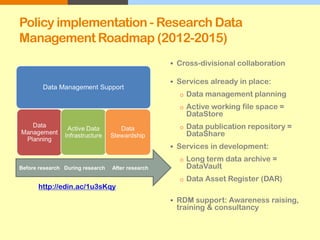
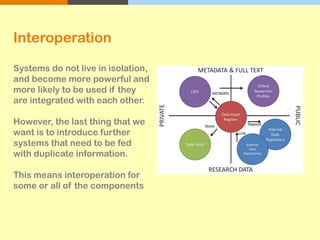
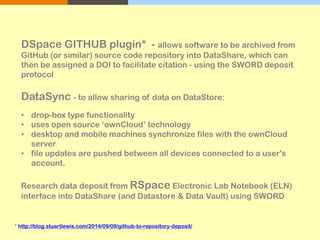
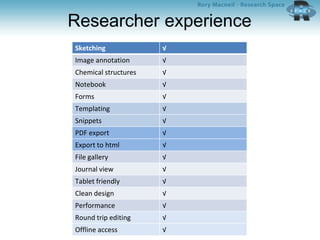
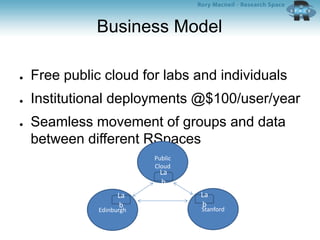
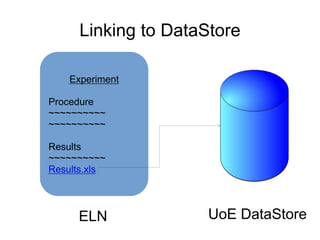
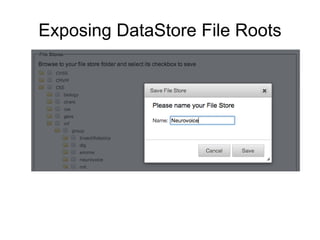
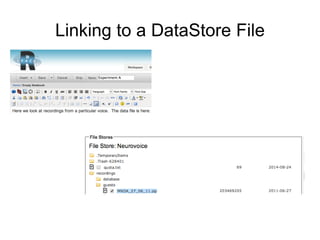
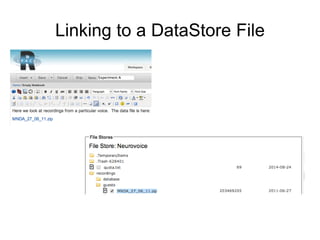
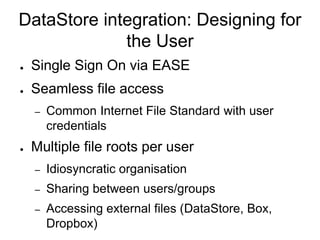
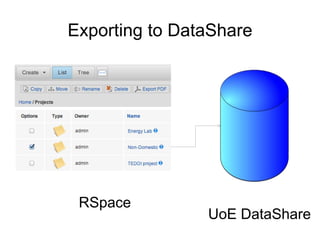
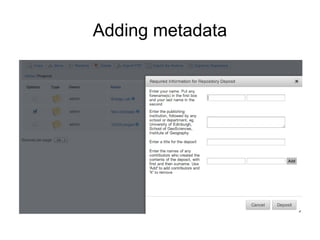
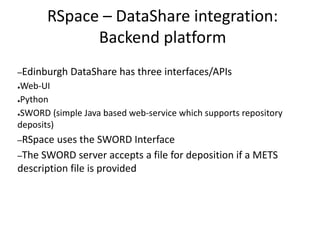
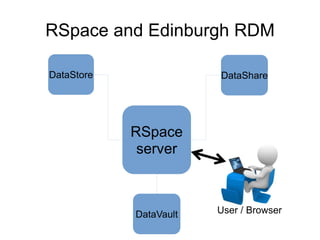
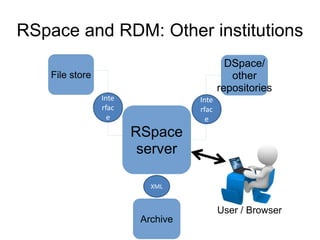
The document outlines the University of Edinburgh's Research Data Management (RDM) strategy, including its policies, services, and infrastructure for managing research data. It details systems such as Datastore for active data storage, Datashare for data publication, and Datavault for long-term storage, along with training and support for researchers. Additionally, it discusses the integration of the RSpace electronic lab notebook with these systems to enhance data management and accessibility.