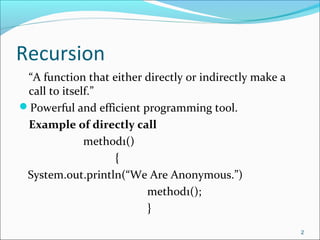
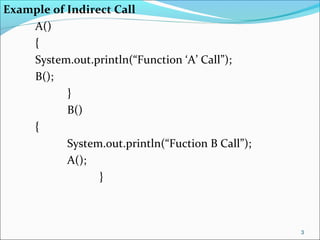
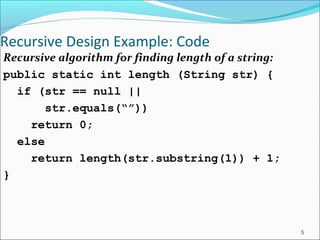
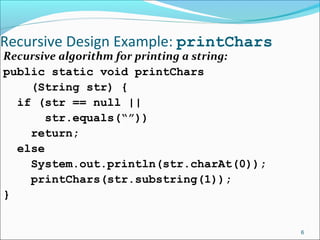
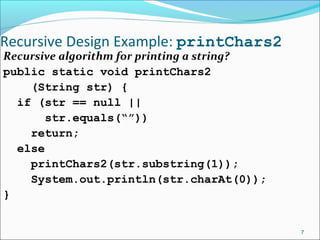
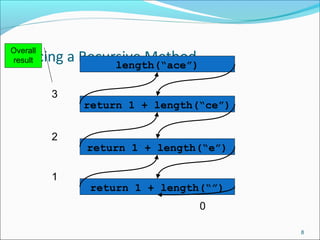
The document discusses recursion, which is when a function calls itself directly or indirectly. It provides examples of directly and indirectly recursive functions. It notes the requirements for a recursive solution, including having a base case and breaking the problem down into smaller subproblems of the same kind. The document gives examples of recursively finding the length and printing characters of a string. It also discusses tracing a recursive method call stack and defines the Fibonacci series recursively, providing an example recursive Fibonacci function that is inefficient due to redundant calls.