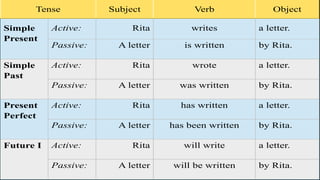
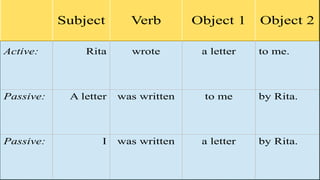
The document discusses the passive voice in English. It begins by explaining that the passive voice focuses on the action rather than the subject performing the action. It provides examples of active and passive sentences. It then notes that the passive voice can sometimes sound more polite by omitting reference to who performed an action. The document goes on to explain the formation of the passive voice using the subject, form of "to be", and past participle. It also discusses how the subject and object of an active sentence change in the passive form. Finally, it distinguishes between personal and impersonal passive, noting impersonal passive is rarer and only used with verbs of perception.