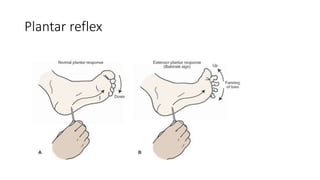
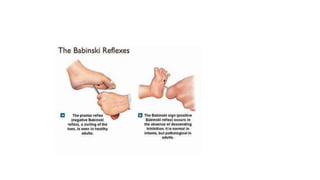
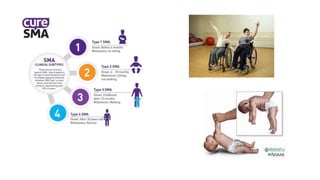
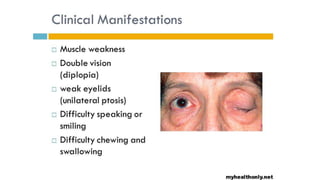
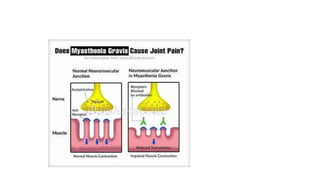
The document discusses reflex arcs, the Babinski sign, and motor neuron diseases, emphasizing their roles in the nervous system and their clinical significance. It explains the components of a reflex arc, the normal and pathological implications of the Babinski sign, and provides insights into various motor neuron diseases, including symptoms and treatments like Spinraza for spinal muscular atrophy. Additionally, it highlights notable cases, such as Stephen Hawking's experience with ALS.