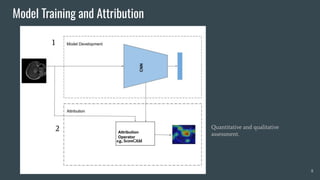
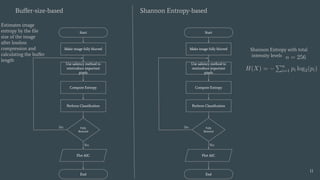
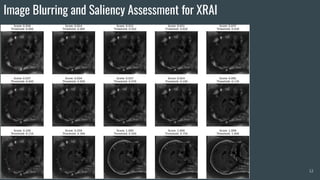
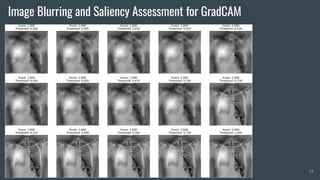
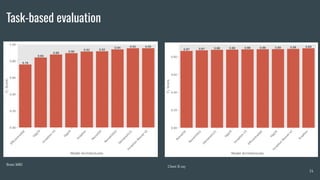
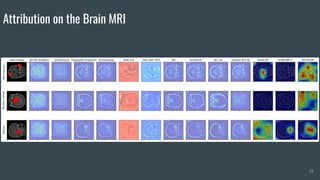
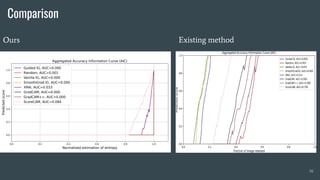
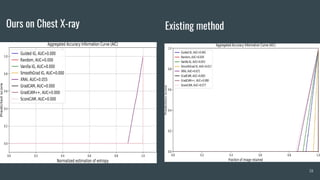
The document discusses the evaluation of explainable deep learning techniques in medical image analysis, focusing on saliency methods applied to datasets like brain tumor MRI and COVID-19 chest X-rays. It highlights the significance of explainability for clinical adoption and the lack of quantitative analysis in existing methods. Key findings include the effectiveness of specific saliency methods and the proposal of a framework combining qualitative and quantitative assessments to enhance model explainability.