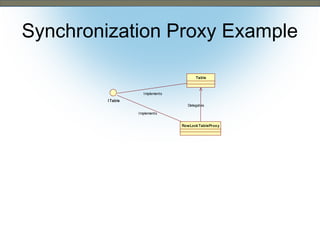
This document discusses the adapter and proxy patterns. The adapter pattern converts the interface of one class into another interface that clients expect. It allows classes to work together that otherwise could not due to incompatible interfaces. The proxy pattern provides a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it. There are several types of proxies including virtual, cache, protection, remote, synchronization, copy-on-write, smart reference, and firewall proxies. Examples of each pattern are provided.