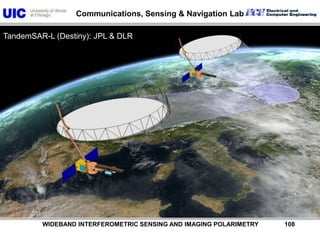
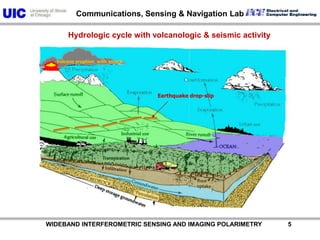
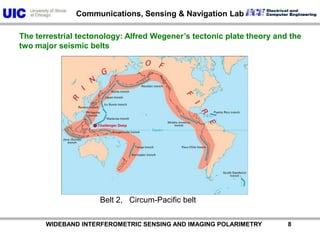
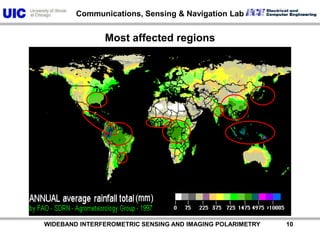
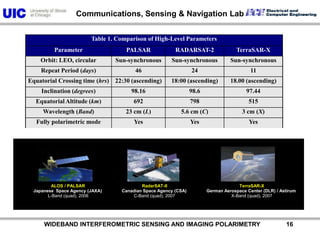
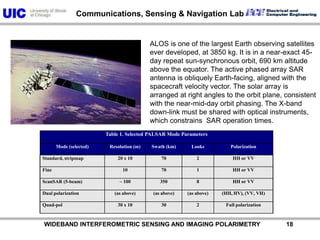
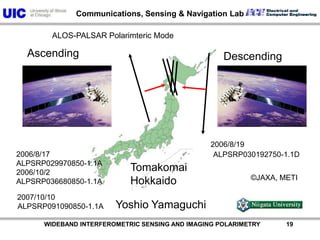
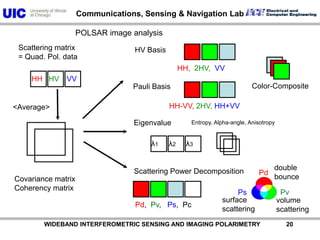
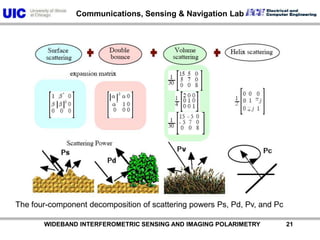
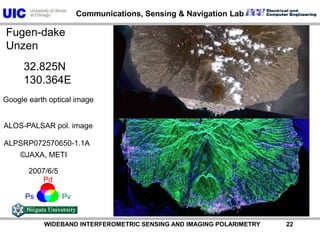
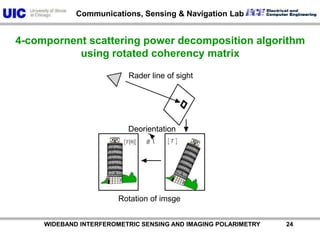
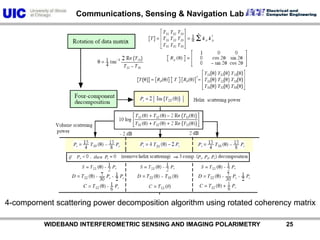
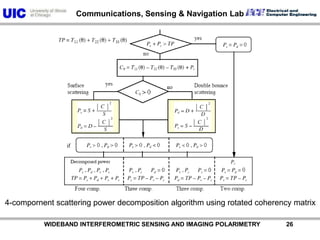
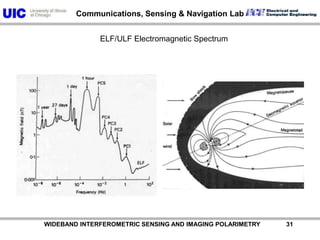
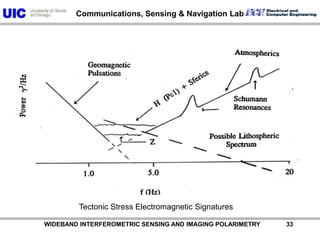
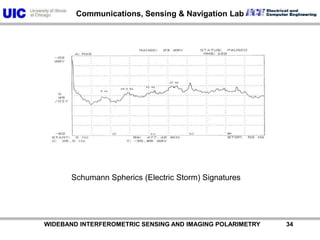
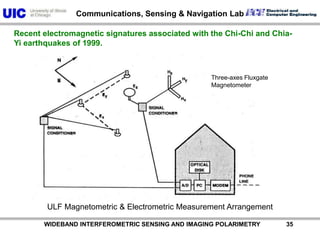
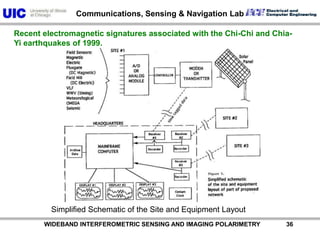
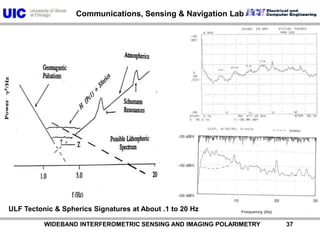
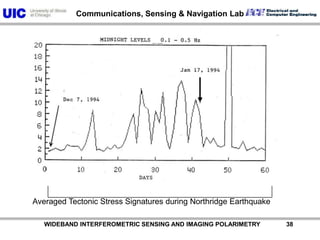
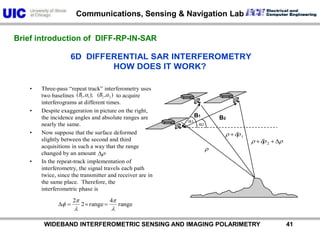
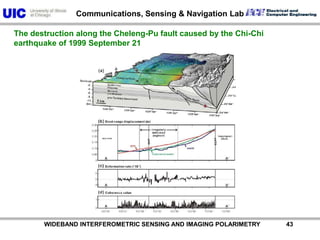
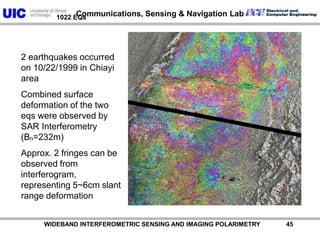
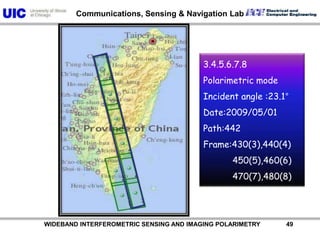
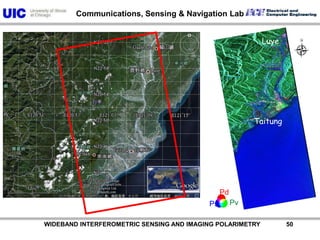
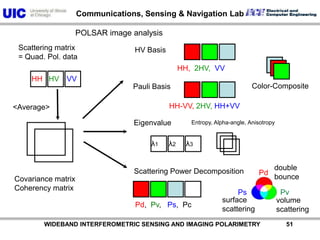
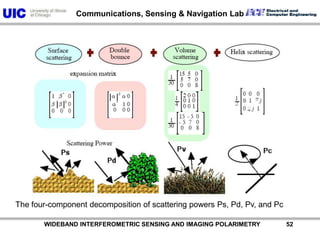
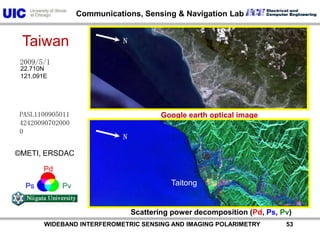
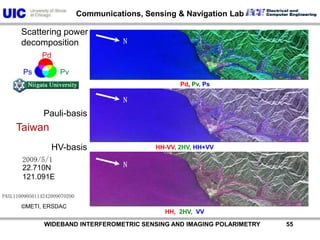
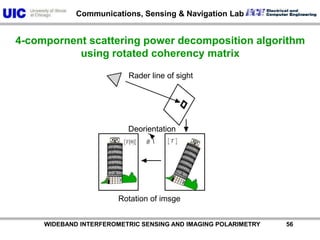
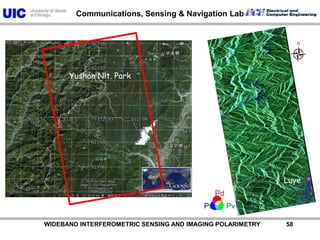
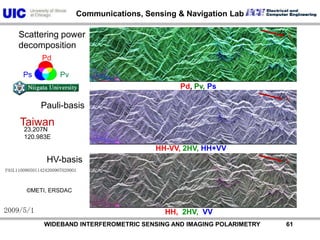
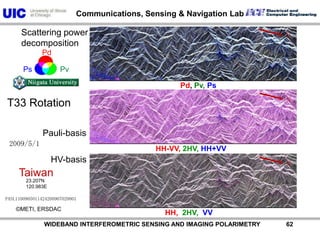
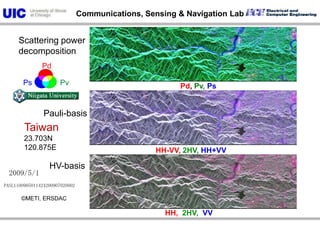
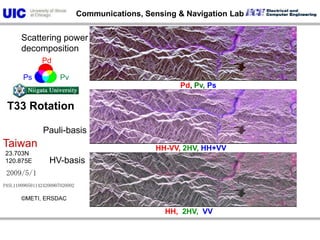
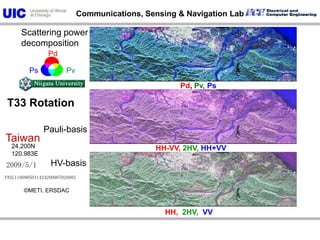
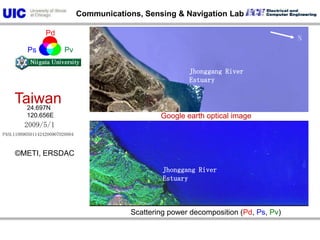
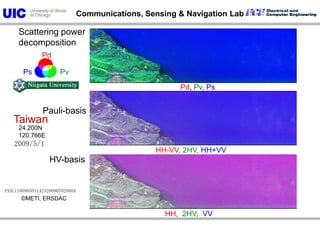
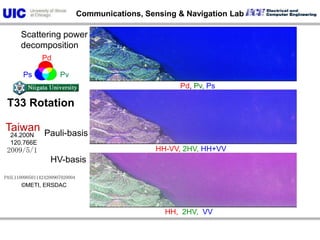
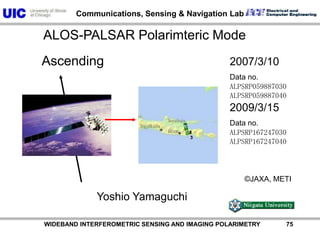
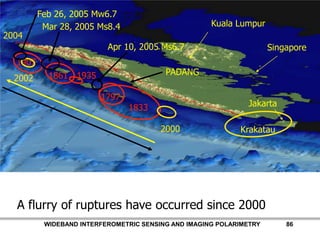
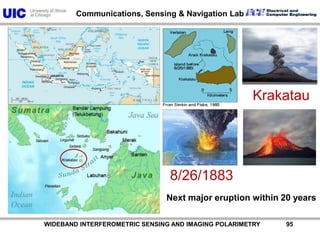
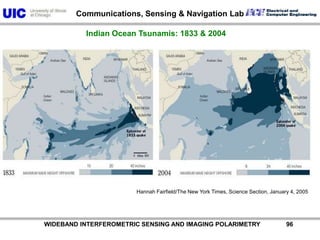
The document discusses the need for multi-modal, multi-band polarimetric interferometric synthetic aperture radar (POLinSAR) satellite systems for monitoring the Earth. It analyzes how POLinSAR can provide information that polarimetric SAR and interferometric SAR alone cannot by combining data from multiple passes. It argues that such systems are urgently required to monitor population growth and reduce conflicts by enabling continuous global monitoring of the biosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and impacts like pollution, natural disasters, and climate change. Examples of POLinSAR data from existing satellites like ALOS are presented to demonstrate techniques like scattering decomposition.





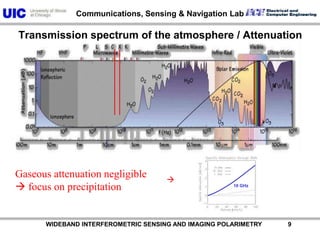














































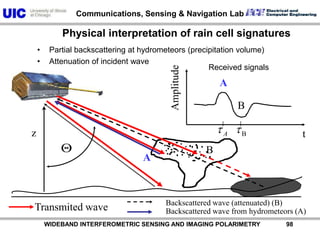
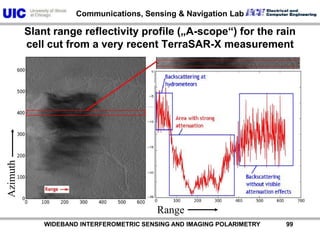
![AzimuthRange Slant range reflectivity profile („A-scope“) for the rain cell cut from a very recent TerraSAR-X measurementPower [dB] WIDEBAND INTERFEROMETRIC SENSING AND IMAGING POLARIMETRY 99](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancesinfullypolarimetric-100727134854-phpapp01/85/TU1-L09-RECENT-ADVANCES-IN-FULLY-POLARIMETRIC-SPACE-SAR-SENSOR-DESIGN-AND-ITS-APPLICATIONS-100-320.jpg)