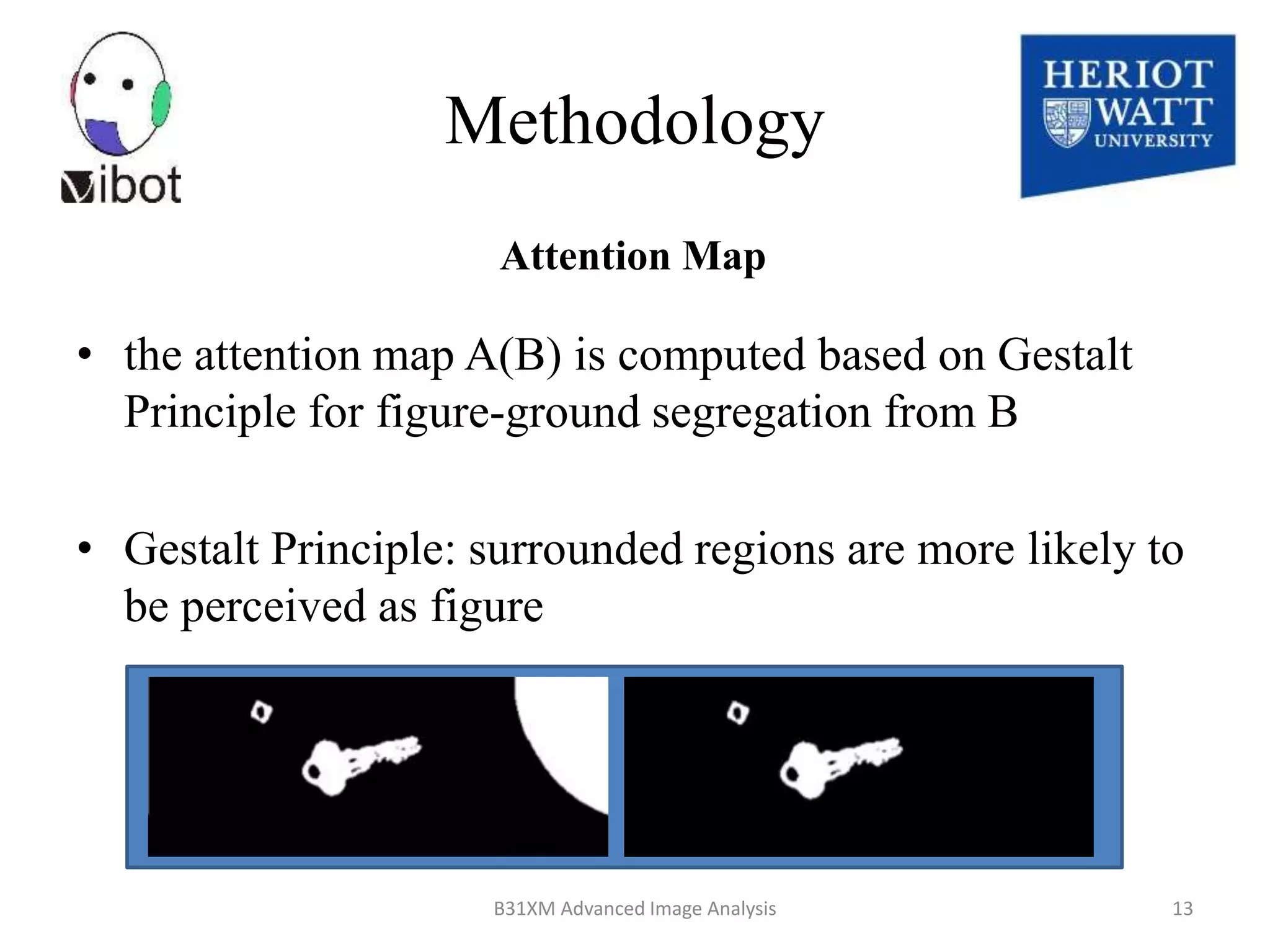
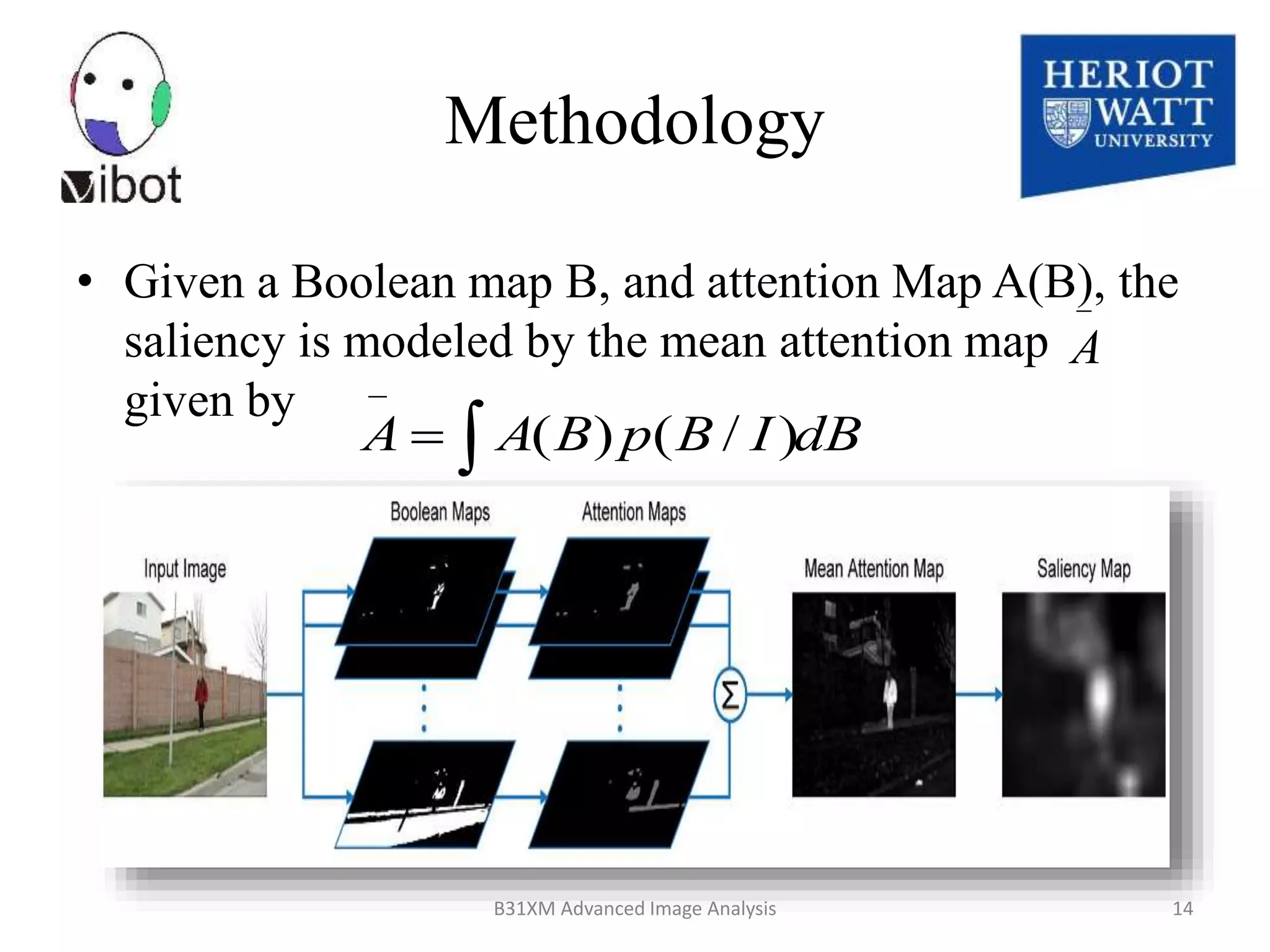
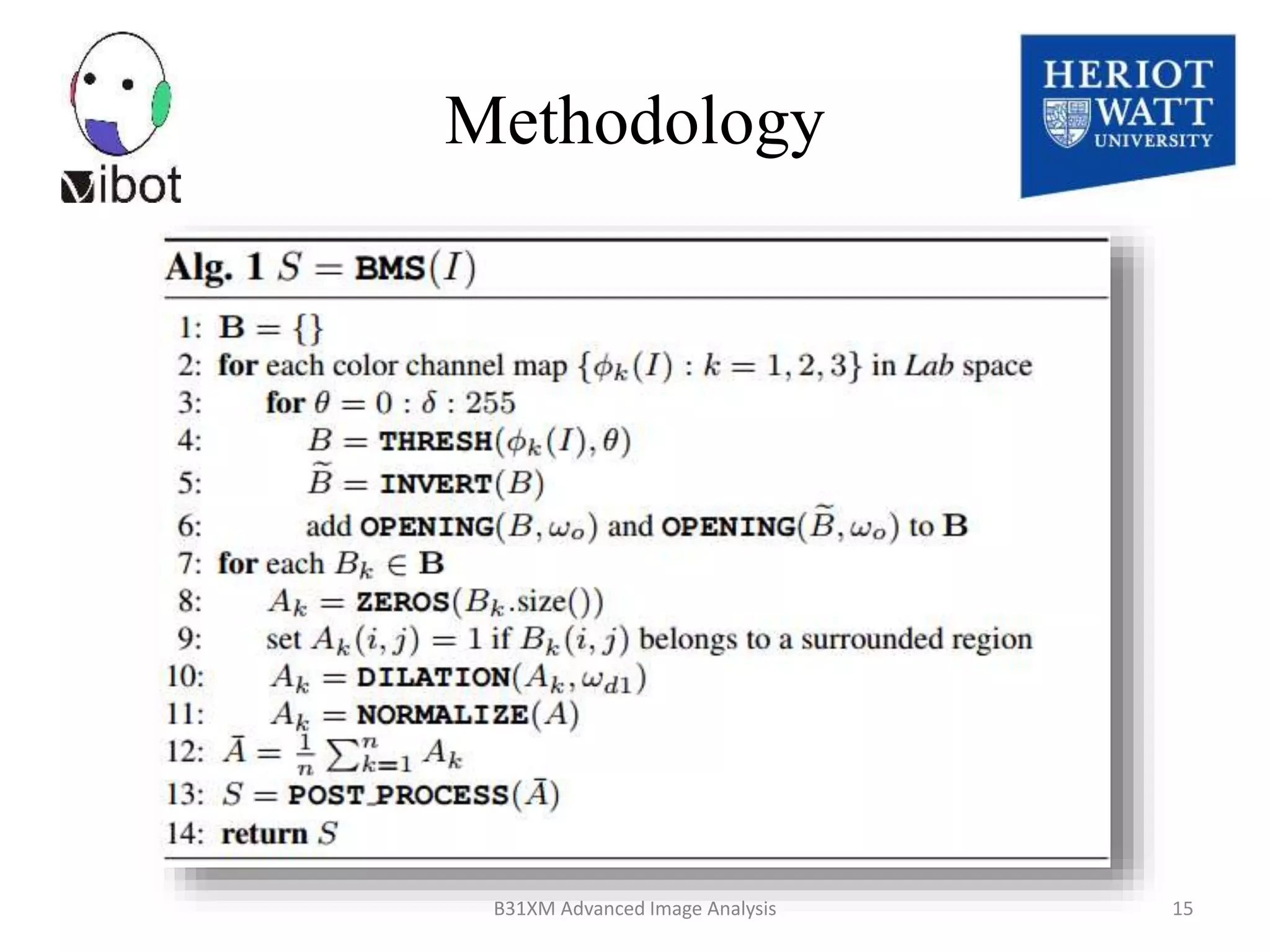
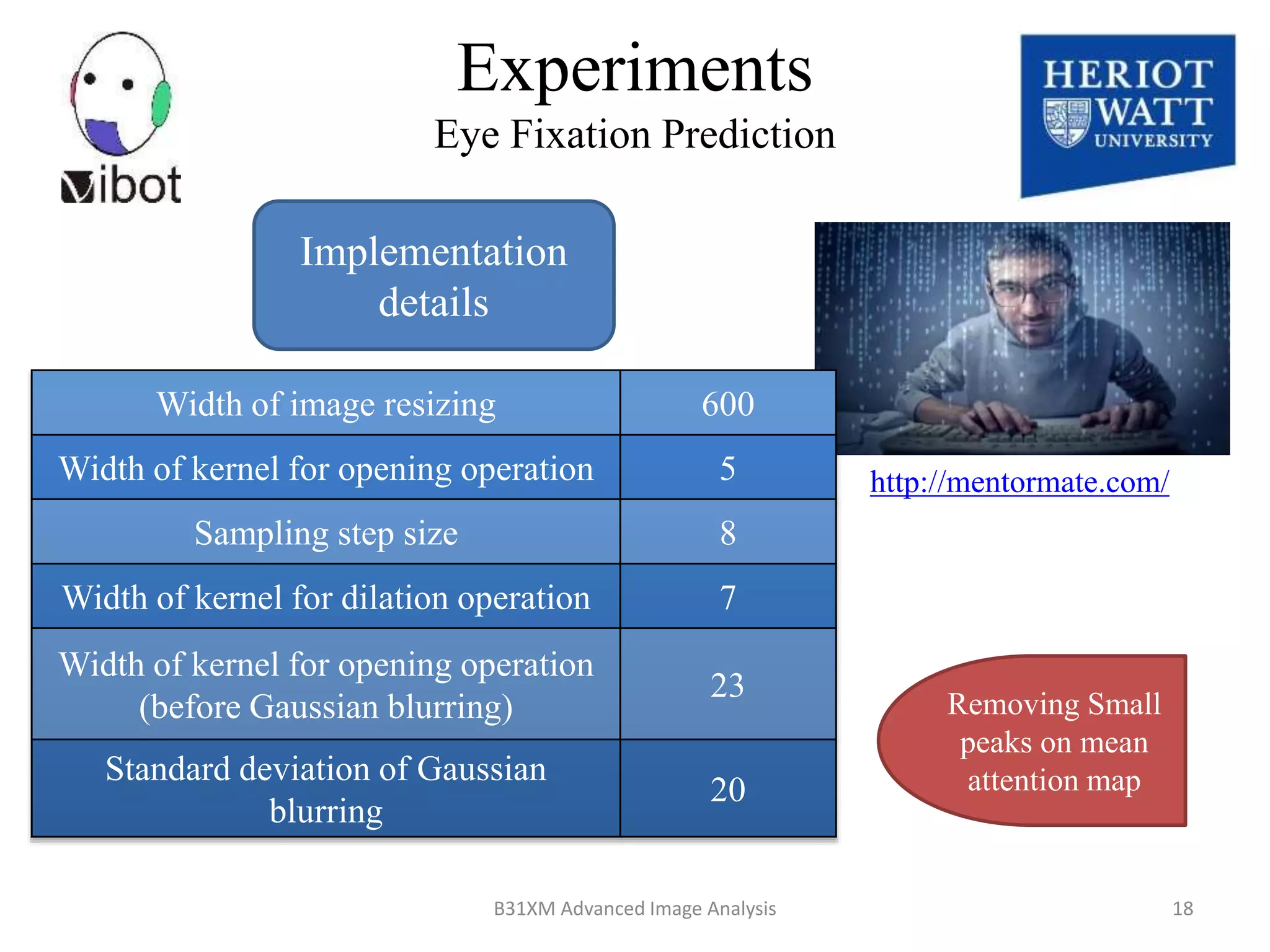
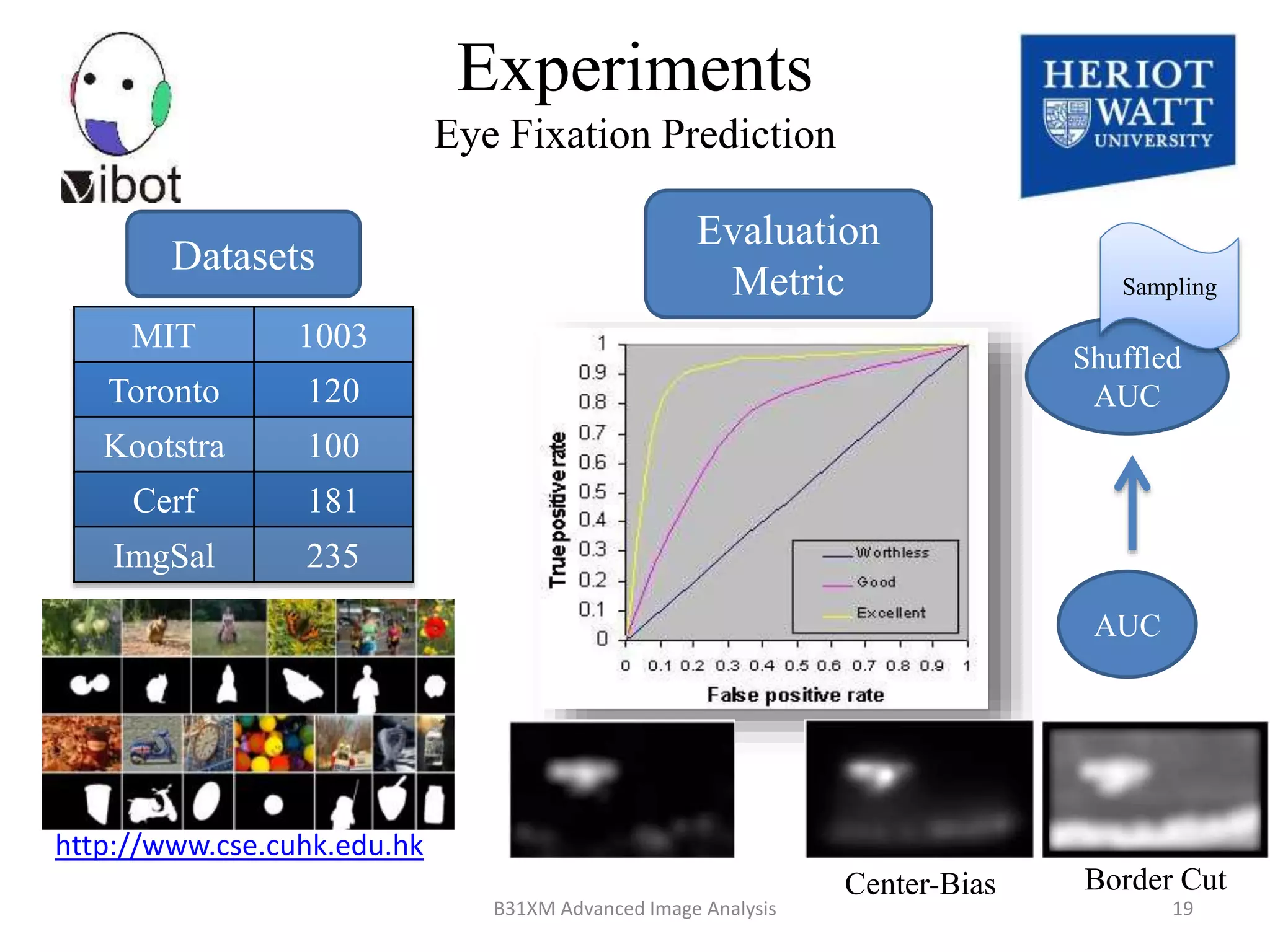
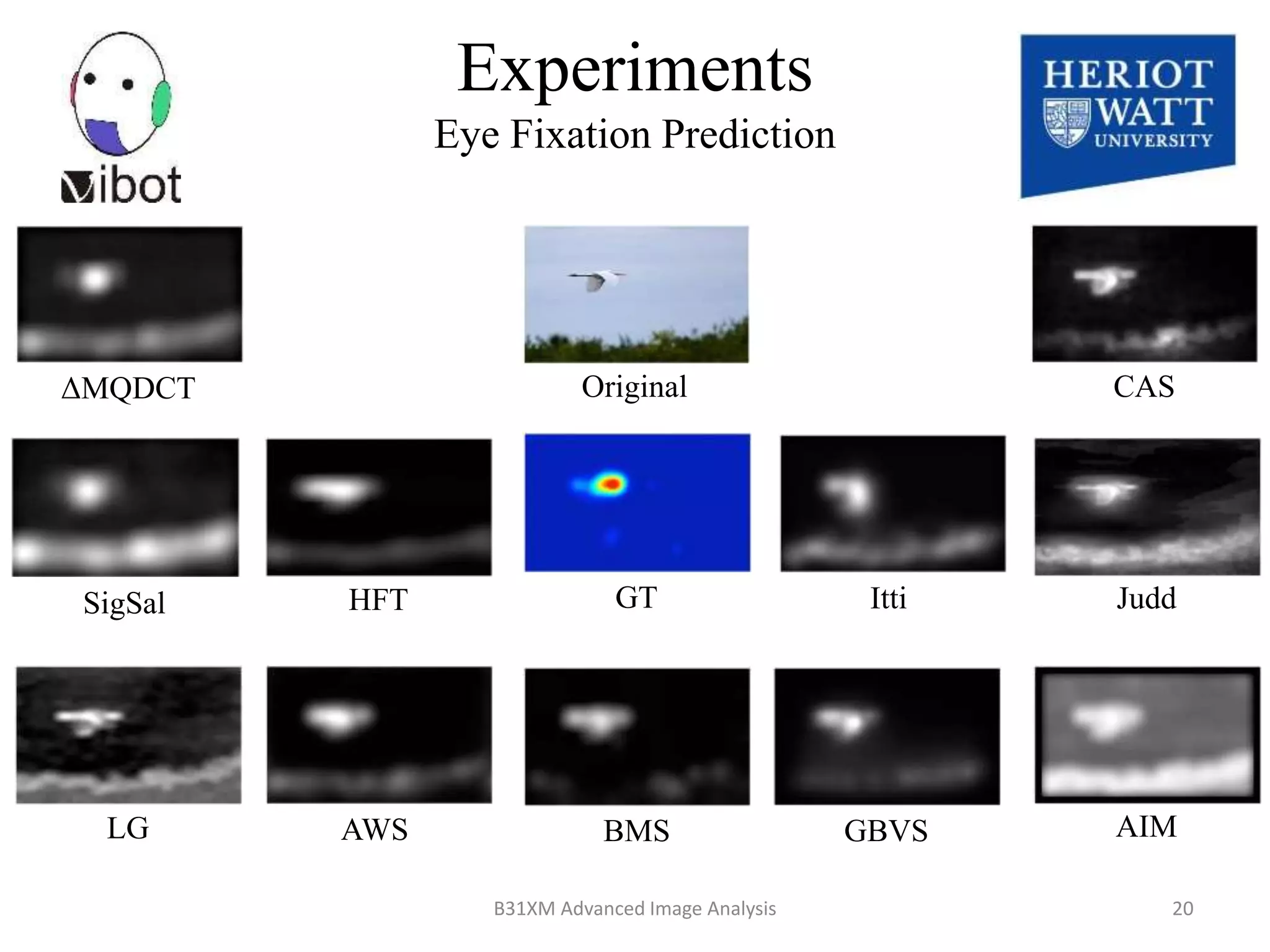
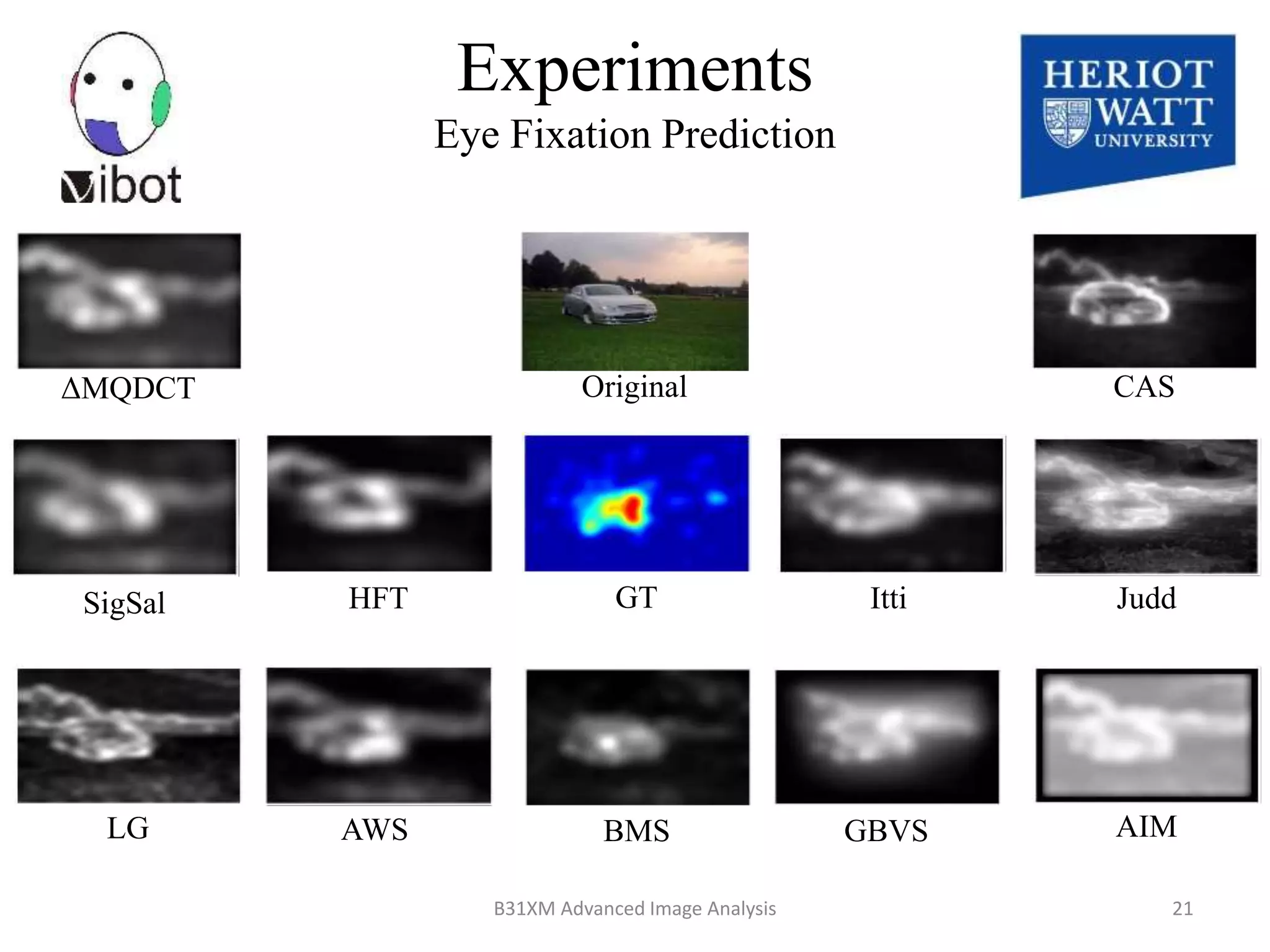
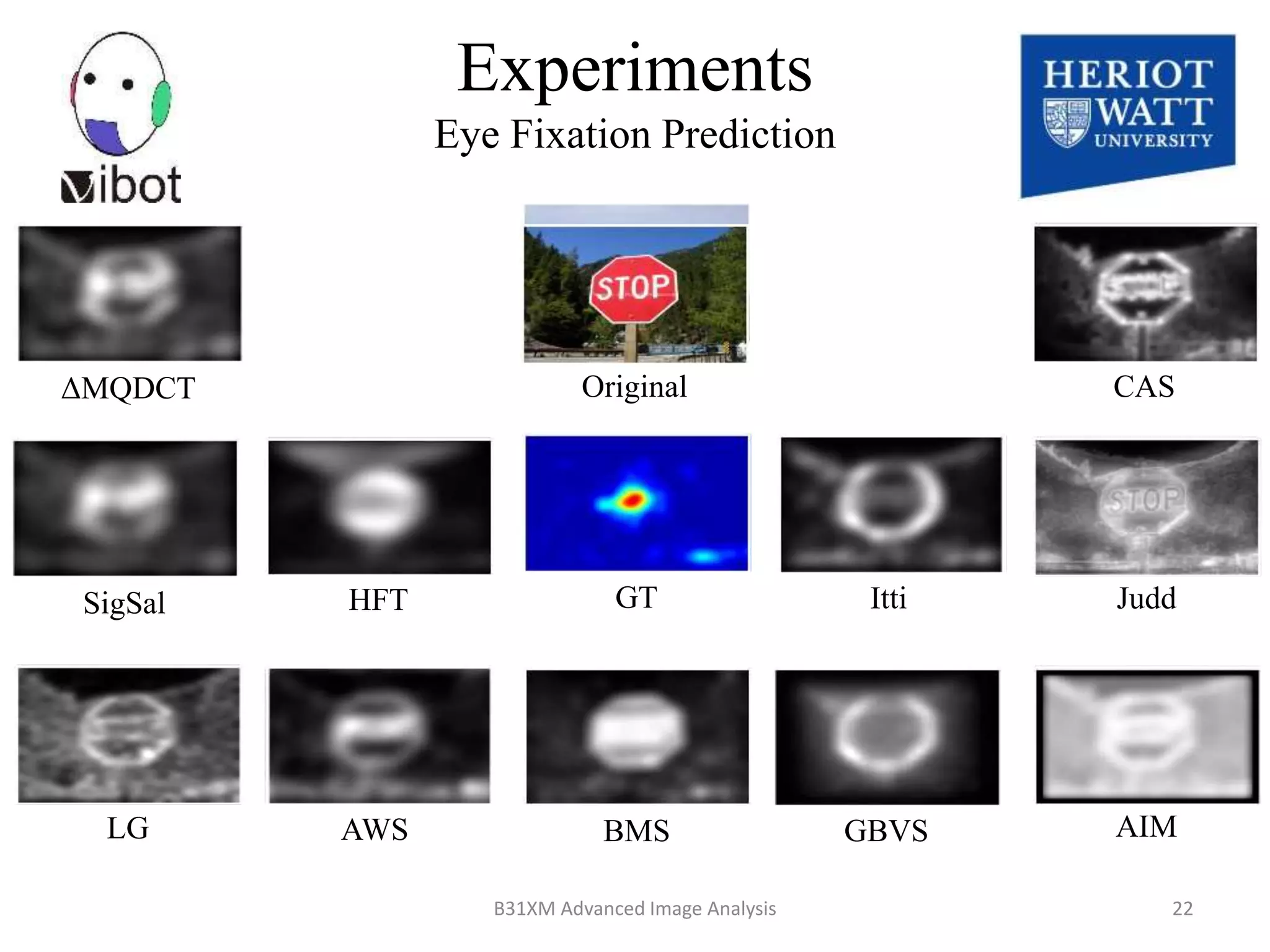
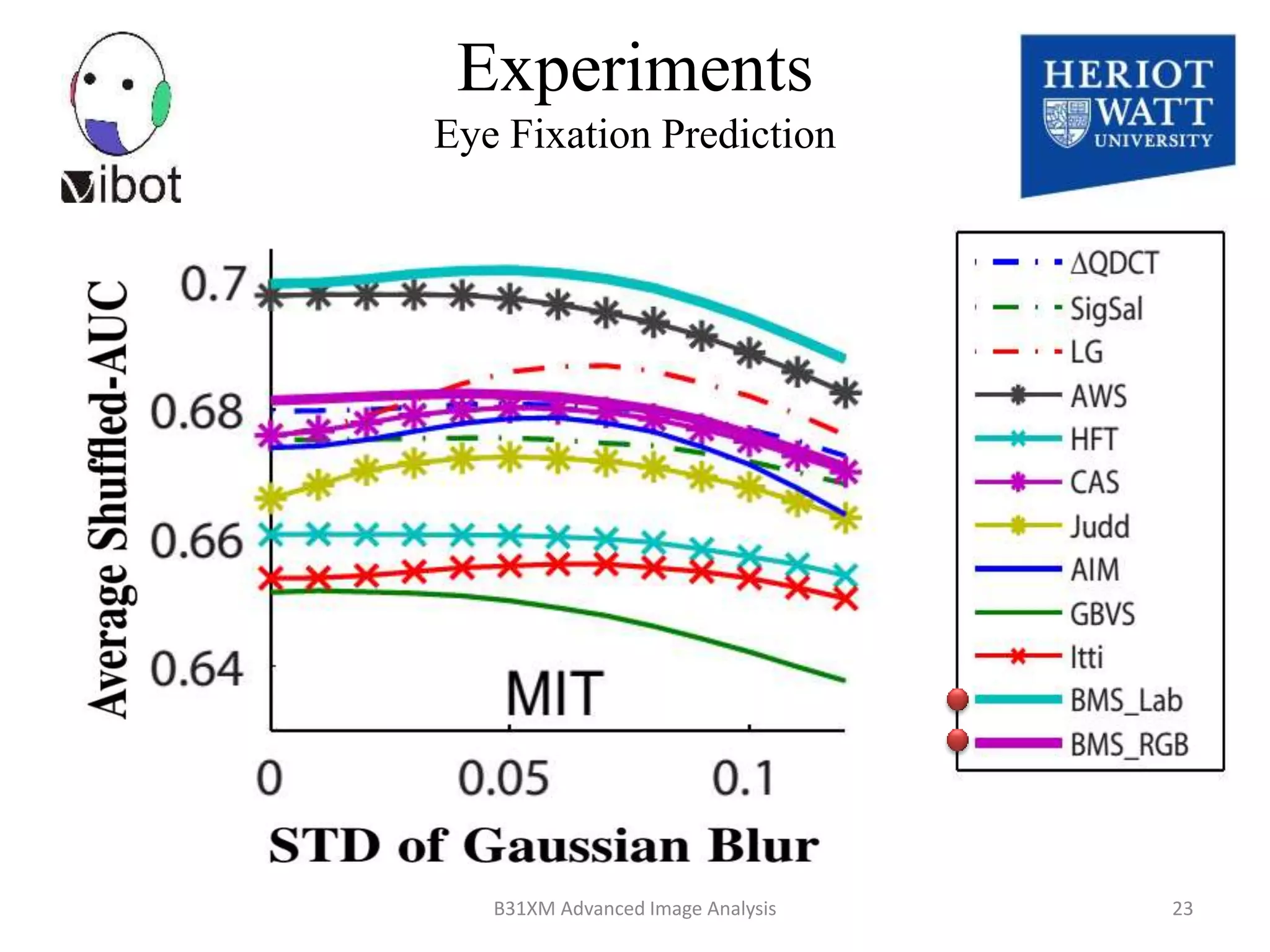
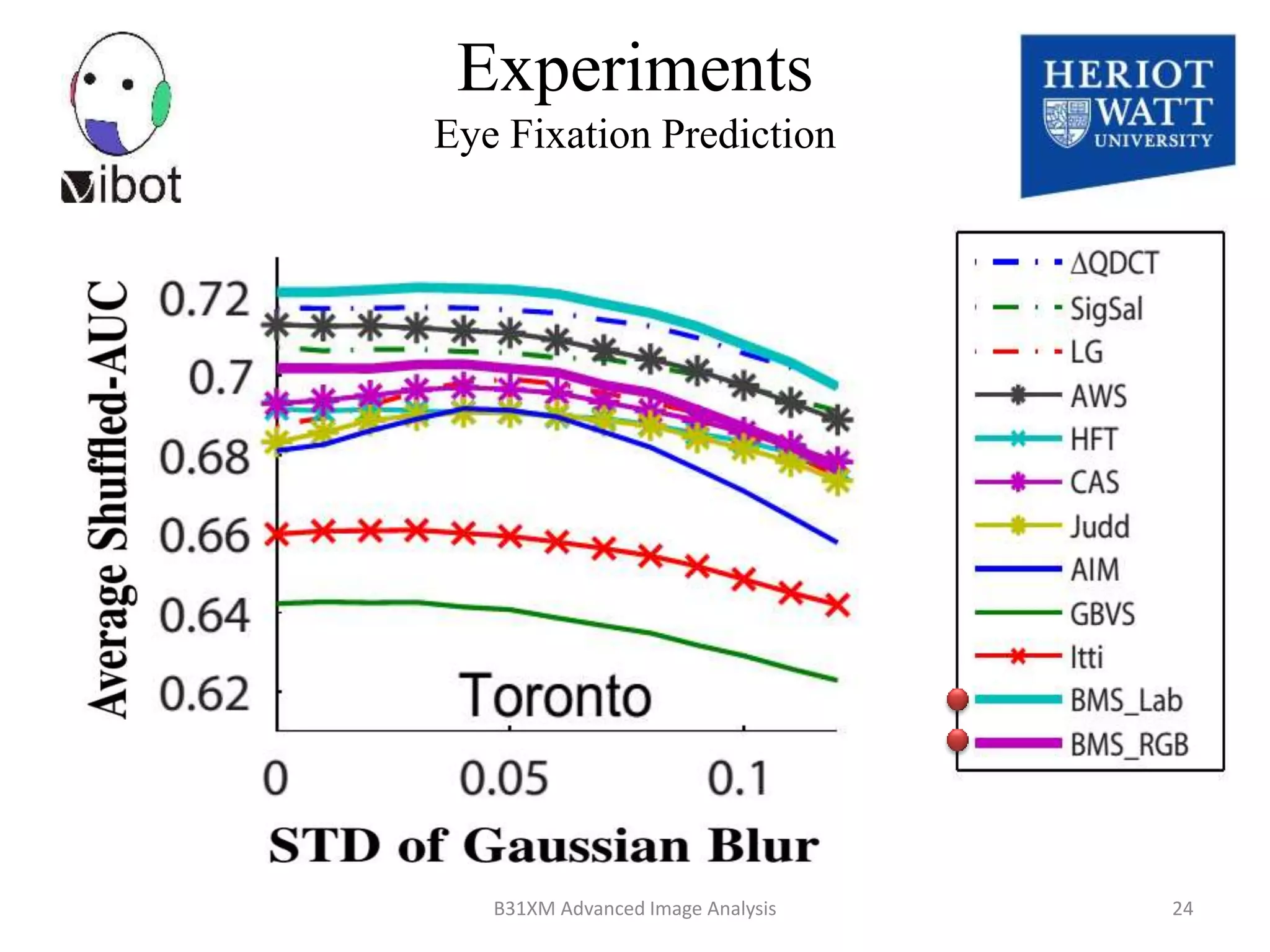
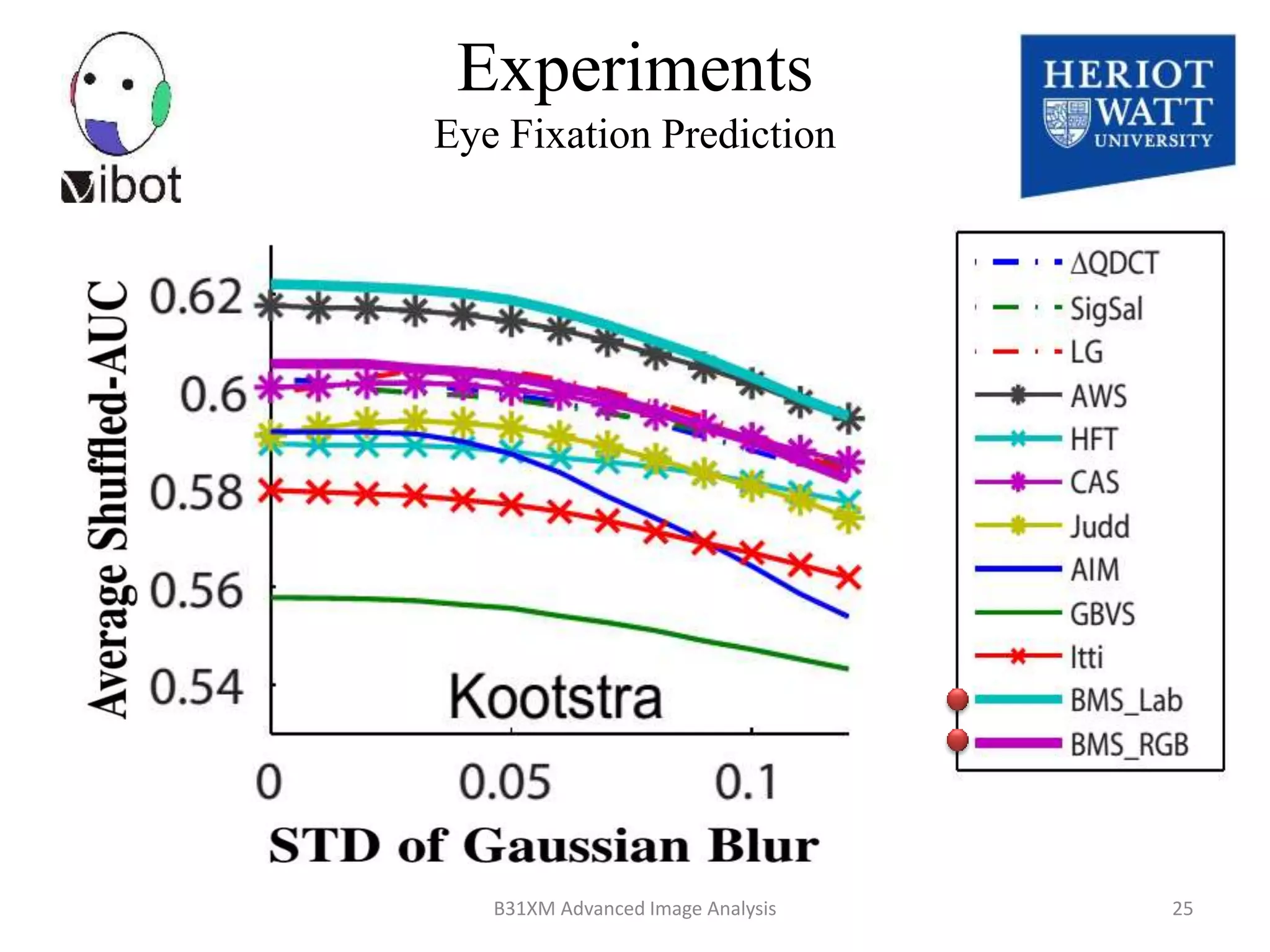
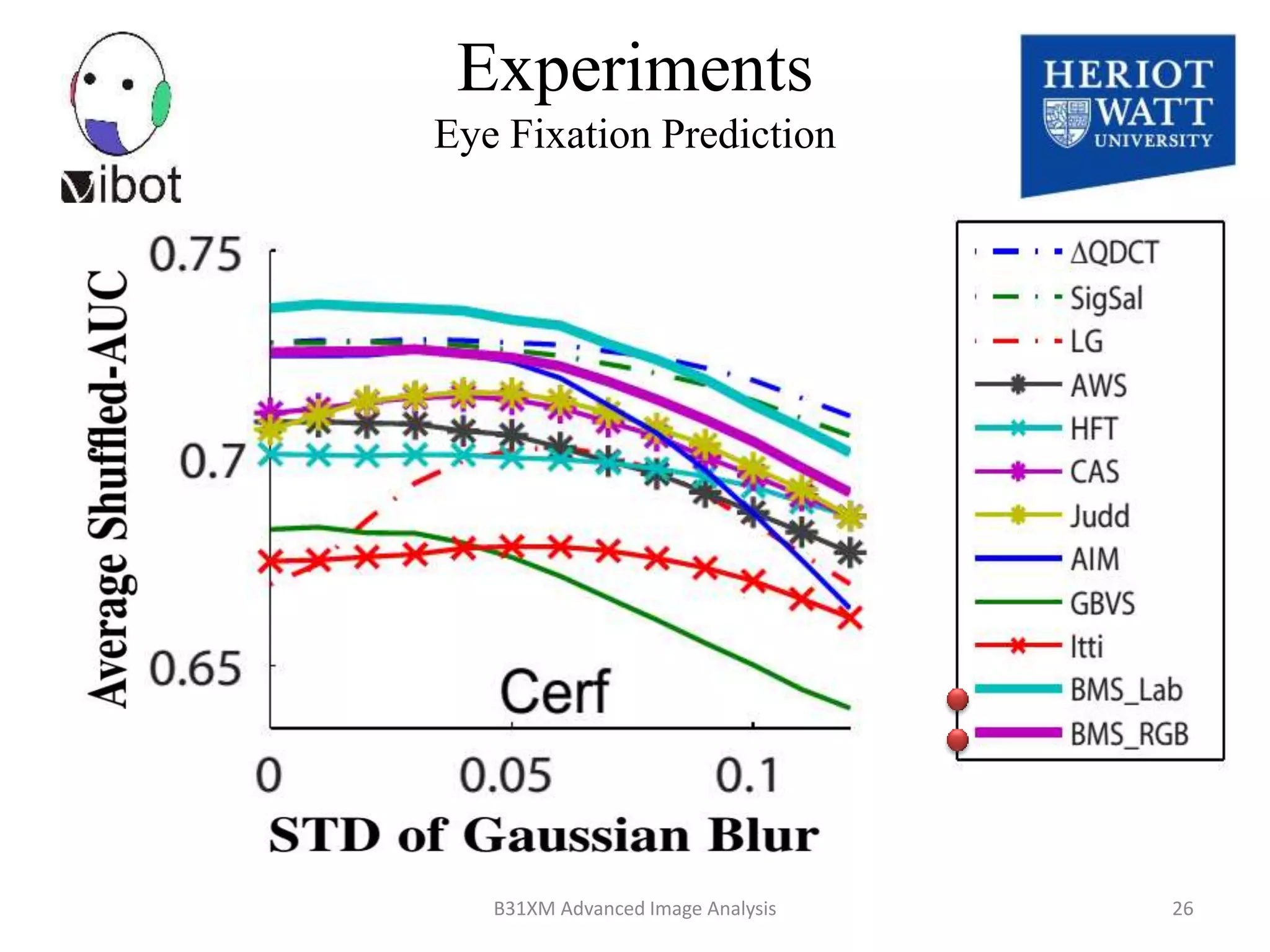
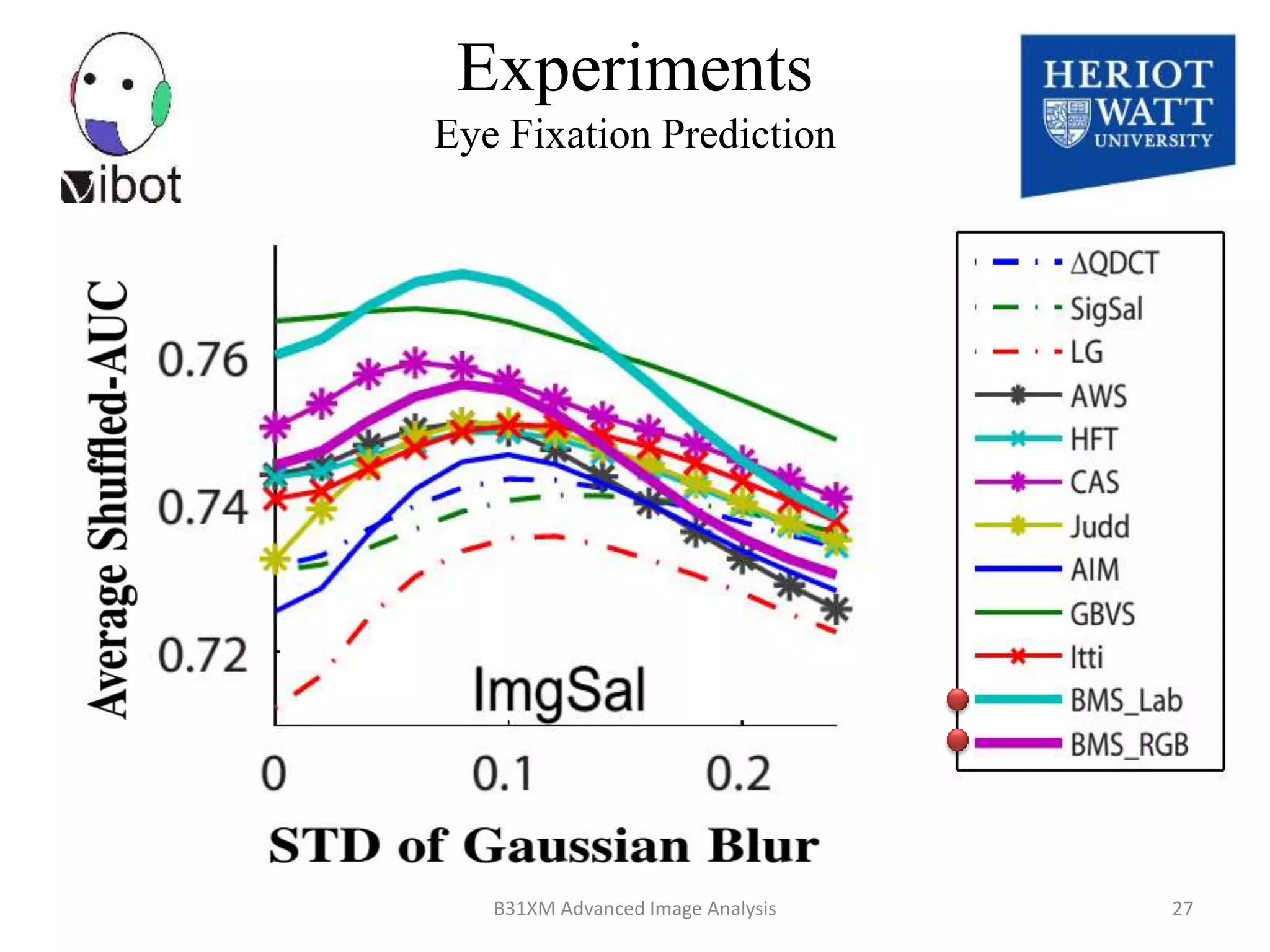
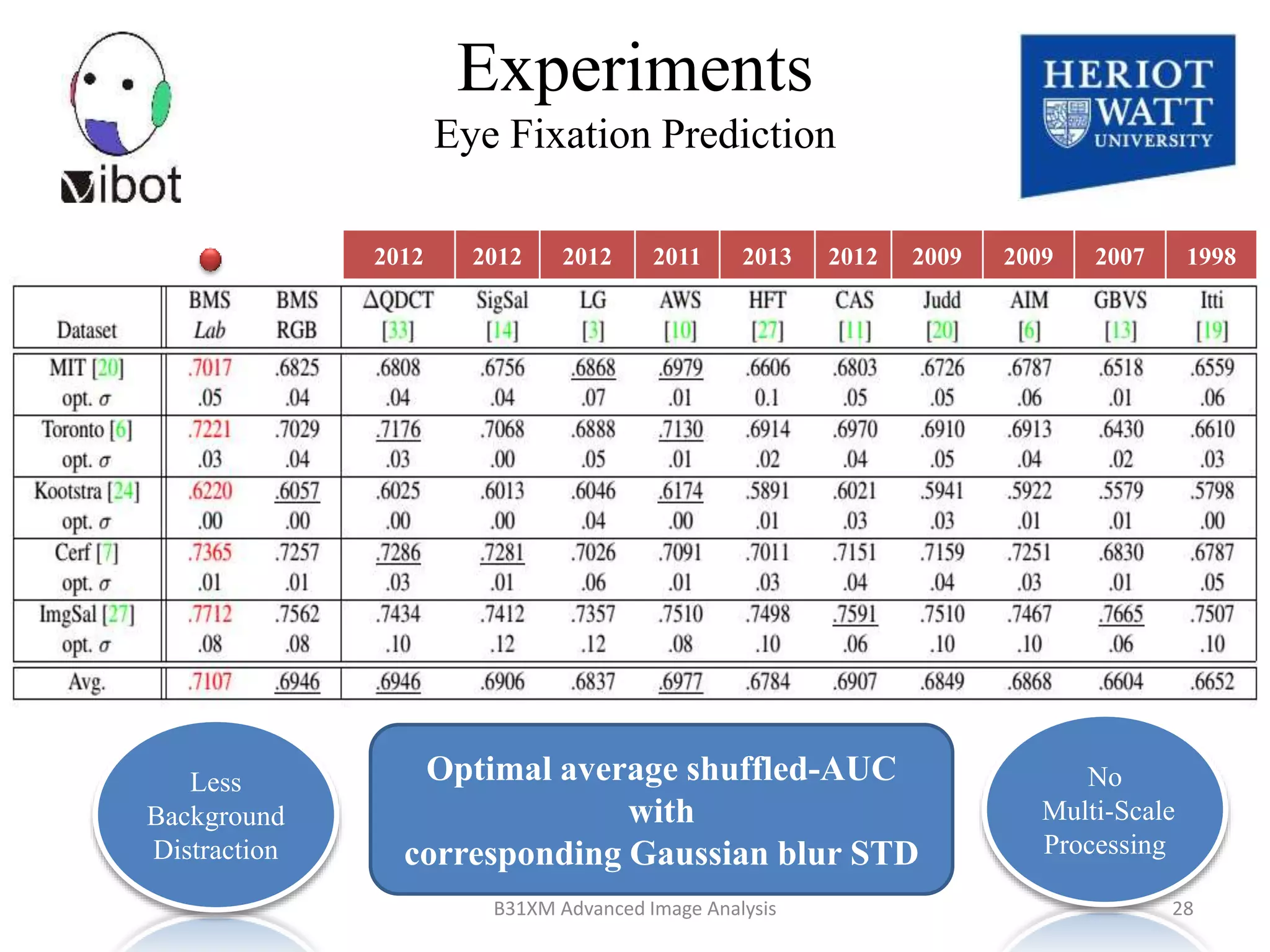
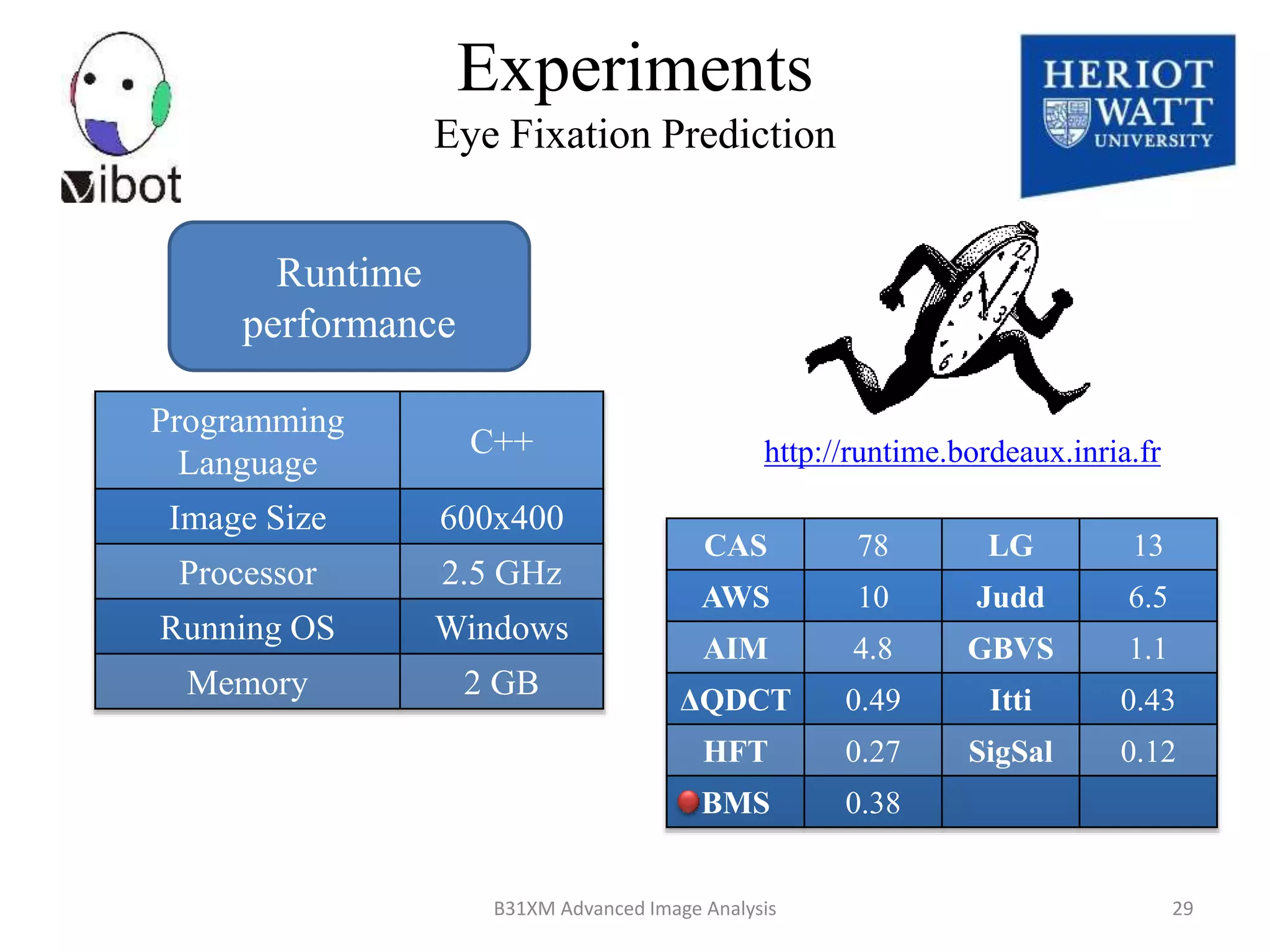
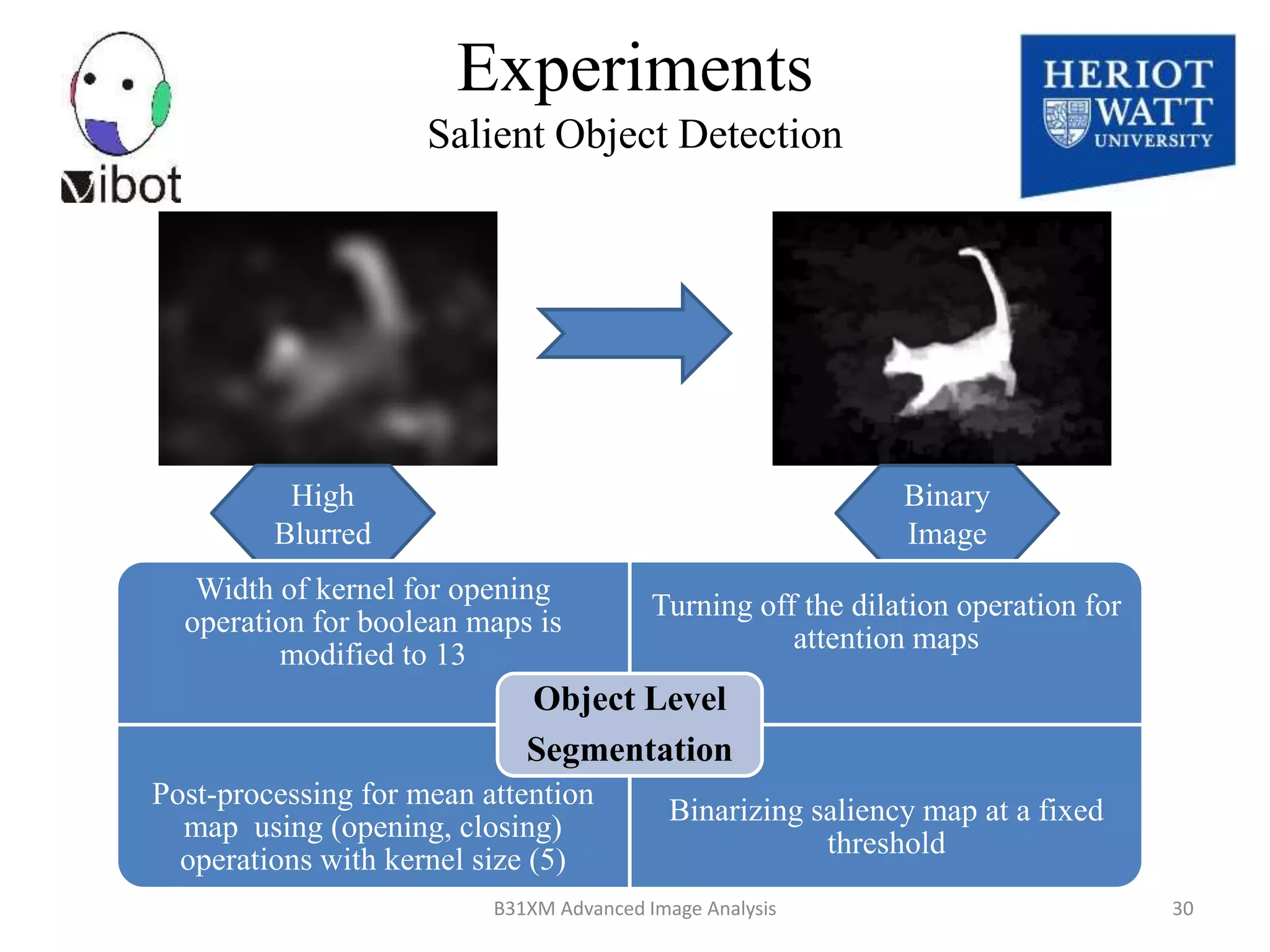
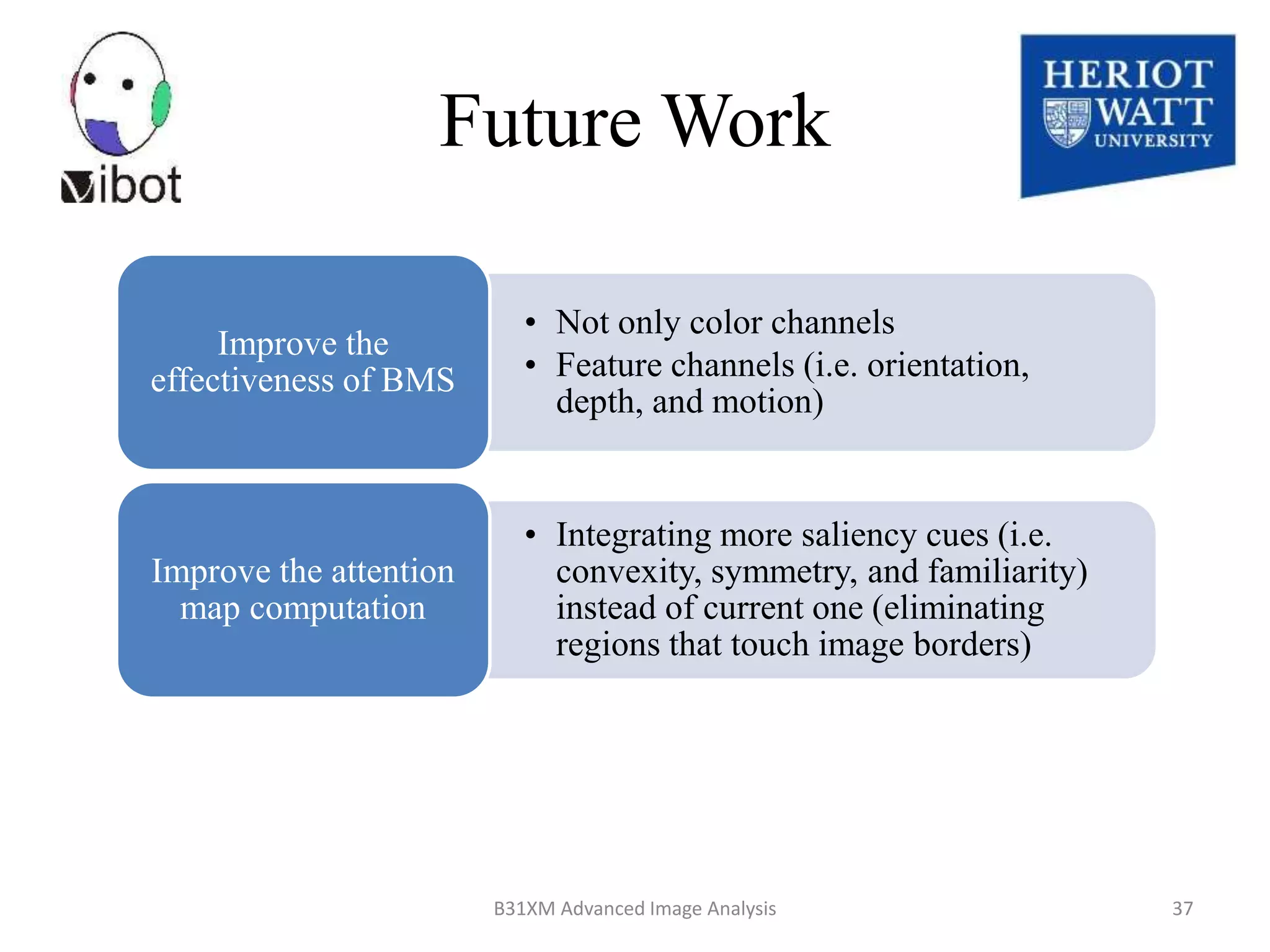
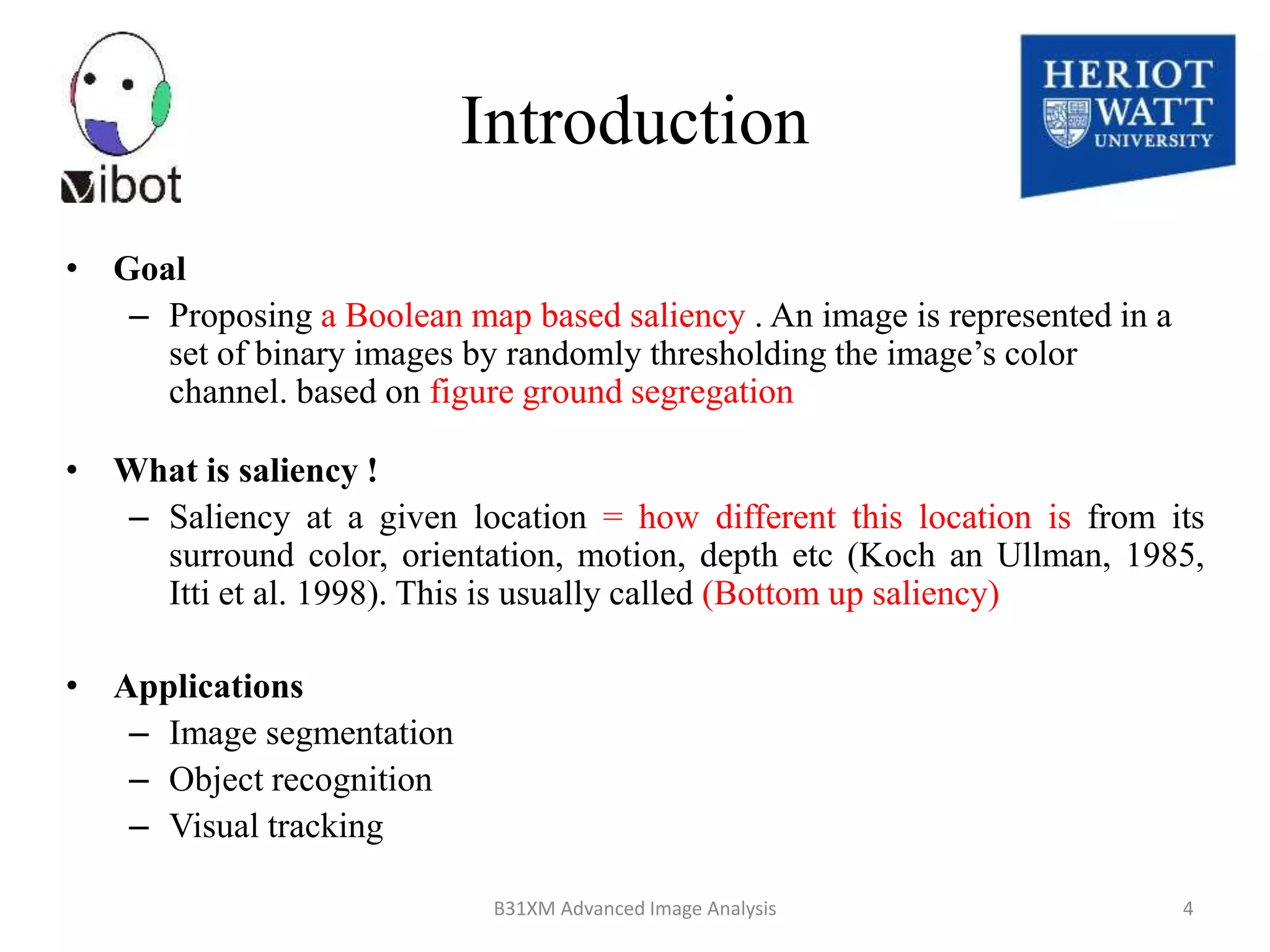
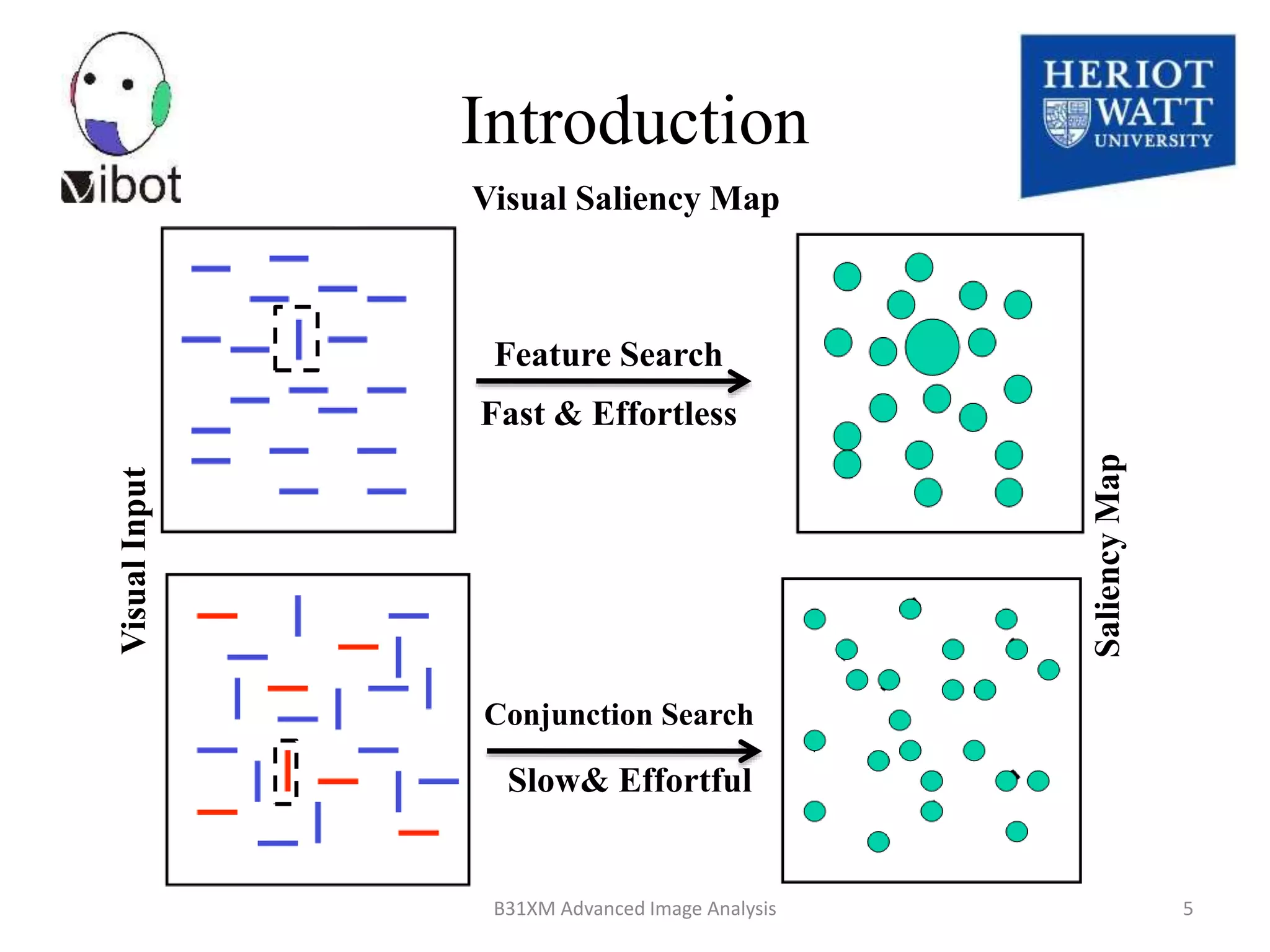
The document presents a novel boolean map approach for saliency detection, emphasizing the identification of significant image areas through binary representations based on color channel thresholds. It details methodologies and experiments that demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach in applications like image segmentation and object recognition. The findings indicate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting eye fixation and suggests future enhancements by incorporating additional feature channels.





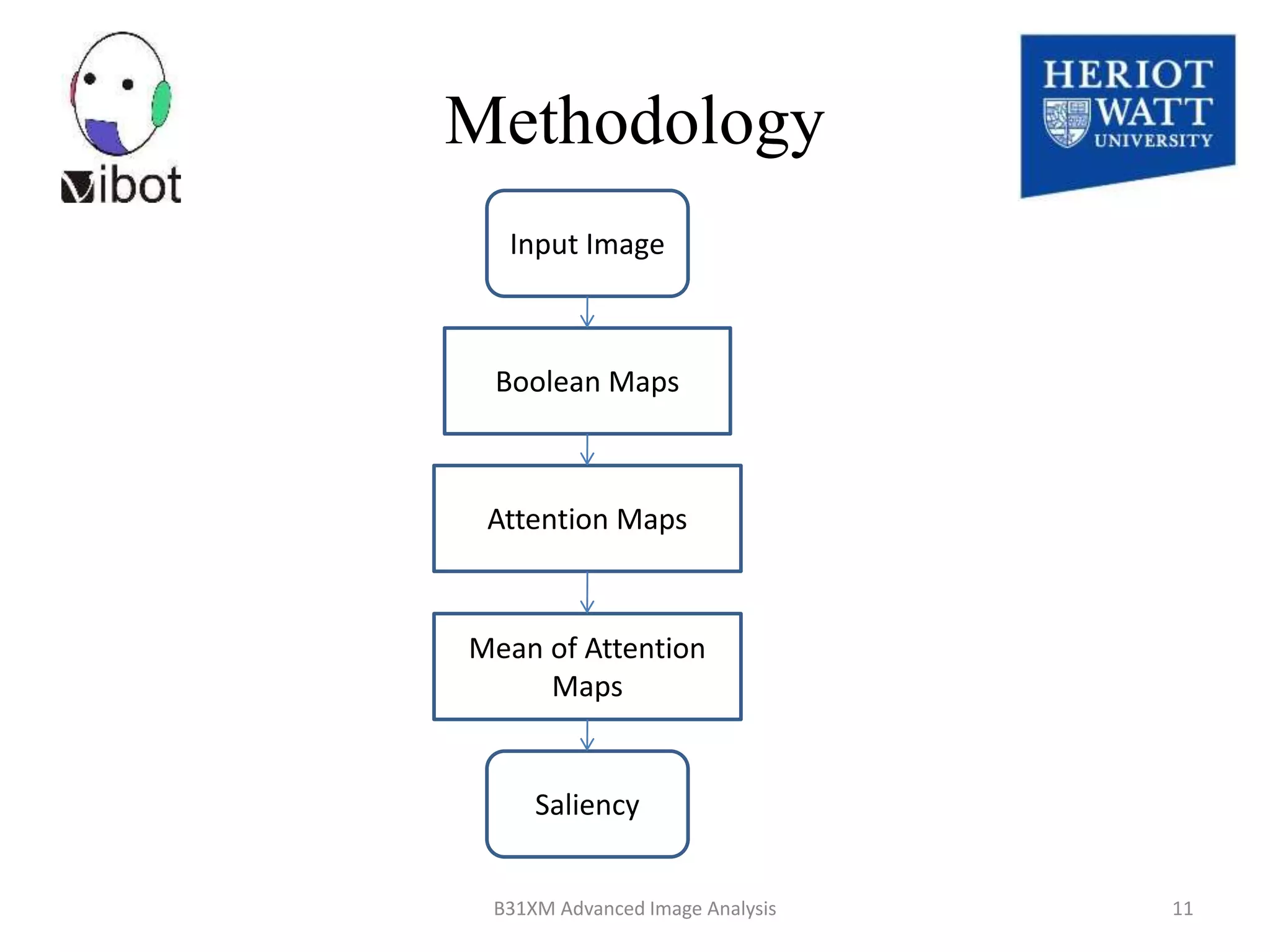
![It is generated by randomly thresholding an input image I
Where
donates feature map of I
Randomly generated threshold in the range [0, 255]
CIE lab color space (perceptual uniformity)
8/18/2014 B31XM Advanced Image Analysis 12
Boolean MAP
)),(( ITHRESHBi
)(I
Methodology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageprocessingfinal-140817203236-phpapp02/75/Reading-Group-Saliency-Detection-A-Boolean-Map-Approach-12-2048.jpg)