Embed presentation
Download to read offline


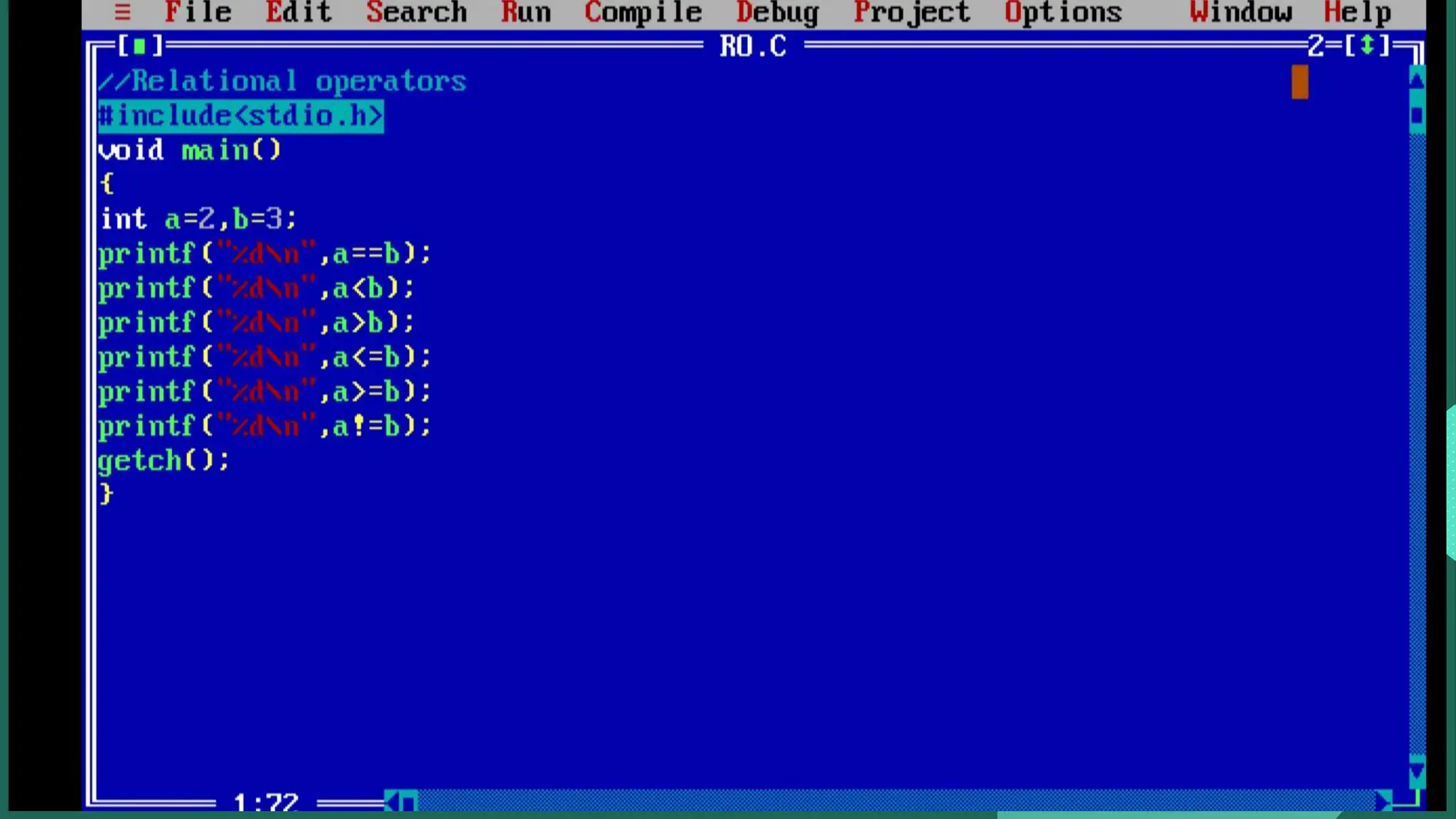

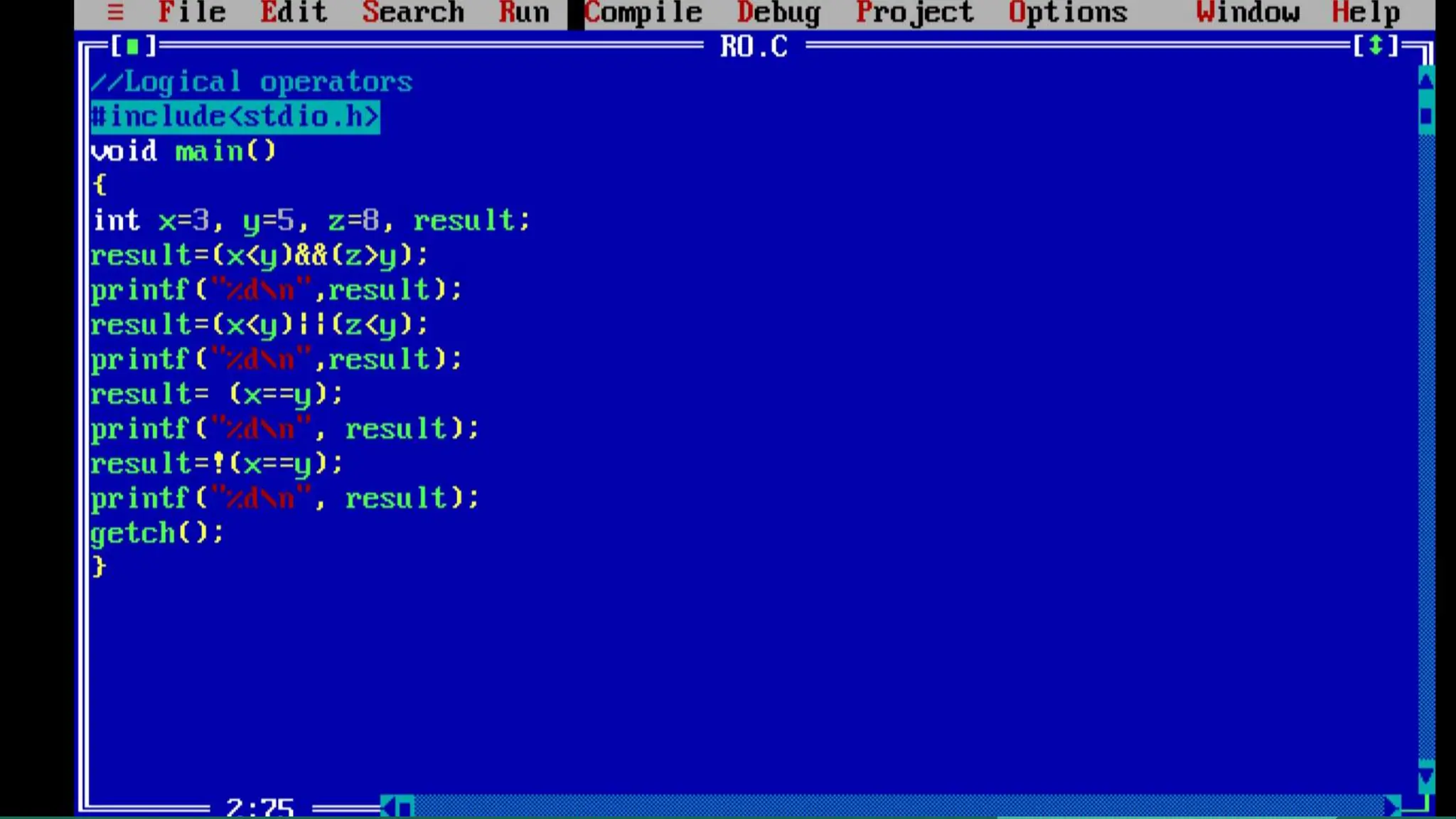


The document discusses operators in C programming language, including relational operators and logical operators. Relational operators (like ==, !=, >, <, >=, <=) are used to check the relationship between two operands and return 1 if the relation is true or 0 if false. Logical operators (&&, ||, !) are used to check multiple conditions in decision making statements. The logical AND (&&) operator returns true only if all conditions are true, while logical OR (||) returns true if either condition is true. The logical NOT (!) operator reverses the logical state of the operand.





