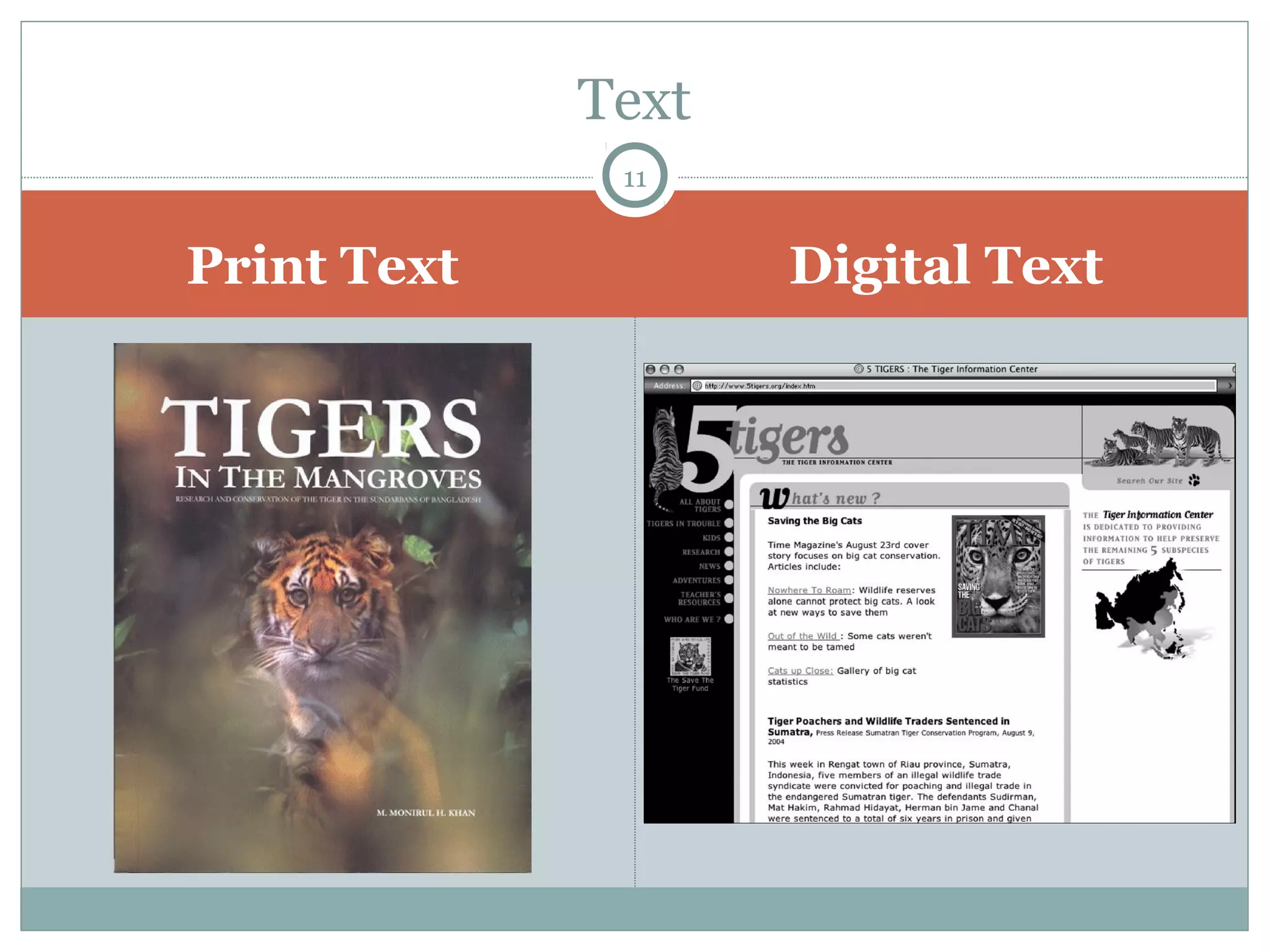
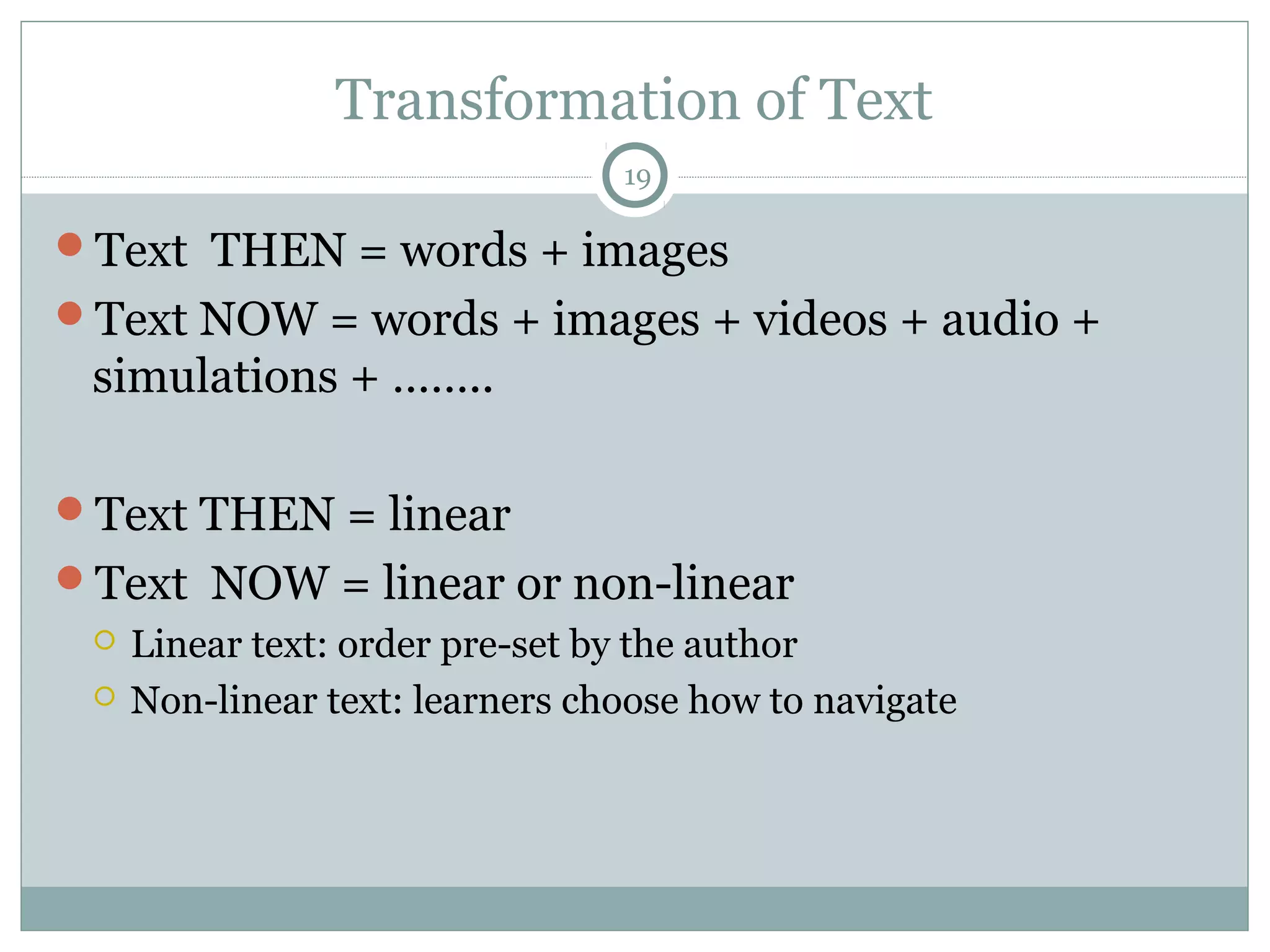
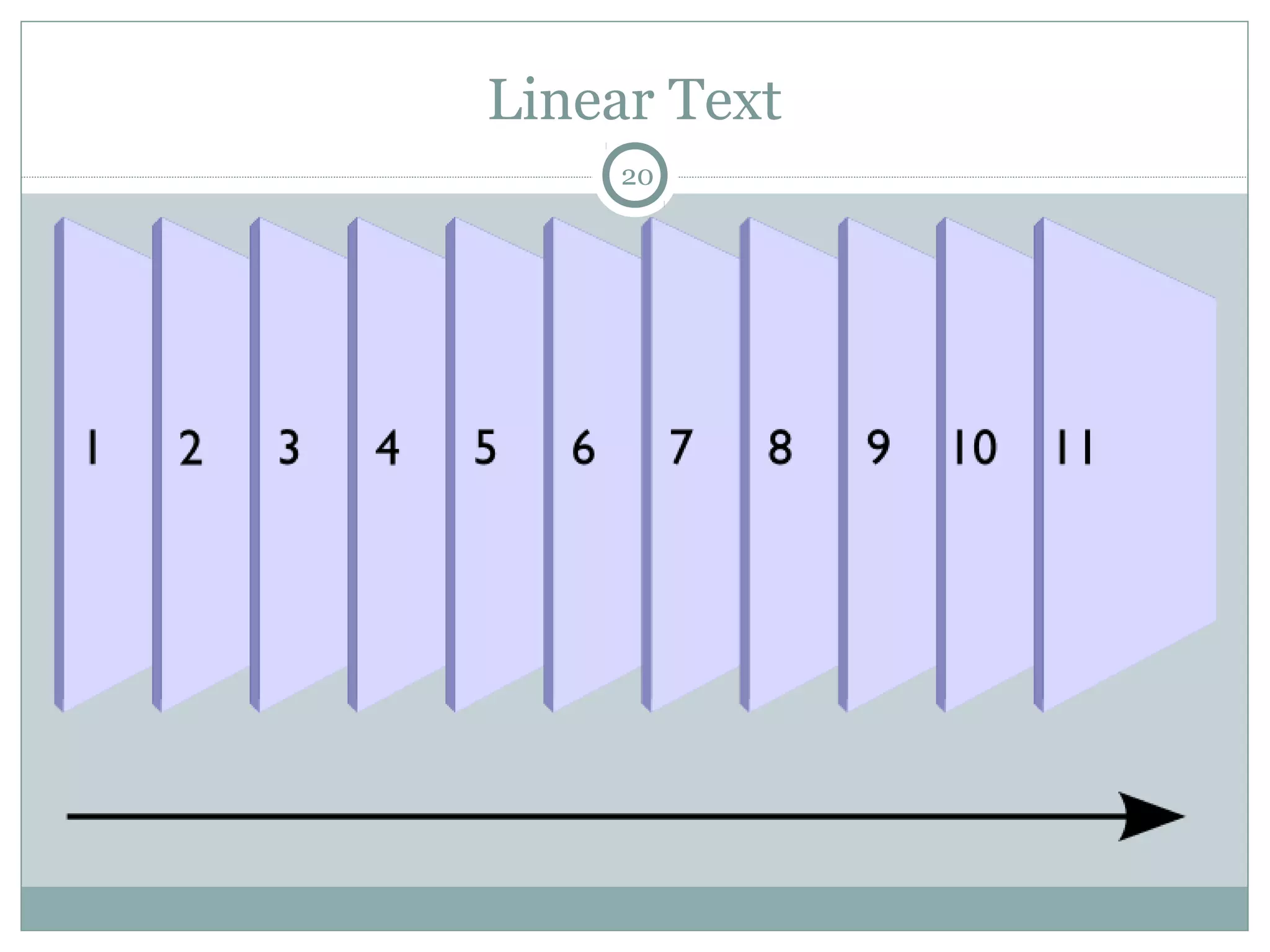
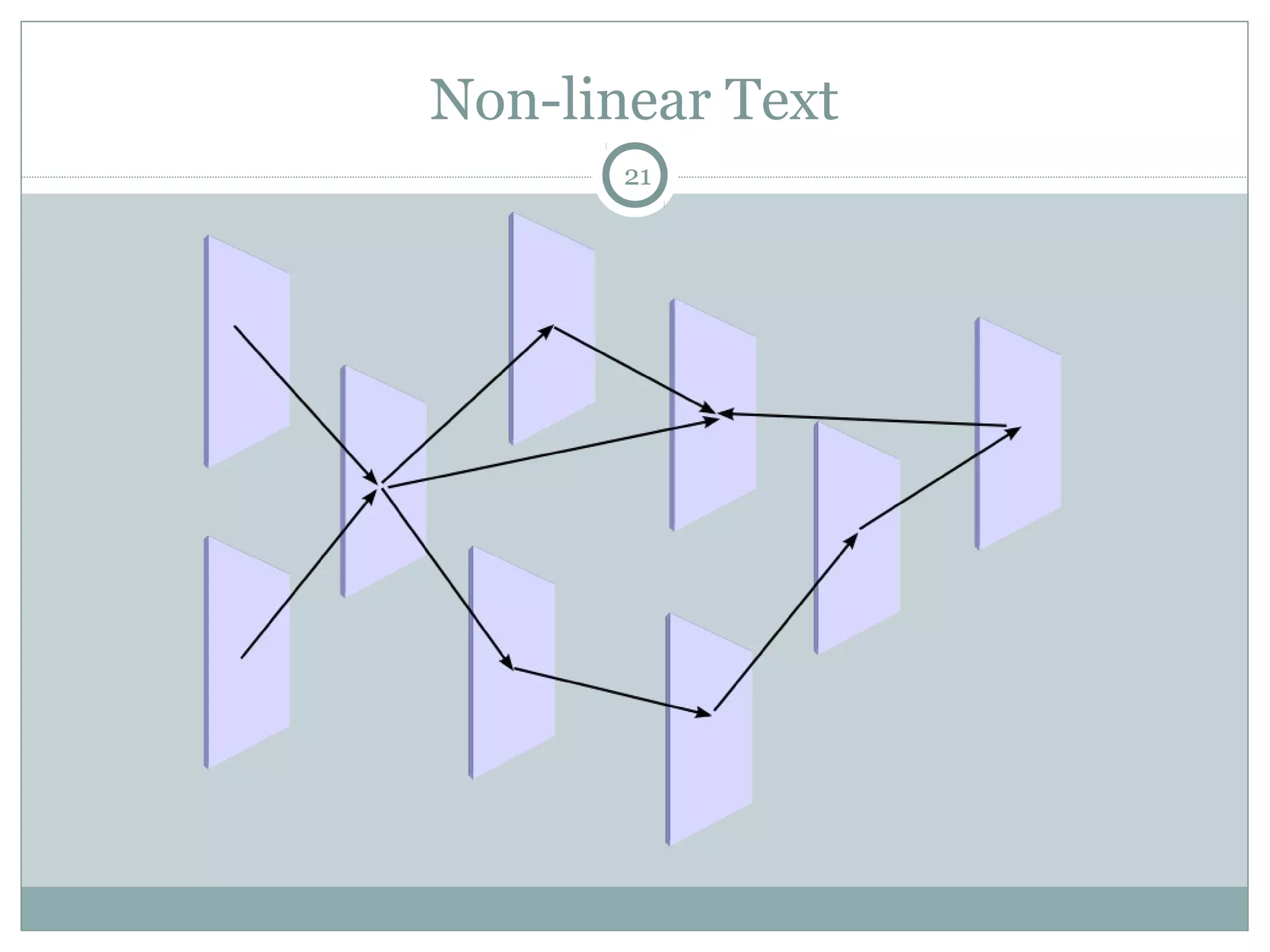
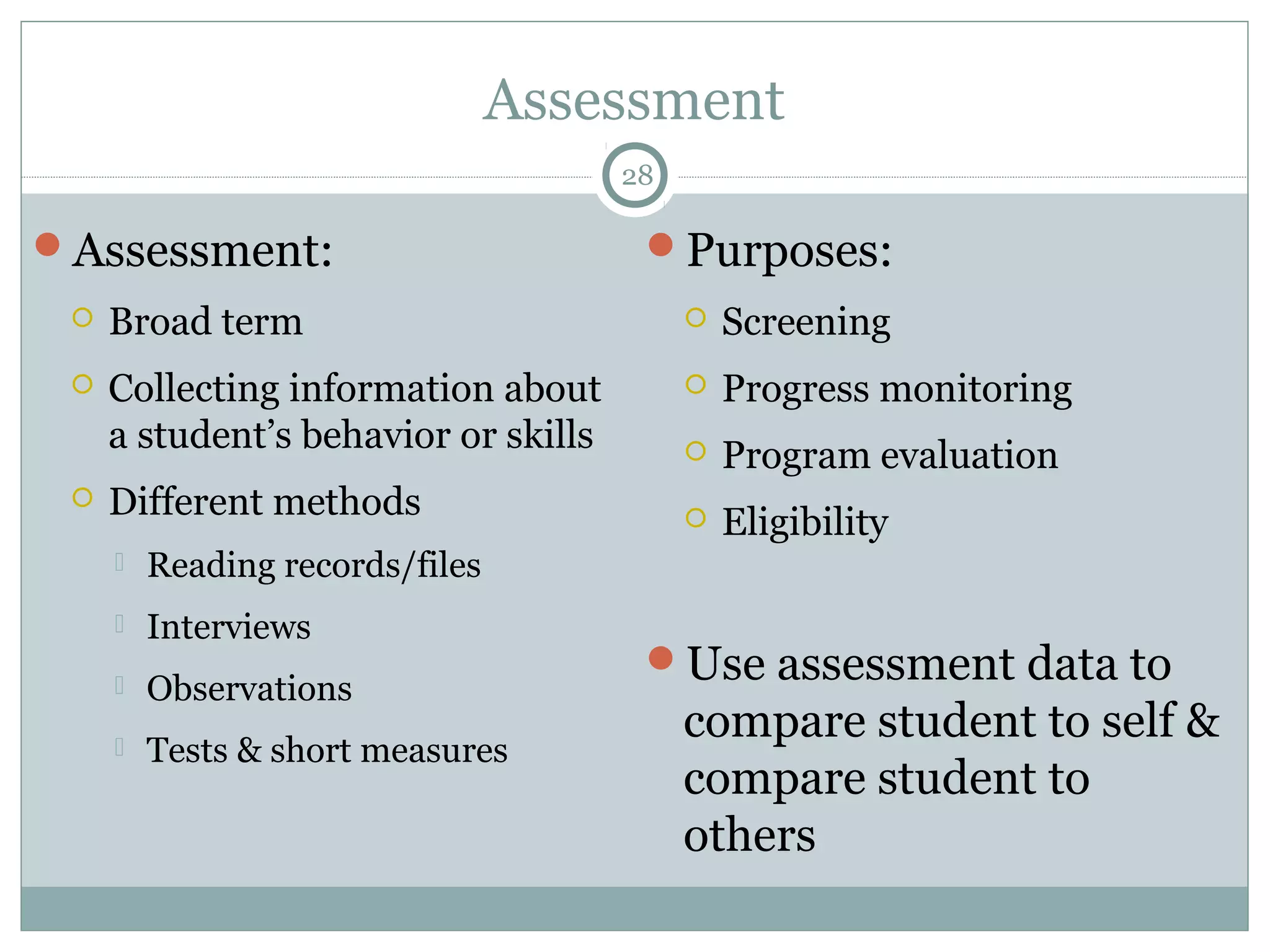
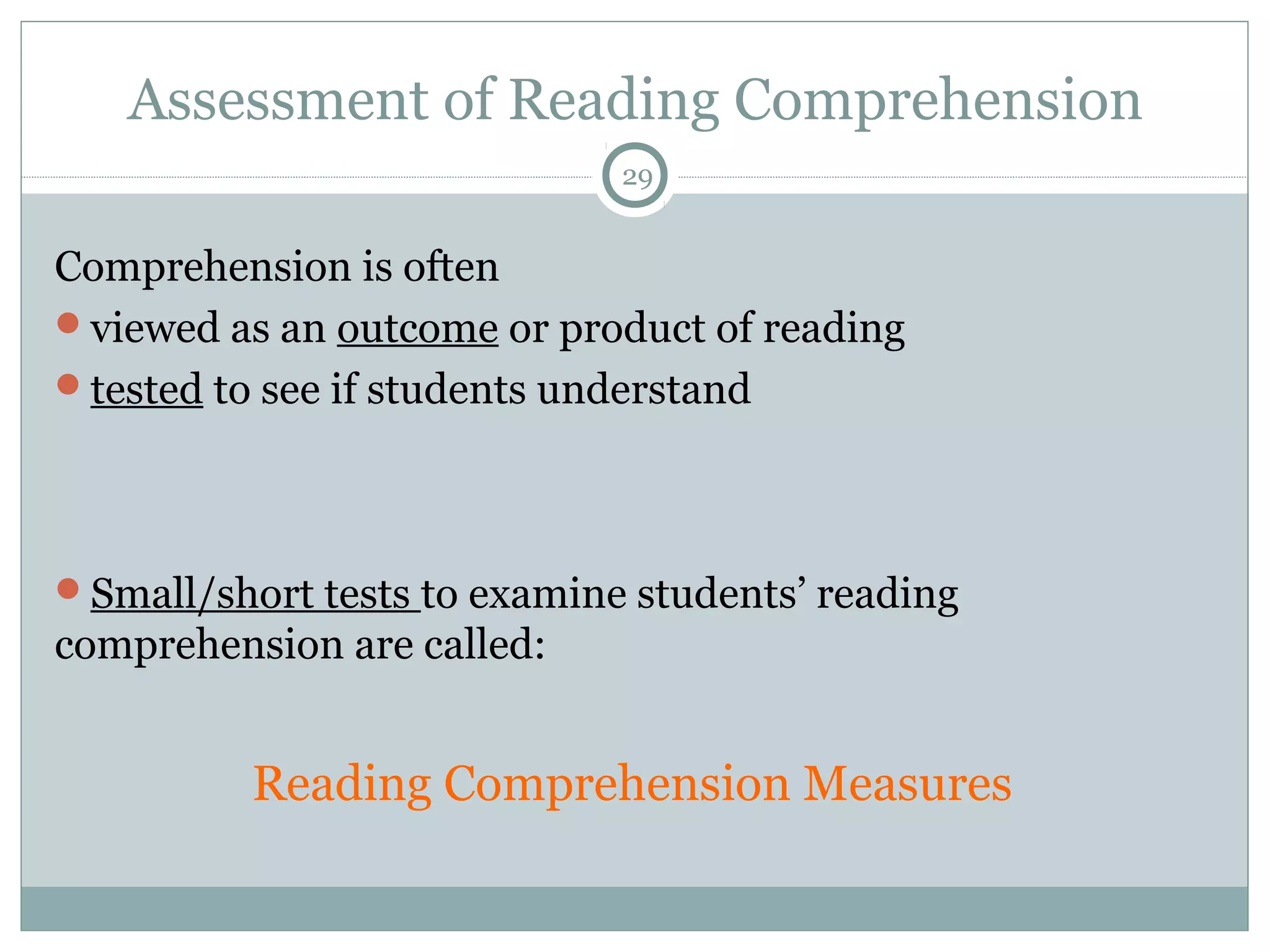
This document discusses reading comprehension in the digital age. It explains that reading comprehension involves an interaction between the reader and text, and strategies have traditionally involved previewing, predicting, questioning, and organizing information. However, digital text is now nonlinear, incorporating various multimedia. This has transformed reading comprehension strategies, which for digital text involve skimming, scanning, and evaluating multiple online sources simultaneously. The document also discusses traditional print-based assessments of comprehension and the need to develop new methods to assess comprehension of digital texts, such as project-based and think-aloud approaches.





















![References & Resources
National Association of School Psychologists www.nasponline.org
Coiro, J., & Dobler, E. (2007). Exploring the online reading comprehension strategies used by sixth-grade skilled
readers to search for and locate information on the internet. Reading Research Quarterly, 42 (2), 214-257.
doi: 10.1598/RRQ42.2.2
International Reading Association (IRA) & National Association for the Education of Young Children (NAEYC)
(adopted 1998). Learning to read and write: Developmentally appropriate practices for young children [a joint
position statement]. Newark, DE and Washington, DC: Author.
McNamara, T., Miller, D., & Bransford, J. D. (2000). Mental models and reading comprehension. In R. Barr, M. L.
Kamil, P. B. Mosenthal & P. D. Pearson (Eds.), Handbook of reading research (Vol. 2, pp. 490-511). New
York: Longman.
Duke, N. K., & Carlisle, J. F. (2011). The development of comprehension. In M. L. Kamil, P. D. Pearson, E. B. Moje,
and P. Afflerbach (Eds.), Handbook of Reading Research, Vol. IV. London: Routledge.
RAND Reading Study Group. (2002). Reading for understanding: Toward an R & D program in reading
comprehension. Santa Monica, CA: RAND.
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readinginthedigitalagechina2012-140901101824-phpapp02/75/Reading-in-the-Digital-Age-China-2012-37-2048.jpg)