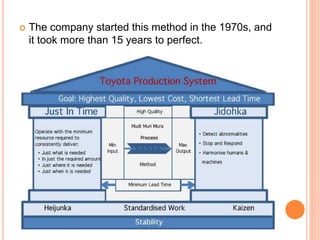
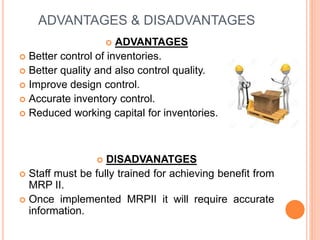
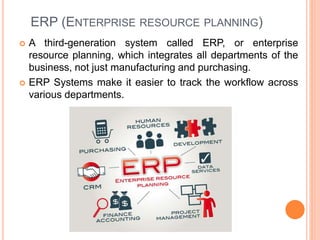
This document discusses recent trends in inventory control, including just-in-time (JIT) systems, material requirements planning (MRP I), manufacturing resource planning (MRP II), and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. JIT aims to reduce inventory costs by receiving goods only as needed. MRP I focuses on manufacturing materials while MRP II adds production planning and tracking. ERP integrates all business departments, making workflow tracking easier across an organization. The trends aim to maximize inventory use and minimize costs through accurate forecasting and coordination of production and resources.