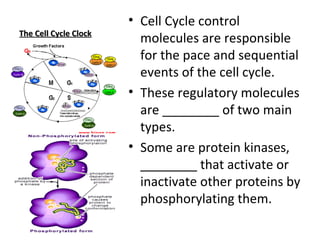
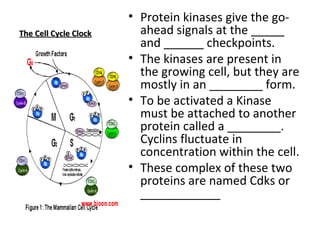
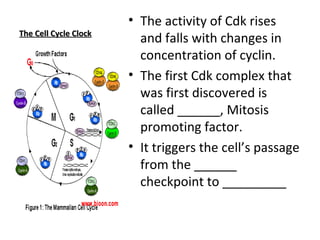
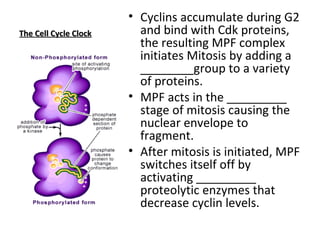
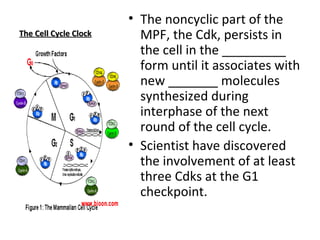
Cell cycle control molecules called cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) regulate the pace and sequence of the cell cycle. Cyclins fluctuate in concentration and bind to Cdk proteins to form active complexes that drive progression through specific cell cycle checkpoints. The first such complex discovered was mitosis promoting factor (MPF), which triggers passage from the G2 checkpoint to mitosis. MPF initiates mitosis by phosphorylating proteins and acts during the prophase stage, causing nuclear envelope fragmentation. It then switches itself off by activating proteolytic enzymes that degrade cyclins.