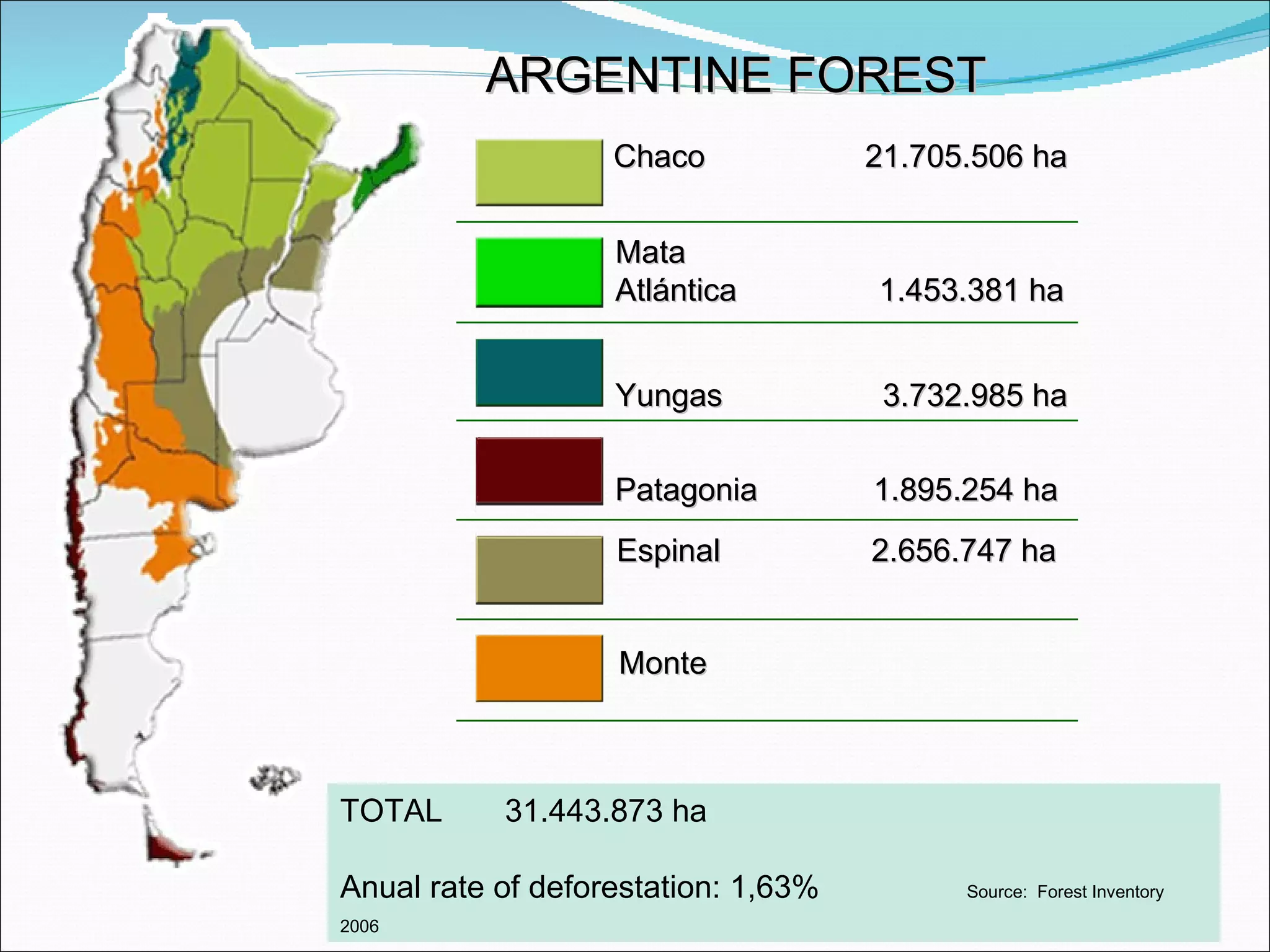
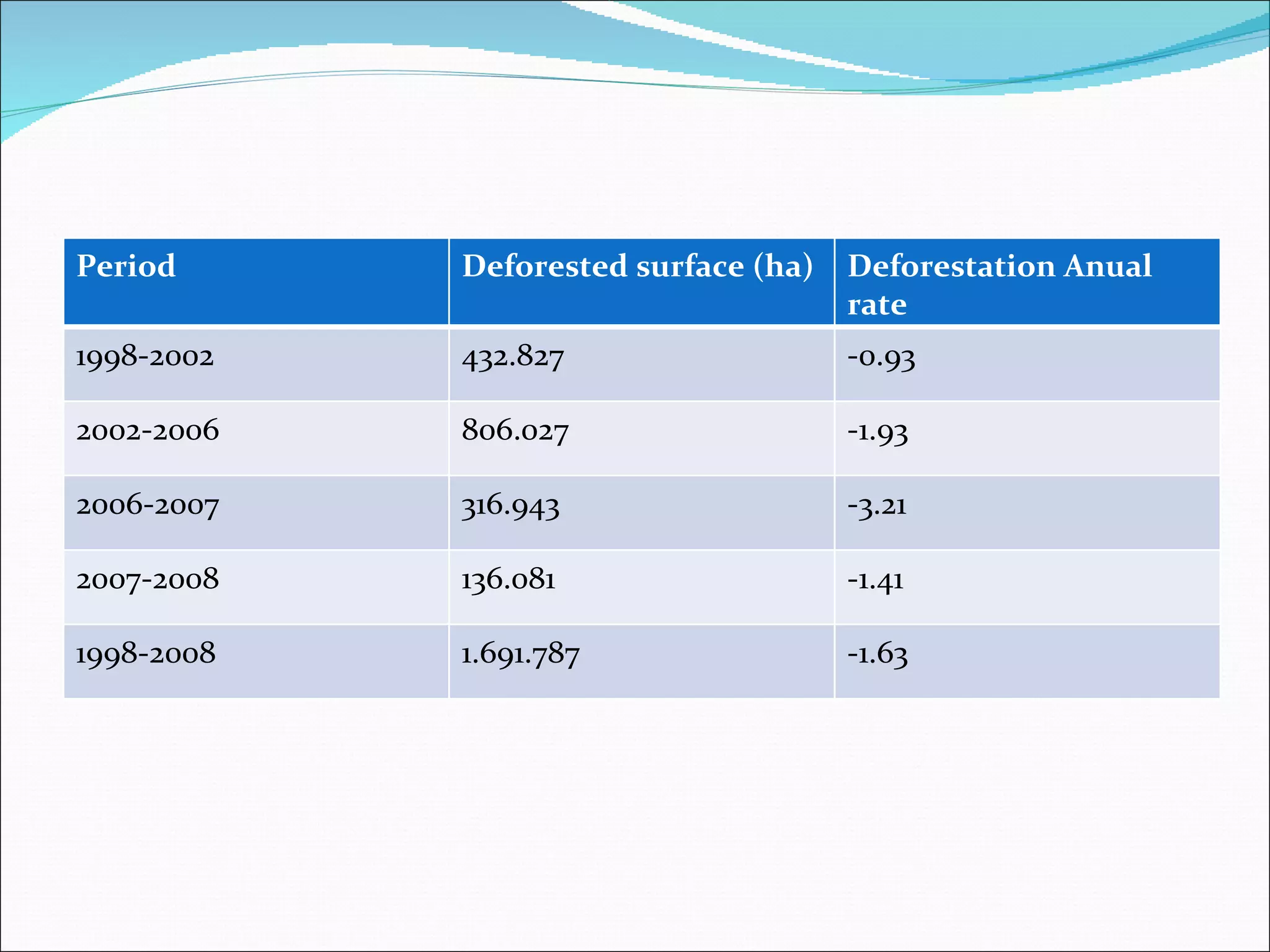
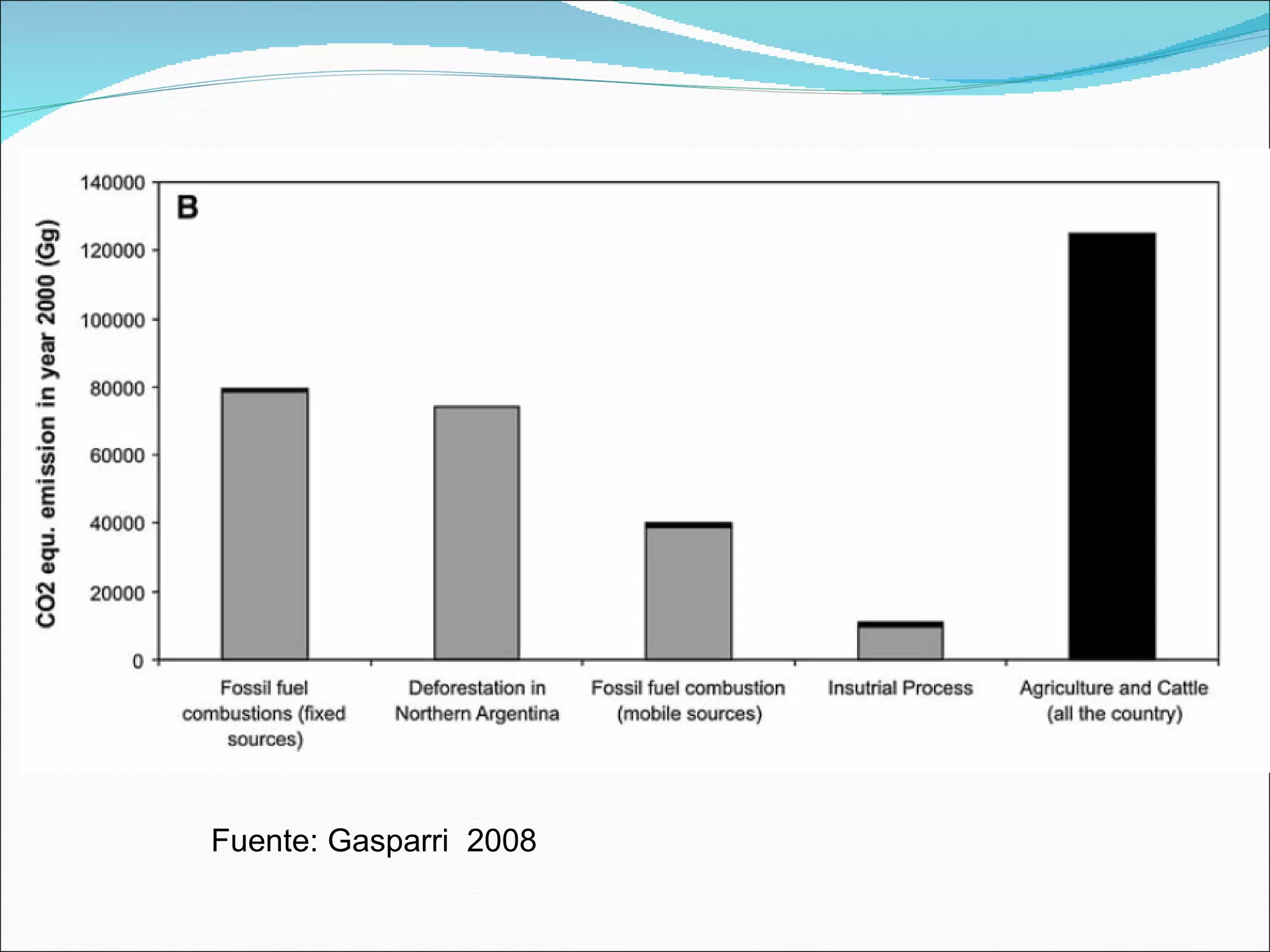
- Argentina has 31.4 million hectares of forest, with an annual deforestation rate of 1.63% from 1998-2008. The main forest types are Chaco (21.7 million ha), Mata Atlantica (1.45 million ha), and Yungas (3.73 million ha).
- To prepare for REDD+, Argentina aims to improve land tenure systems, as over 60% of forests are on private lands, and establish an incentive distribution mechanism.
- The national forest law establishes rules for conservation, management, and carbon stocks. It also creates a national forest fund and mandates state-level forest planning through public participation to access funds.