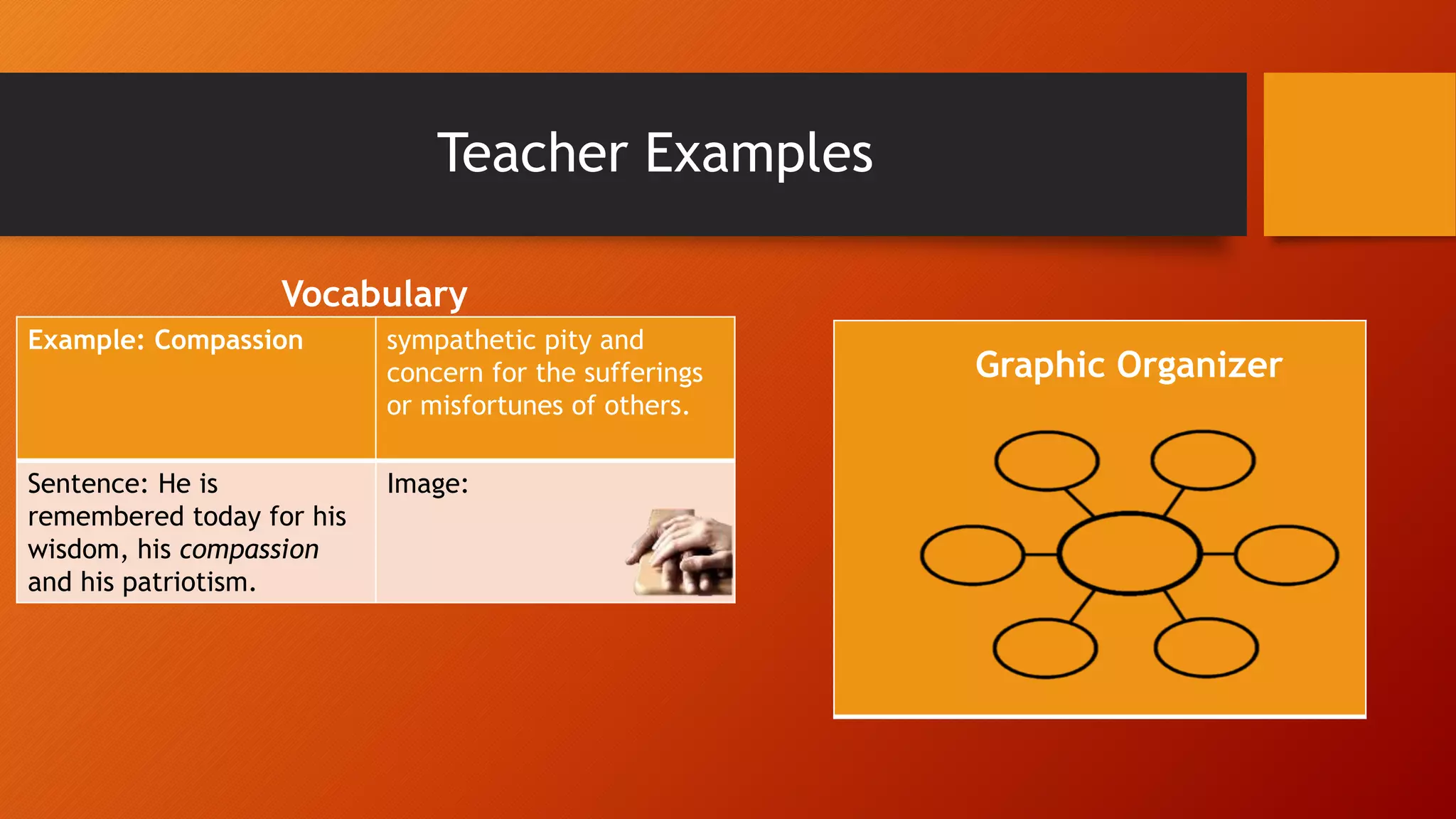
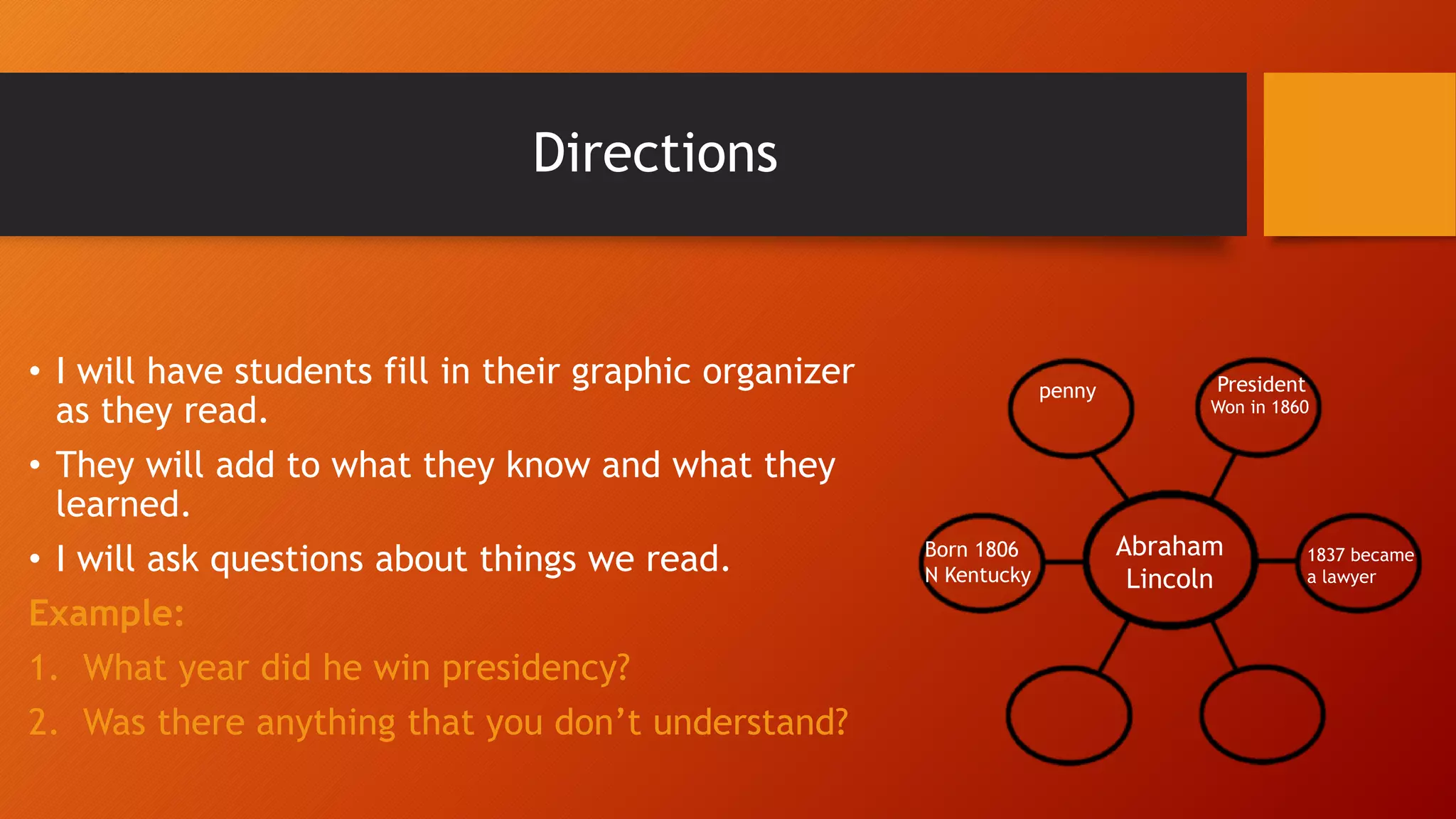
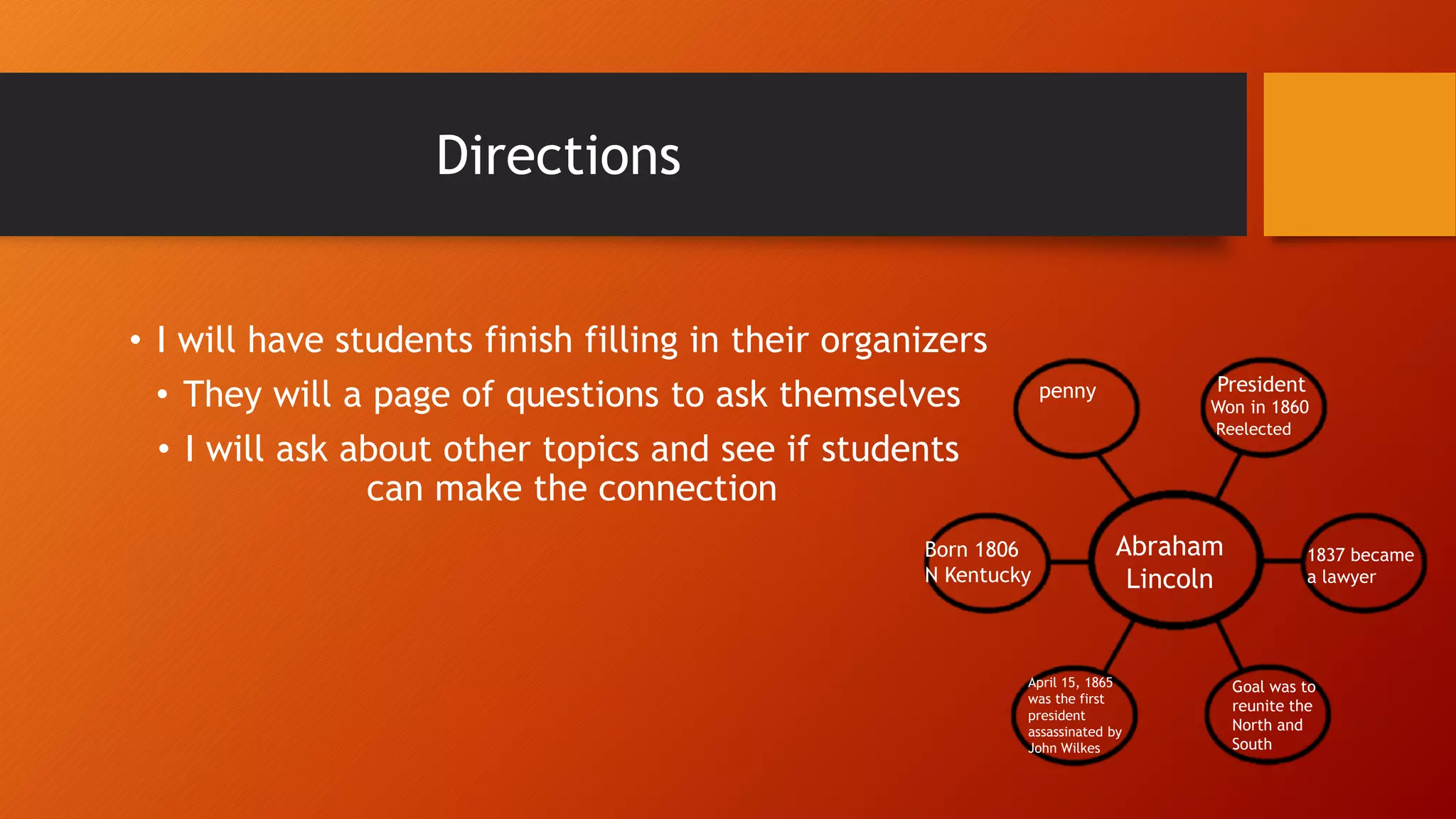
This document outlines strategies for teaching students to read effectively before, during, and after reading. It discusses having students look at titles, pictures and headings to make predictions before reading. During reading, teachers should have students fill out graphic organizers to connect new information to prior knowledge and ask comprehension questions. After reading, students summarize what they learned and generate questions while teachers evaluate comprehension. The goal is to help students understand, retain information, and think critically about what they read.