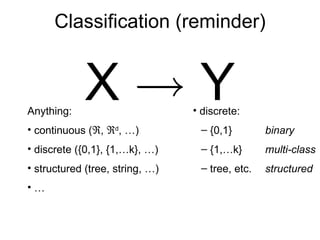
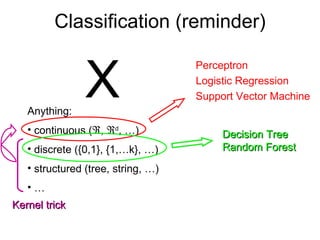
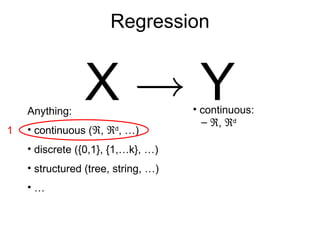
The document outlines various regression techniques including:
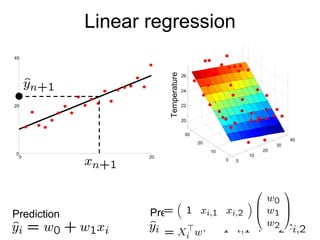
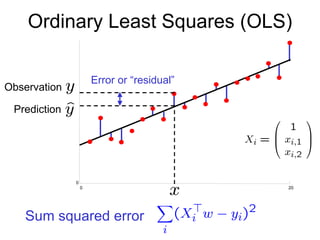
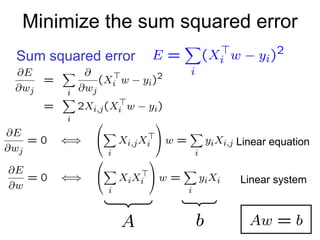
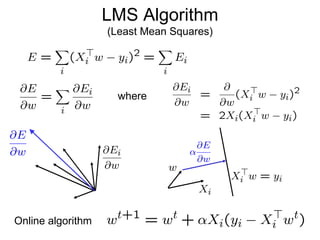
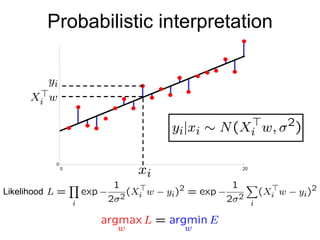
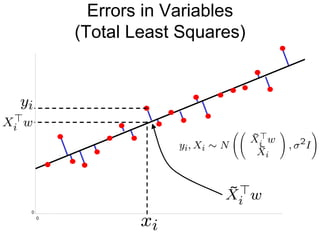
1) Ordinary Least Squares regression which finds the best fitting linear model by minimizing the sum of squared errors between predicted and actual values.
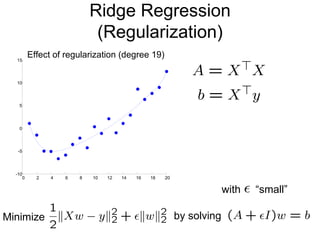
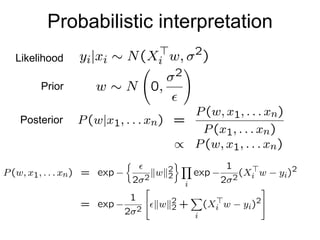
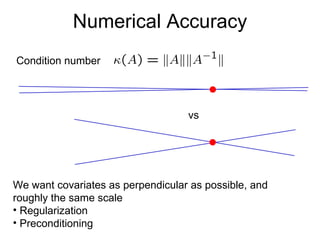
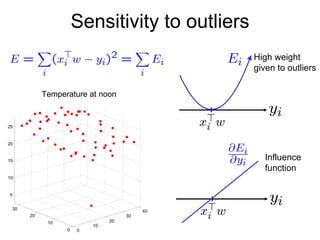
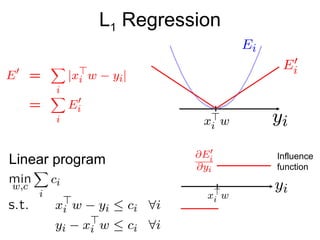
2) Overfitting can occur when the model learns from noise in the data. Regularization addresses this by imposing a penalty on complexity.
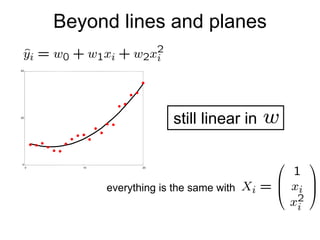
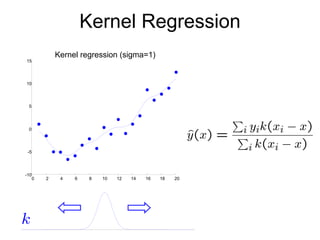
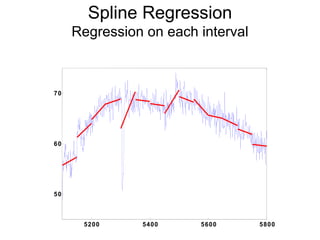
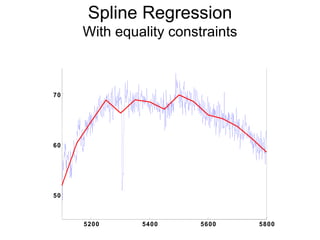
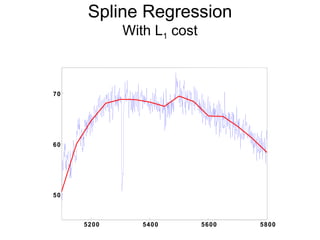
3) Kernel regression, spline regression, and Multiple Adaptive Regression Splines (MARS) allow for nonlinear relationships between variables.



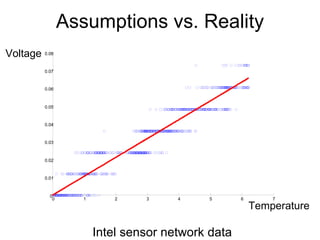
![Examples Voltage ! Temperature Processes, memory ! Power consumption Protein structure ! Energy [next week] Robot arm controls ! Torque at effector Location, industry, past losses ! Premium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regression-100808235129-phpapp02/85/Regression-7-320.jpg)
![Linear regression 0 10 20 30 40 0 10 20 30 20 22 24 26 Temperature 0 10 20 0 20 40 [start Matlab demo lecture2.m] Given examples Predict given a new point](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regression-100808235129-phpapp02/85/Regression-8-320.jpg)

![Geometric interpretation [Matlab demo] 0 10 20 0 100 200 300 400 -10 0 10 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regression-100808235129-phpapp02/85/Regression-15-320.jpg)
![Ordinary Least Squares [summary] n d Let For example Let Minimize by solving Given examples Predict](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regression-100808235129-phpapp02/85/Regression-16-320.jpg)
![Overfitting 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 [Matlab demo] Degree 15 polynomial](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regression-100808235129-phpapp02/85/Regression-19-320.jpg)

![Further topics Generalized Linear Models Gaussian process regression Local Linear regression Feature Selection [next class]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regression-100808235129-phpapp02/85/Regression-32-320.jpg)