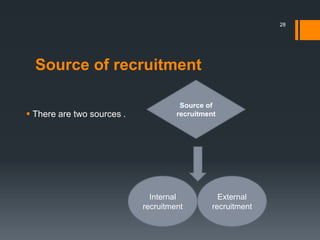
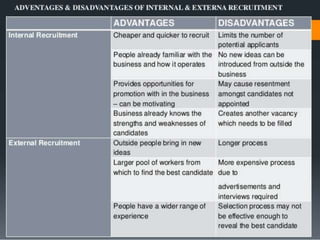
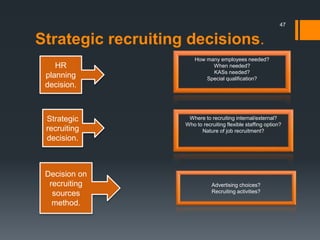
The document discusses recruitment sources for human resource management. It identifies internal sources such as promotions, rehiring and employee referrals. External sources mentioned include advertisements, campus recruitment, online recruitment, walk-ins, employment agencies, schools/universities, job fairs, professional organizations, unsolicited applicants, and online sources like job boards and company career websites. A variety of recruiting sources can help organizations attract qualified candidates efficiently.