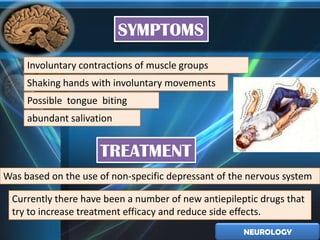
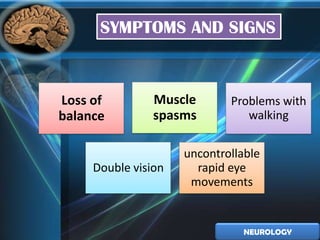
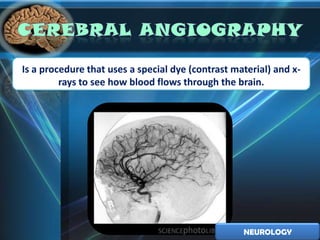
1. Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures from abnormal neuronal activity in the brain. Common symptoms include involuntary muscle contractions and shaking. Treatment was historically based on nervous system depressants, but now focuses on newer antiepileptic drugs.
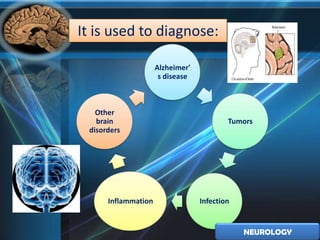
2. Alzheimer's disease causes memory loss and cognitive impairment. Early symptoms are subtle memory loss worsening over time. Currently there is no cure, but medications can help control symptoms.
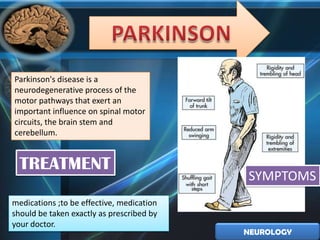
3. Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative process affecting motor pathways in the brain. Symptoms include tremors and impaired movement. Treatment focuses on medications to manage symptoms.