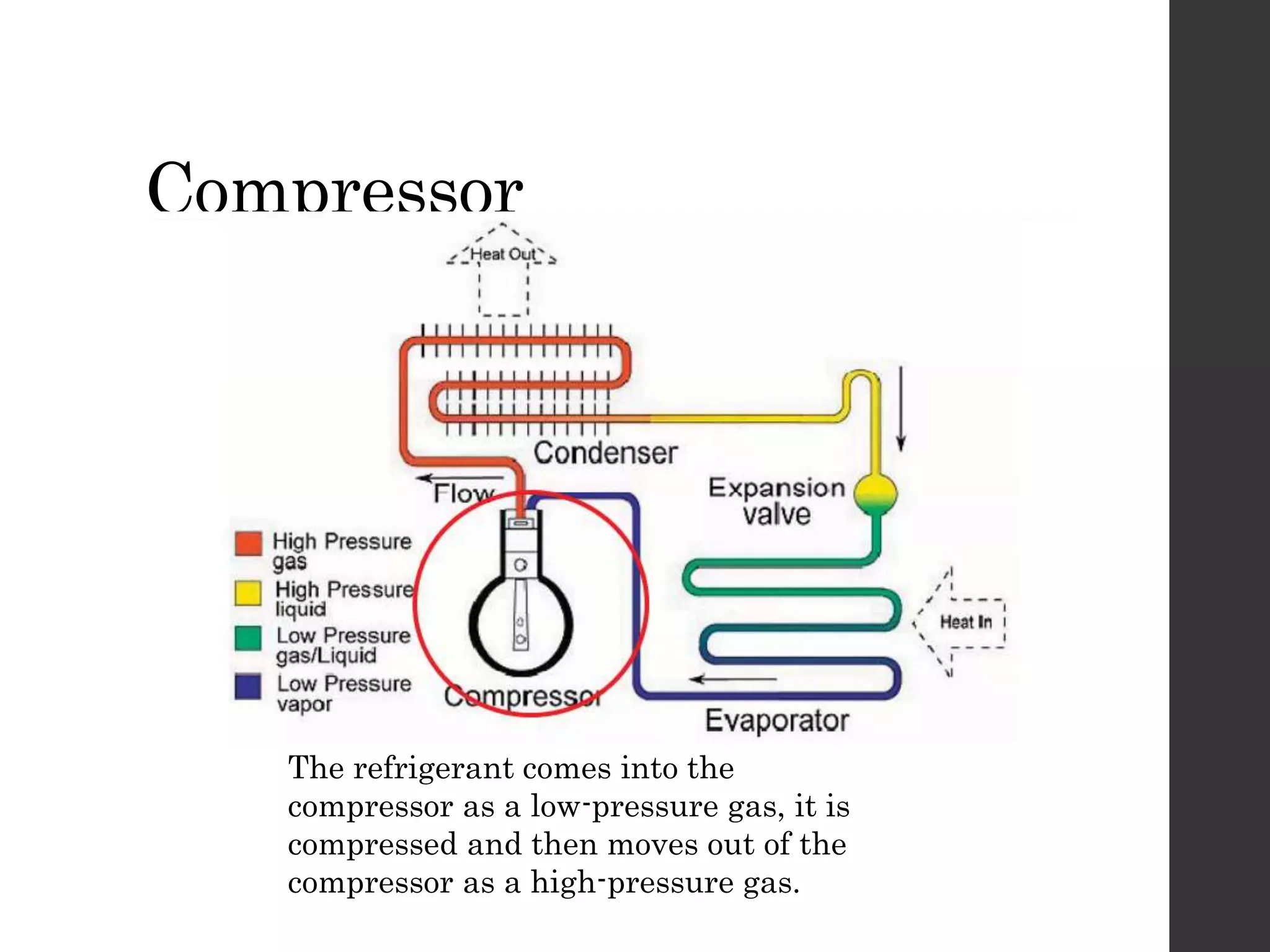
The document summarizes the refrigeration cycle. It describes the four basic processes: (1) isentropic compression in the compressor, (2) constant pressure heat rejection in the condenser, (3) isentropic expansion in the expansion valve/metering device, and (4) constant pressure heat addition in the evaporator. The refrigerant is compressed in the vapor phase, condensed, expanded, and evaporated alternately to provide cooling. Key components are the compressor, condenser, expansion valve, and evaporator. The coefficient of performance (COP) measures efficiency as the cooling effect divided by the work input. Selecting the right refrigerant depends on the application and factors like cost, toxicity, and environmental impact