1. The document discusses recursion and provides examples of recursively defined problems and their solutions, including factorials, powers, greatest common divisor, Fibonacci series, Towers of Hanoi, and counting cells in a blob.
2. Recursion involves breaking a problem into smaller subproblems of the same type until reaching a base case that can be solved directly. The solutions to subproblems are then combined to solve the original problem.
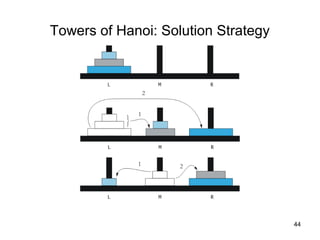
3. Examples of recursively defined problems include mathematical formulas, searching and sorting algorithms like binary search, and problems like Towers of Hanoi that are naturally broken down recursively.


































![35
Linear Array Search Code
template<typename Item_Type>
int linear_search (
const std::vector<Item_Type>& items,
const Item_Type& target) {
return linear_search(items, target, 0);
}
template<typename Item_Type>
int linear_search (
const std::vector<Item_Type>& items,
const Item_Type& target, size_t pos_first) {
if (pos_first == items.size()) return -1;
else if (target == items[pos_first])
return pos_first;
else
return linear_search(items, target, pos_first+1);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recursion-141106083531-conversion-gate01/85/Recursion-35-320.jpg)




![40
Binary Search Code
template <typename Item_Type>
int binary_search(const std::vector<Item_Type>& items,
int first, int last, const Item_Type& target) {
if (first > last)
return -1; // Base case for unsuccessful search.
else {
int middle = (first + last) / 2; // Next probe index.
if (target < items[middle])
return binary_search(items, first, middle - 1, target);
else if (items[middle] < target)
return binary_search(items, middle + 1, last, target);
else
return middle; // Base case for successful search.
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recursion-141106083531-conversion-gate01/85/Recursion-40-320.jpg)













![55
Count Cells Code
int count_cells(color grid[ROW_SIZE][COL_SIZE], int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= ROW_SIZE || c < 0 || c >= COL_SIZE)
{
return 0;
}
else if (grid[r][c] != ABNORMAL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
grid[r][c] = TEMPORARY;
return 1
+ count_cells(grid, r - 1, c - 1) + count_cells(grid, r - 1, c)
+ count_cells(grid, r - 1, c + 1) + count_cells(grid, r, c + 1)
+ count_cells(grid, r + 1, c + 1) + count_cells(grid, r + 1, c)
+ count_cells(grid, r + 1, c - 1) + count_cells(grid, r, c - 1);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recursion-141106083531-conversion-gate01/85/Recursion-55-320.jpg)



![59
Maze Solving Code
bool findMazePath(color grid[ROW_SIZE][COL_SIZE], int r, int c)
{
if (r < 0 || c < 0 || r >= ROW_SIZE || c >= COL_SIZE)
return false; // Cell is out of bounds.
else if (grid[r][c] != BACKGROUND)
return false; // Cell is on barrier or dead end.
else if (r == ROW_SIZE - 1 && c == COL_SIZE - 1)
{
grid[r][c] = PATH; // Cell is on path
return true; // and is maze exit.
}
else
. . .
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recursion-141106083531-conversion-gate01/85/Recursion-59-320.jpg)
![60
Maze Solving Code (2)
{ // Recursive case.
// Attempt to find a path from each neighbor.
// Tentatively mark cell as on path.
grid[r][c] = PATH;
if (findMazePath(grid, r - 1, c)
|| findMazePath(grid, r + 1, c)
|| findMazePath(grid, r, c - 1)
|| findMazePath(grid, r, c + 1 ) )
{
return true;
}
else
{
grid[r][c] = TEMPORARY; // Dead end.
return false;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recursion-141106083531-conversion-gate01/85/Recursion-60-320.jpg)