The document contains two questions and their answers regarding ratios for a motorcycle rental company.
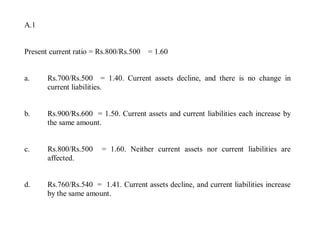
Question 1 asks about the effect of four transactions on the company's current ratio: a) purchasing bikes decreases the ratio, b) borrowing money has no effect, c) issuing stock has no effect, and d) paying a dividend decreases the ratio.
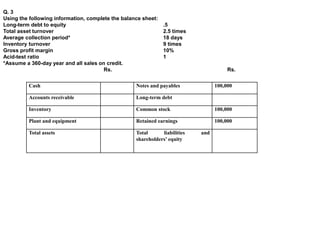
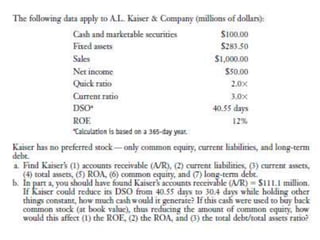
Question 2 provides partial balance sheet information and asks to complete the balance sheet using various ratios. The answer fills in the missing values to complete the balance sheet.