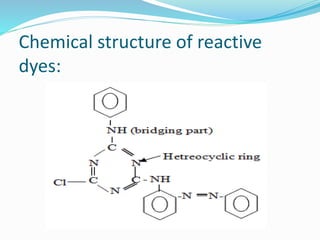
The document summarizes the general structure and properties of reactive dyes. Reactive dyes have a D-B-G-X structure, where D is the dye/chromogen, B is the bridging group, G is the reactive group, and X is the actual reactive functional group. Reactive dyes form covalent bonds with cellulosic fibers and have good wash and light fastness as a result. They are classified based on the number of reactive groups and dyeing temperature. Factors like pH, temperature, electrolyte concentration influence the dyeing process. Defects can occur but are remedied by washing or chemical treatment.