Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times







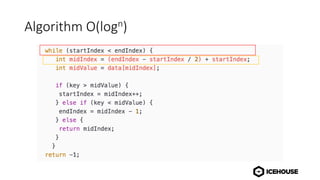

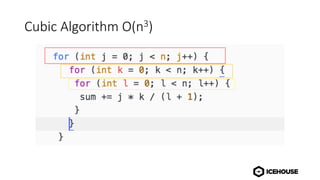




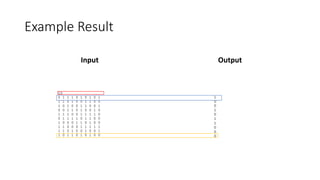
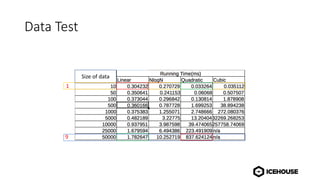

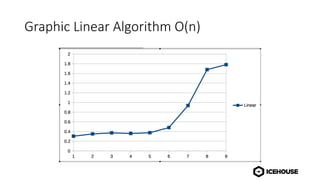
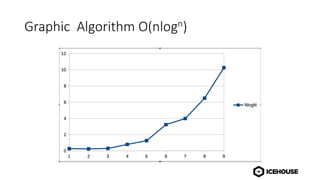
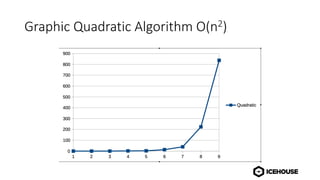
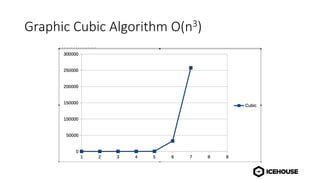
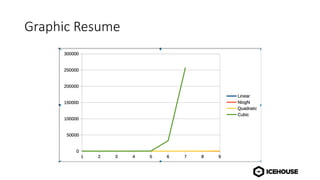


The document discusses algorithm complexity analysis using Big O notation, which describes the growth rate of an algorithm in terms of time and space. It highlights different complexities such as constant (O(1)), linear (O(n)), and quadratic (O(n²)) algorithms, and provides benchmarks for data structures and sorting operations. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of choosing the appropriate data structure and simplifying complexities, especially in the presence of nested loops.






















