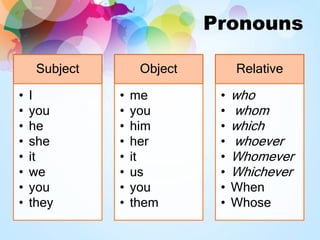
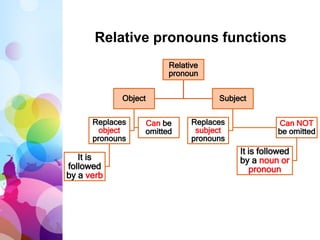
This document defines and provides examples of relative clauses and relative pronouns. It explains that a relative clause contains a subject and verb and begins with a relative pronoun like who, whom, whose, that or which. The relative pronoun introduces the clause and functions as an adjective. Who and whom refer to people, which refers to things, and that can refer to people or things. The document also discusses defining vs non-defining relative clauses and provides examples of using relative pronouns as subjects and objects of clauses and after prepositions. It explains the proper uses of who, whom, whose, when and where.

![DEFINITIONS
• Relative clause—also called an adjective or adjectival
clause
• It contains a subject and verb.
• It begins with a relative pronoun [who, whom, whose, that,
or which,…] .
• It functions as an adjective, answering the questions What
kind? How many? or Which one?
• We use who and whom for people, and which for things.
• We use that for people or things.
• We use relative pronouns to introduce relative clauses,
which tell us more about people and things.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relativeclause-160731064335/85/Relative-clauses-2-320.jpg)