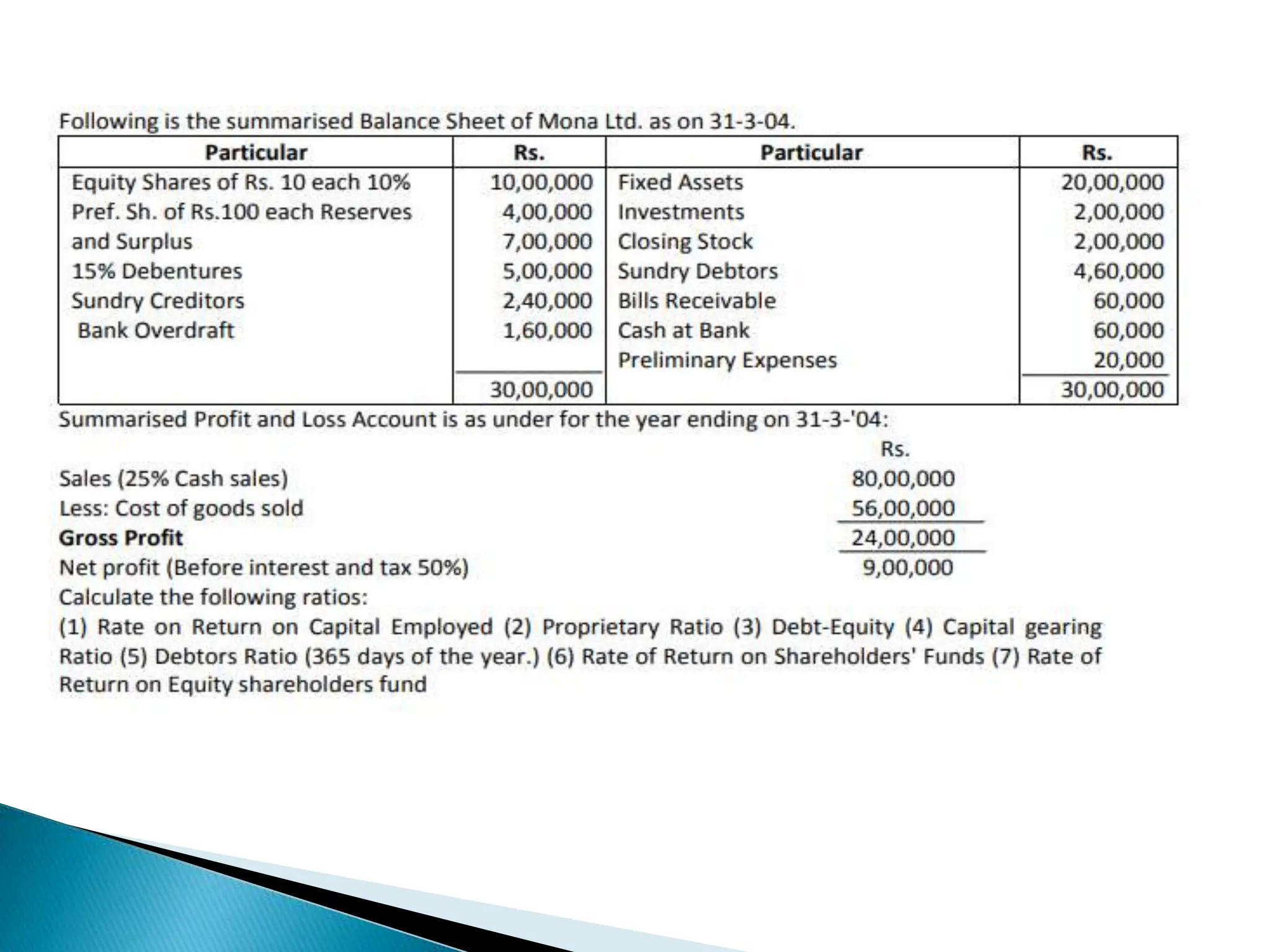
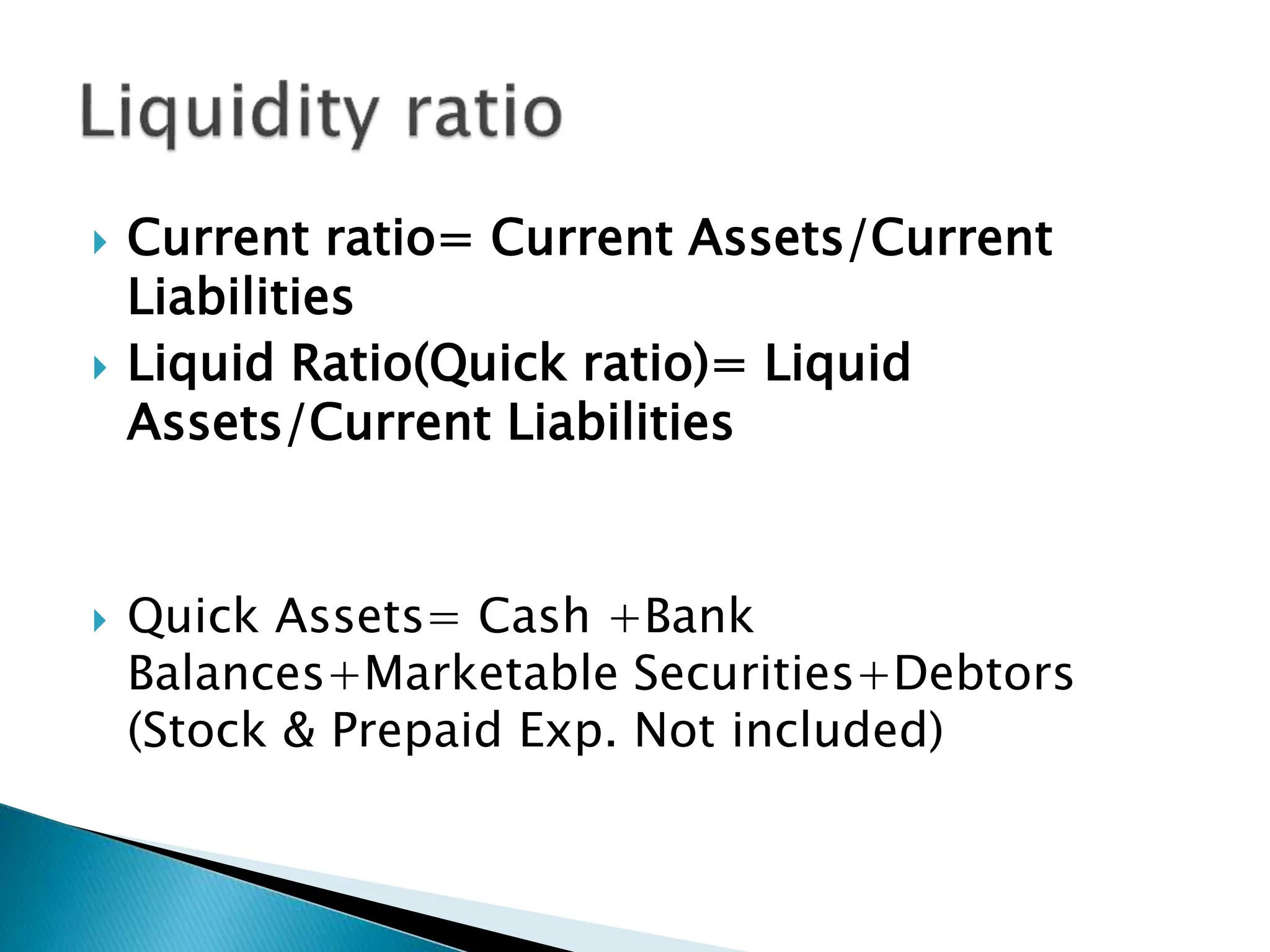
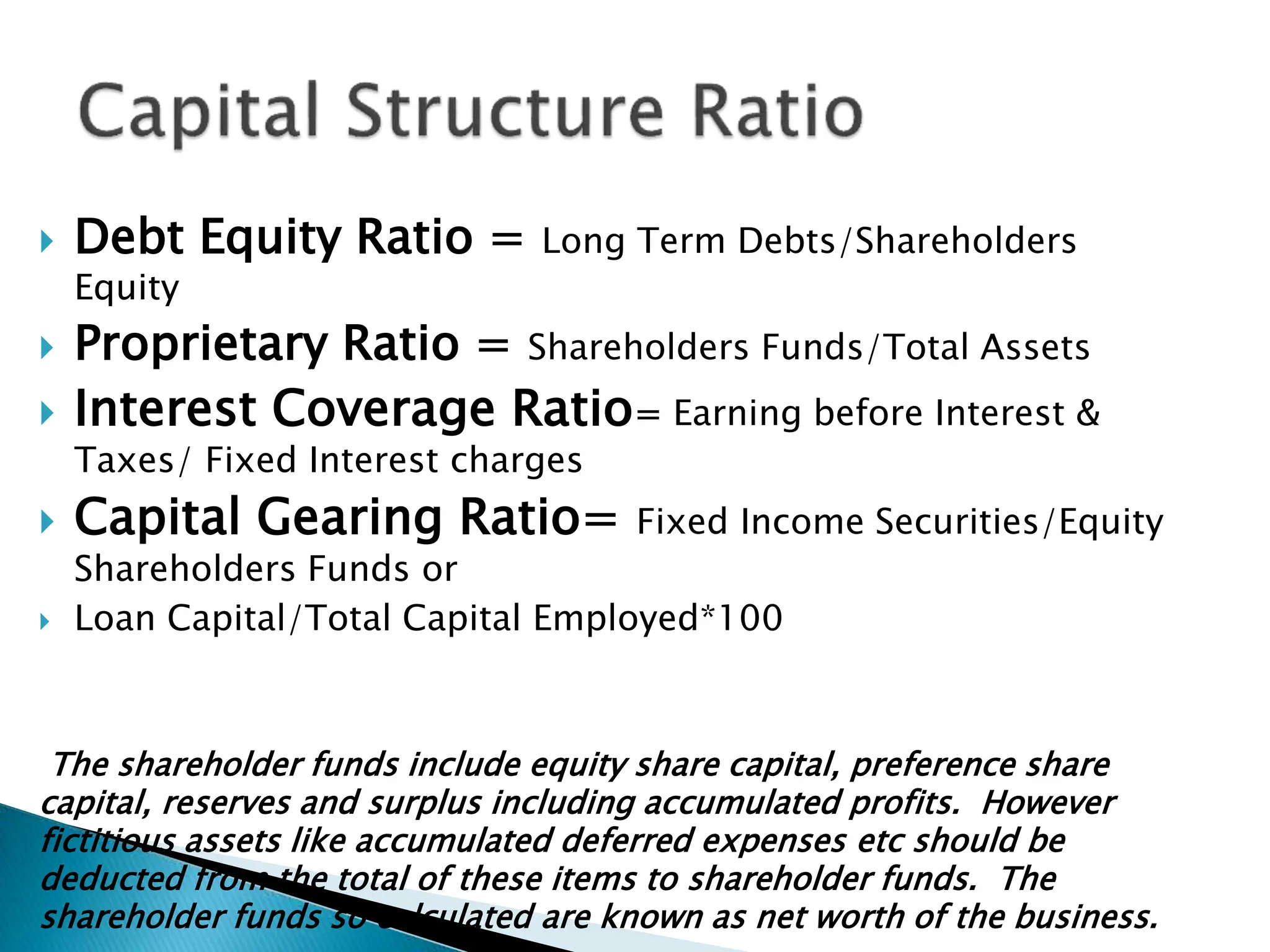
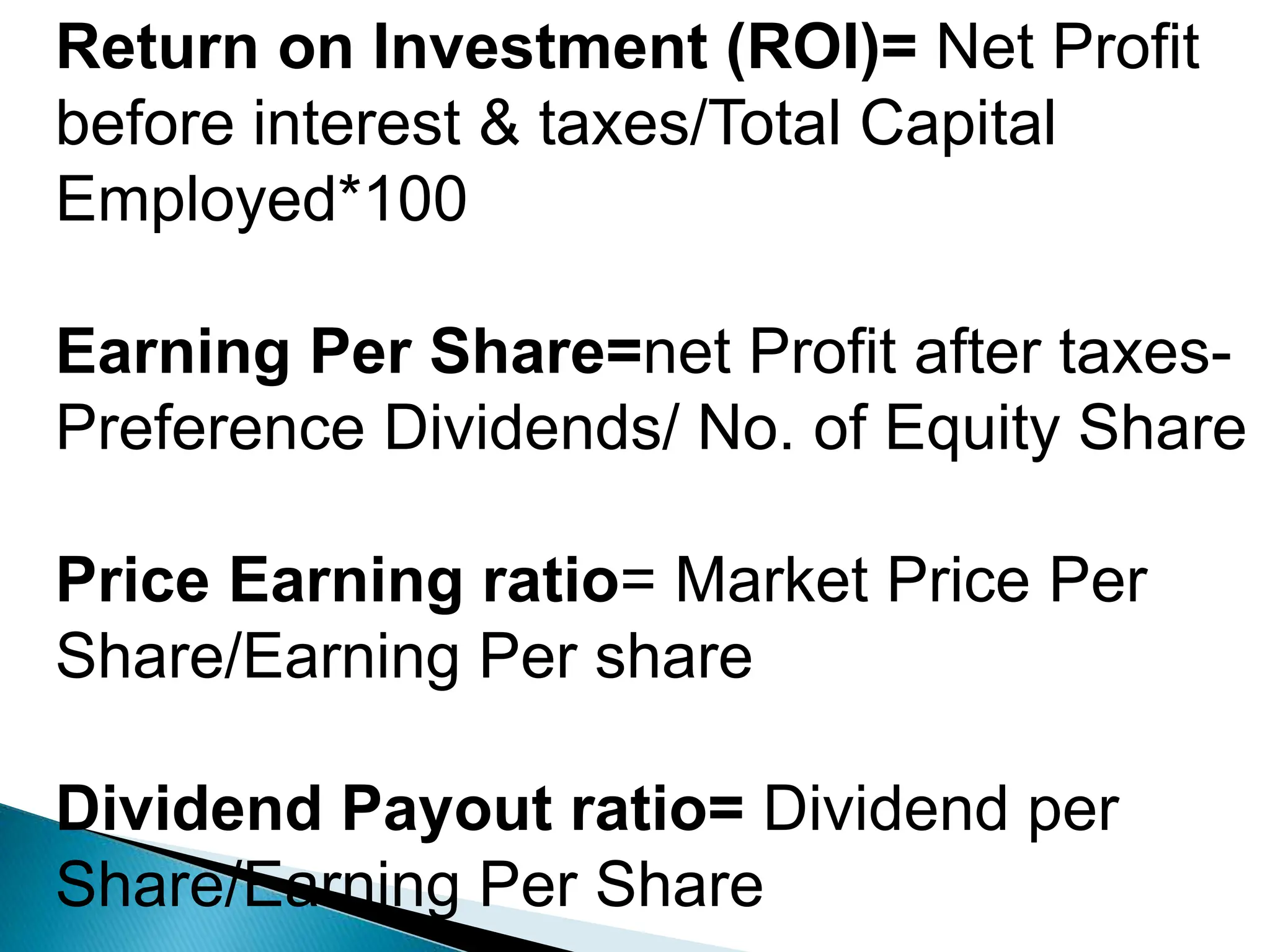
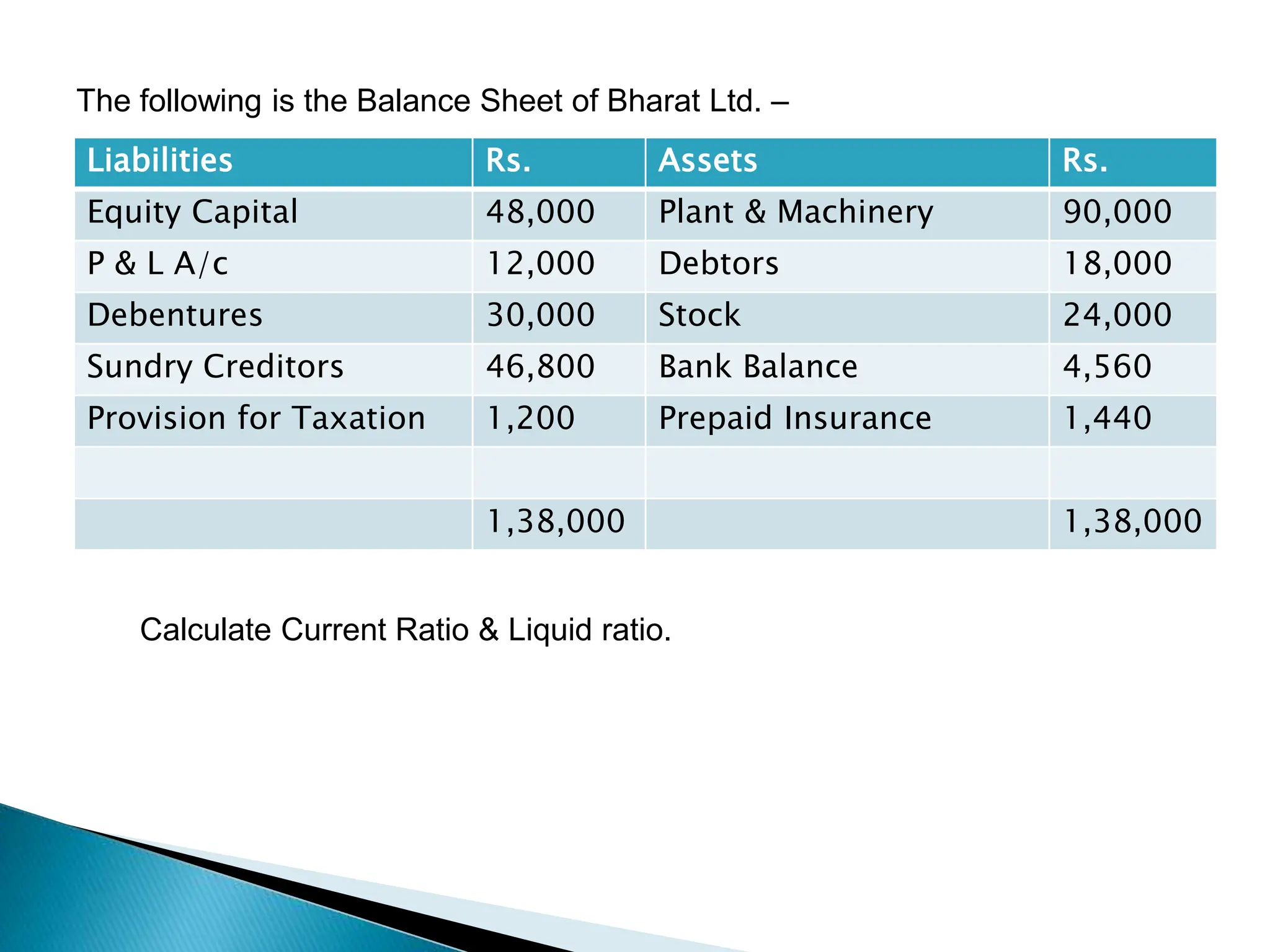
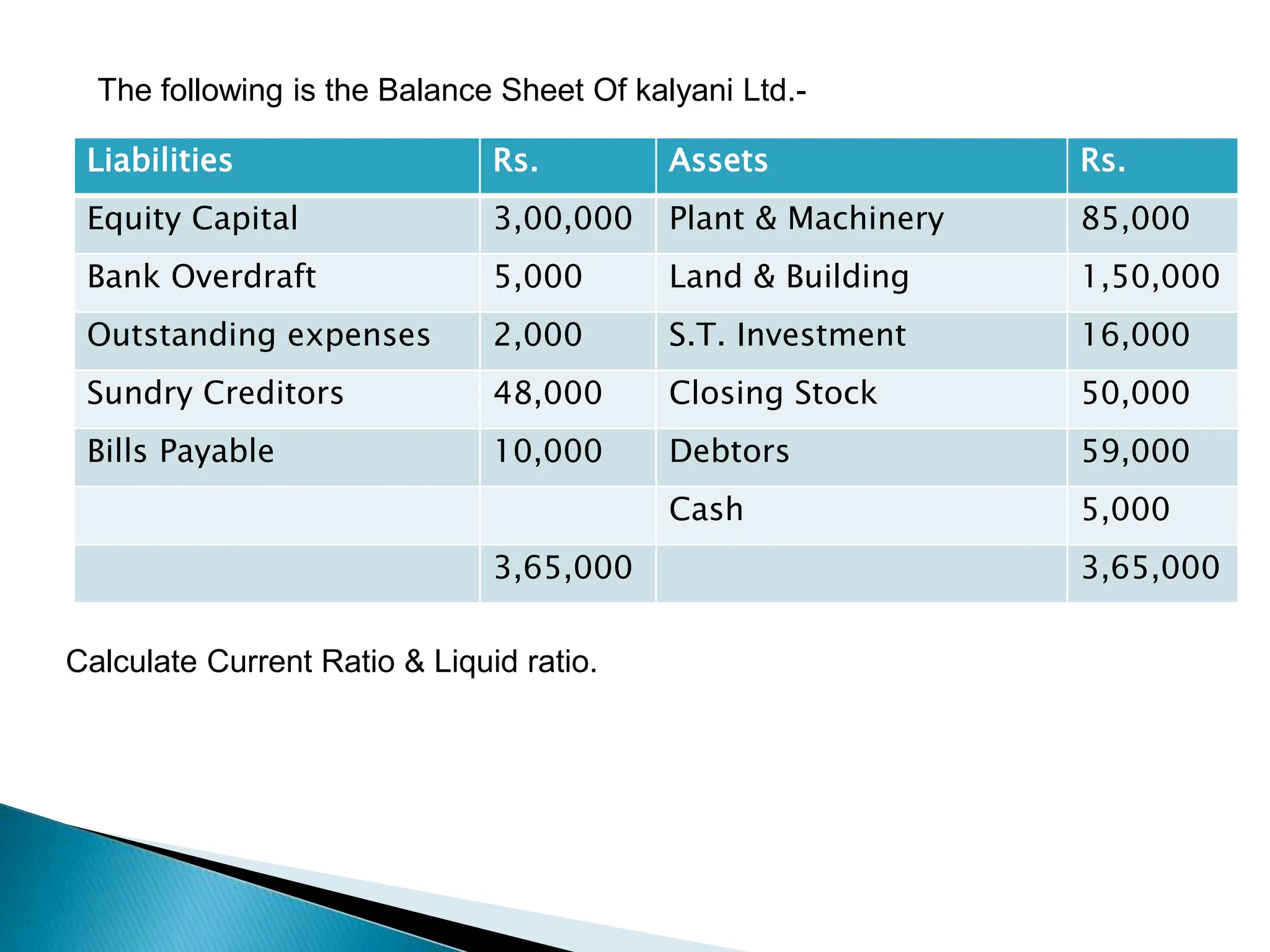
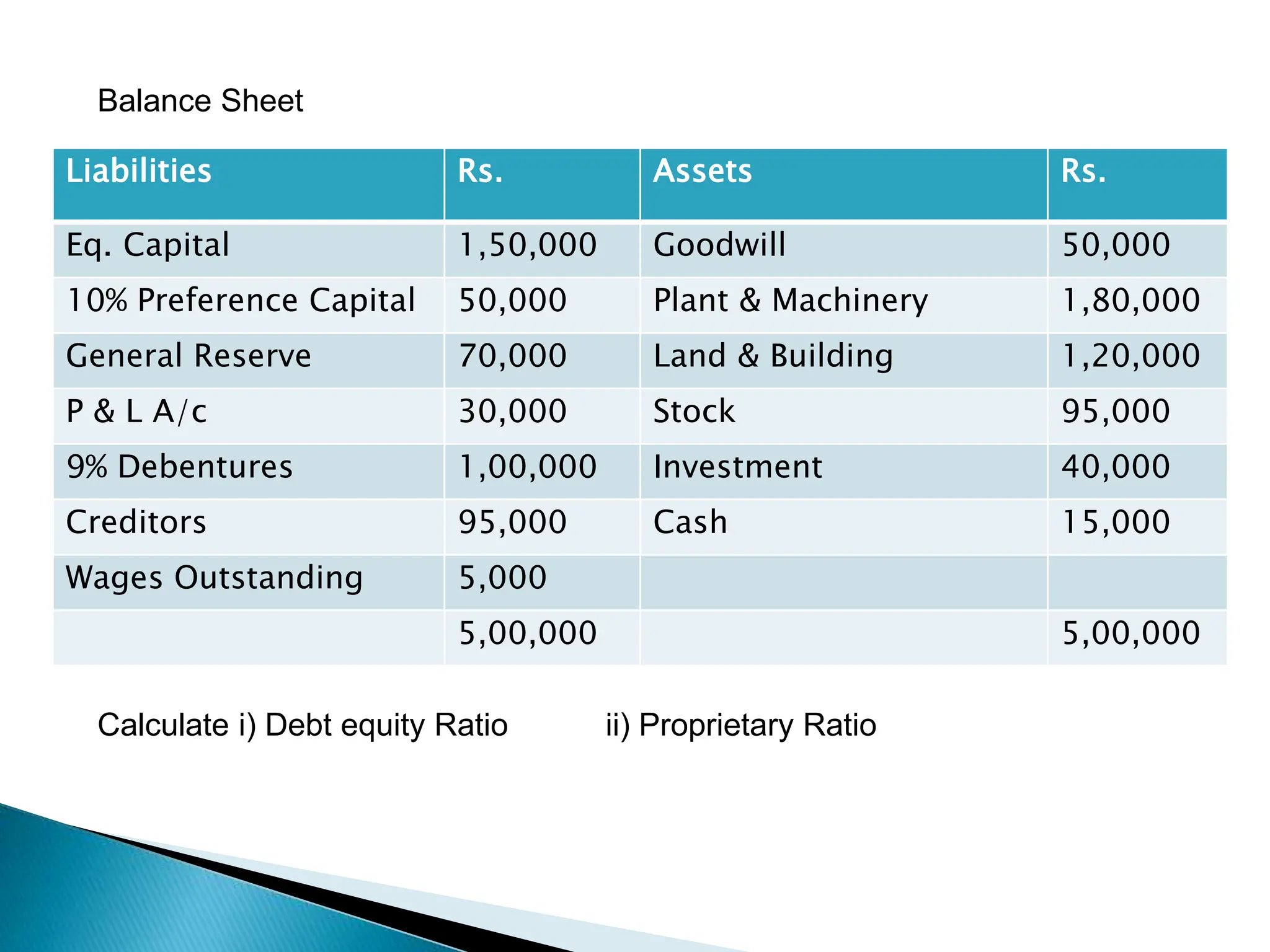
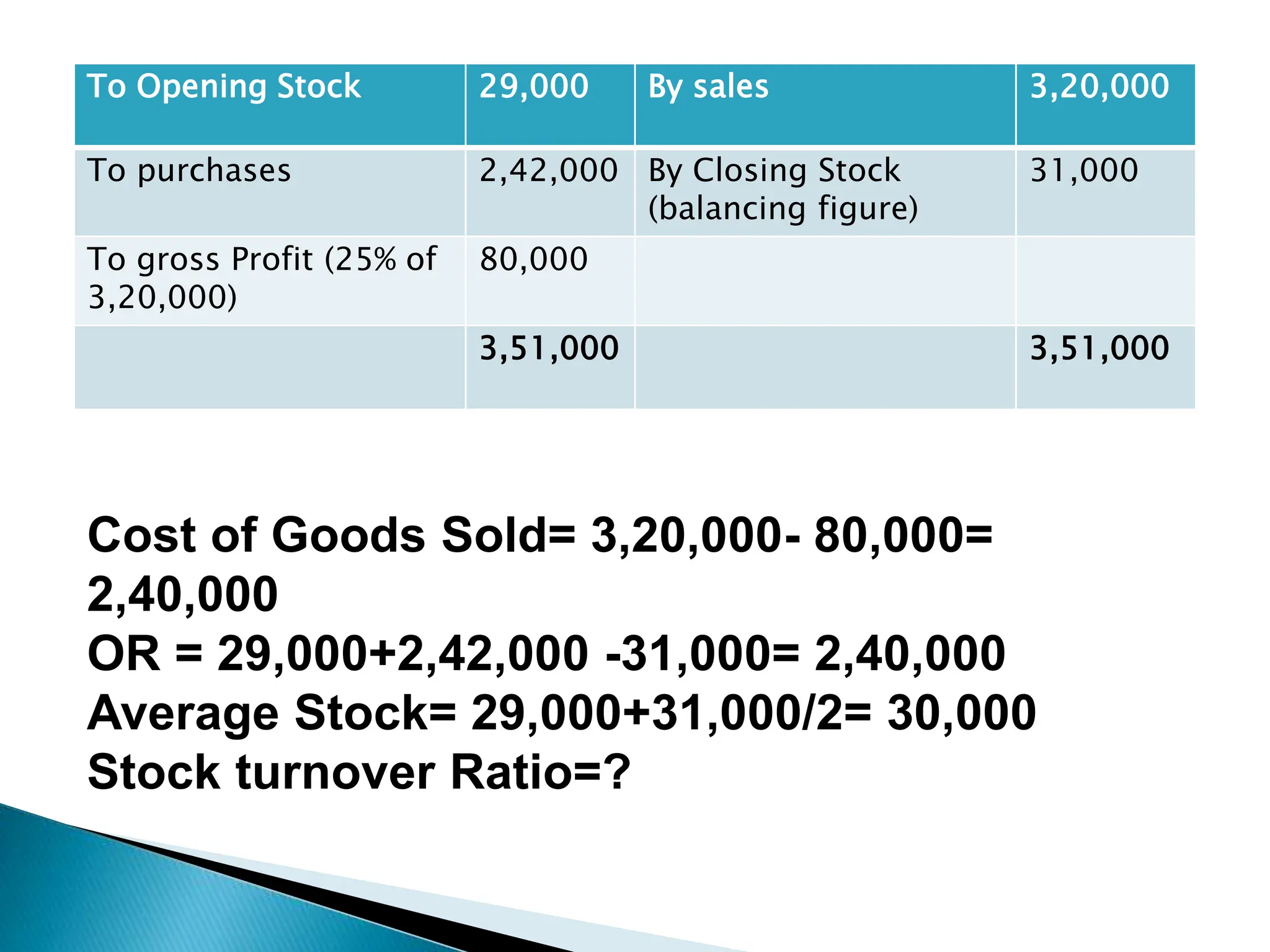
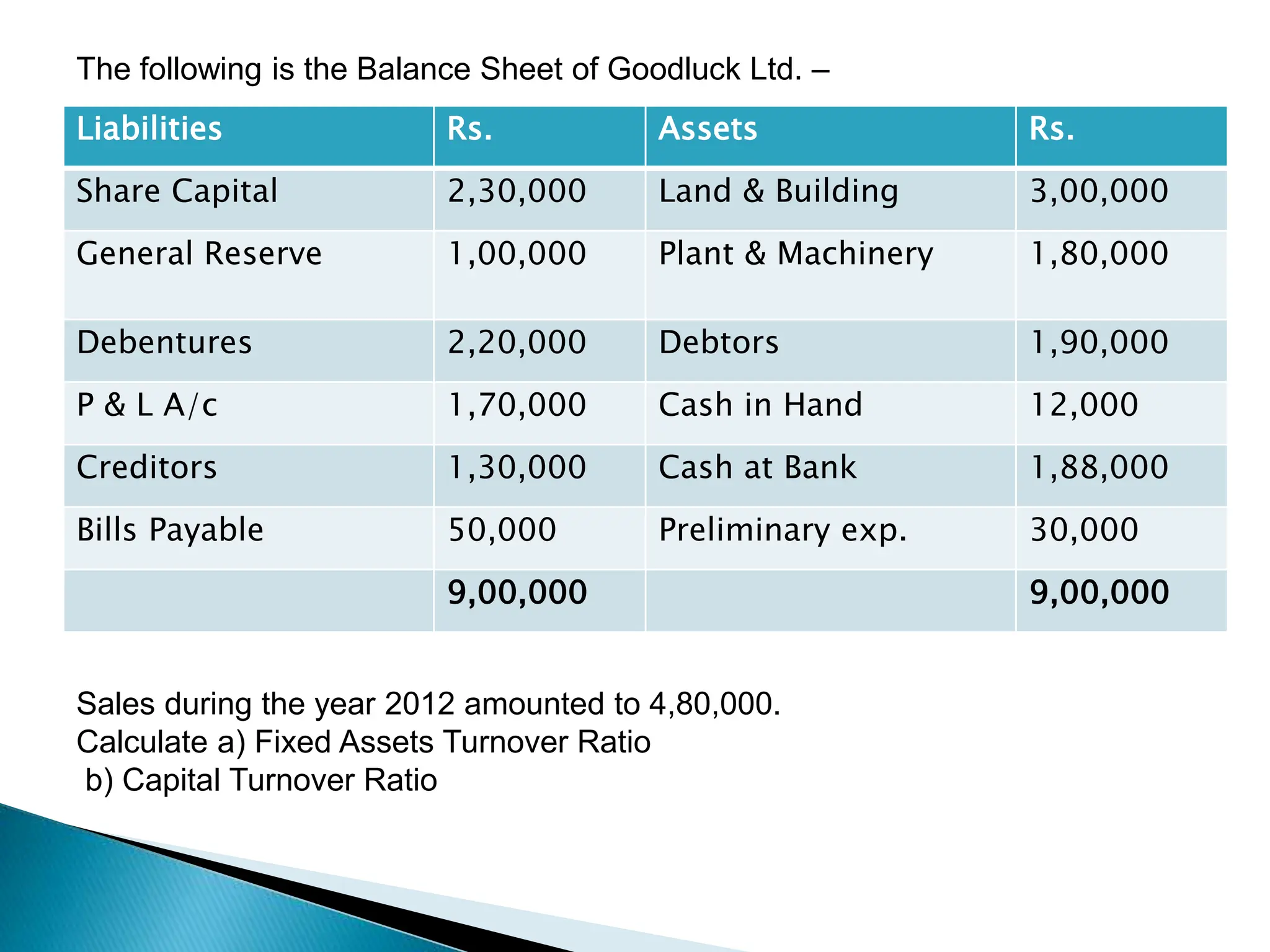
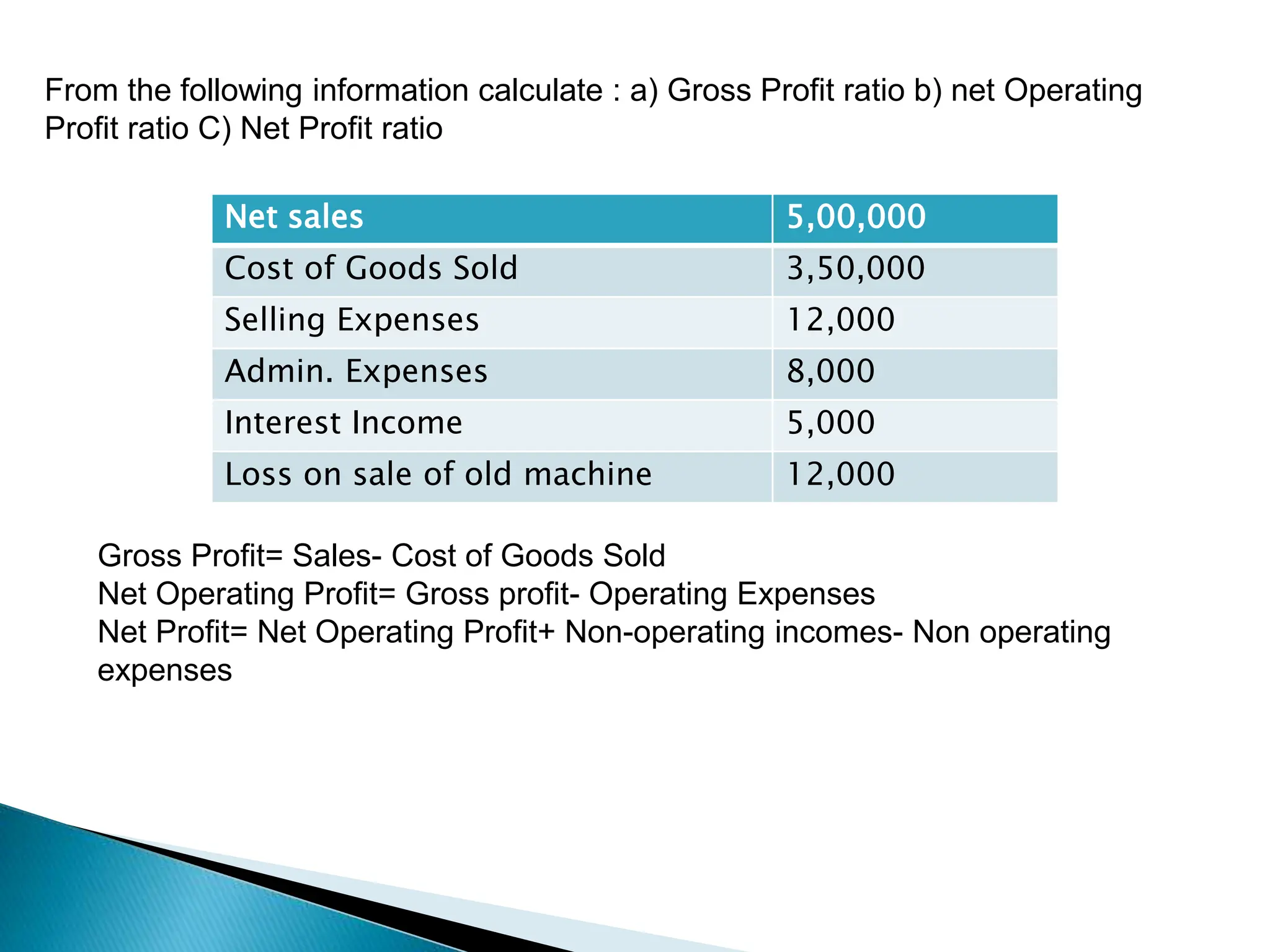
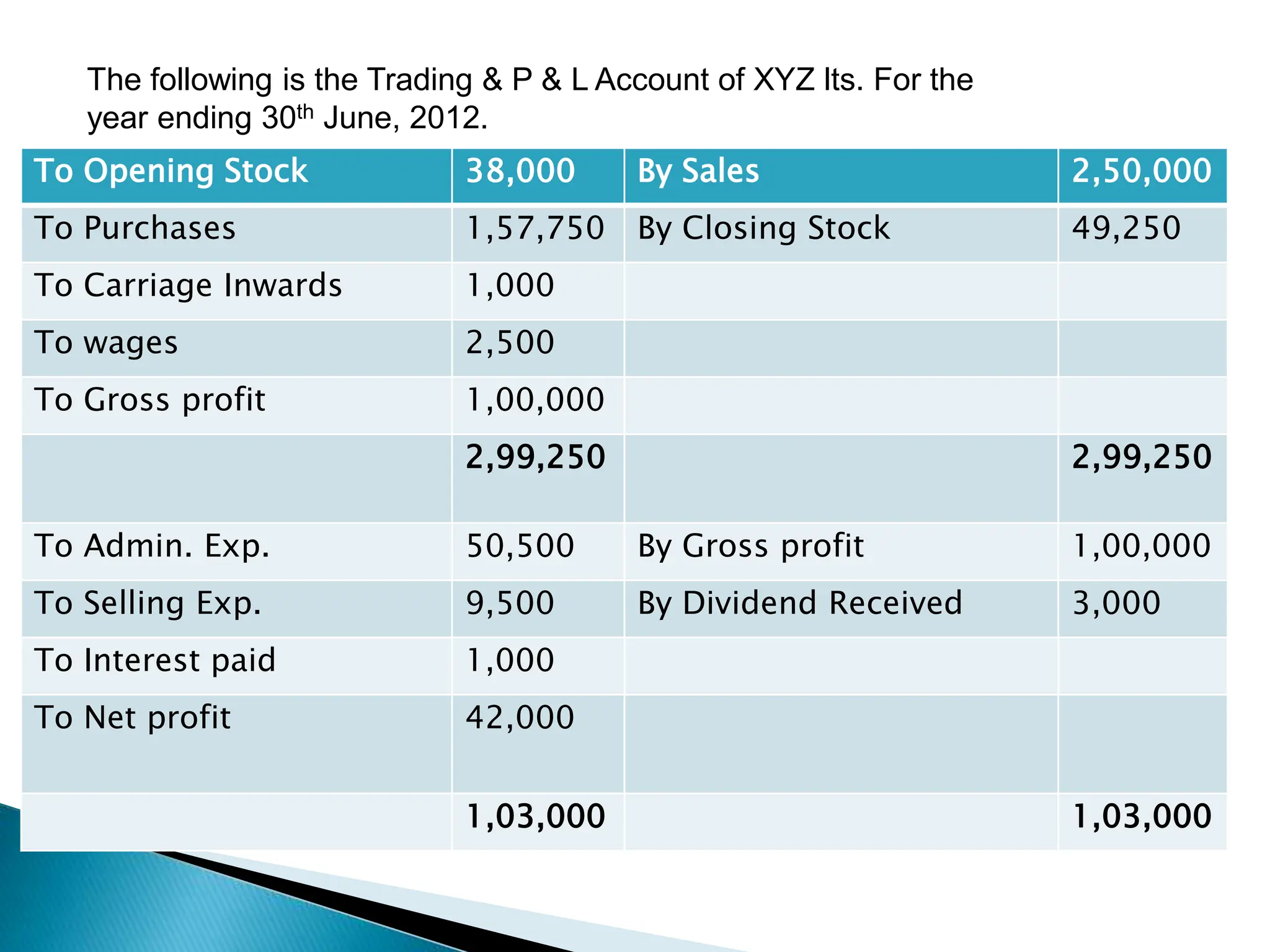
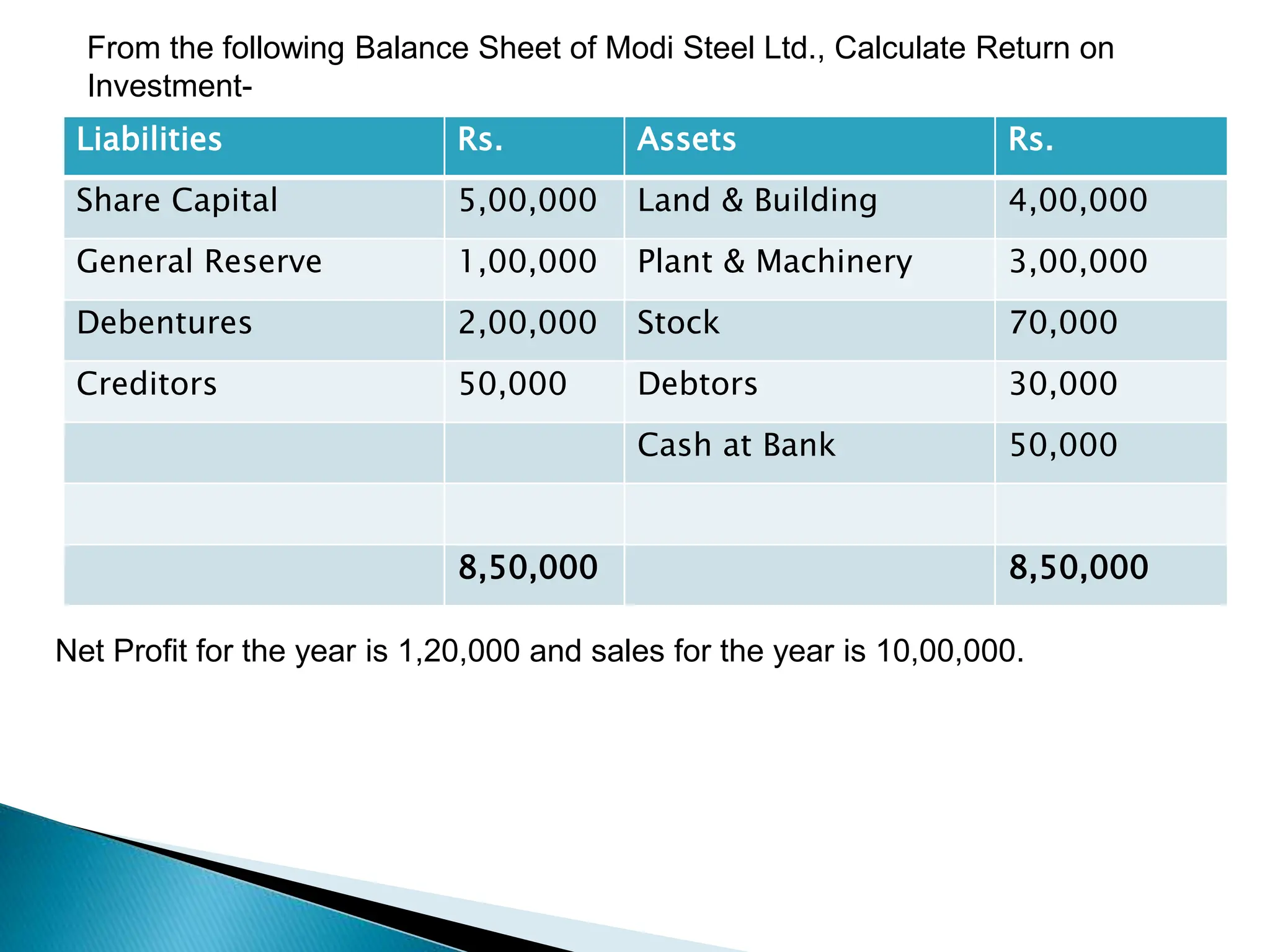
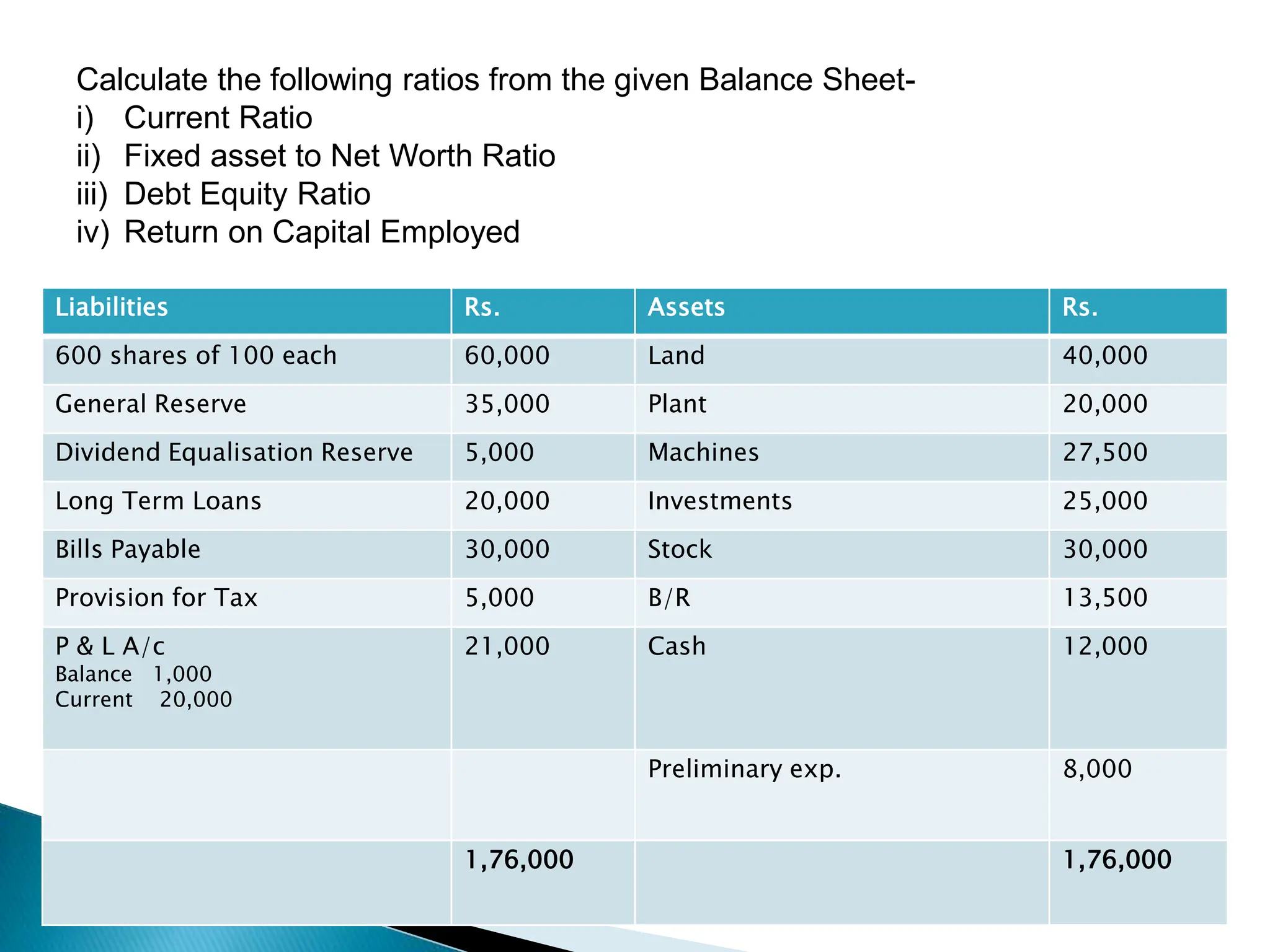
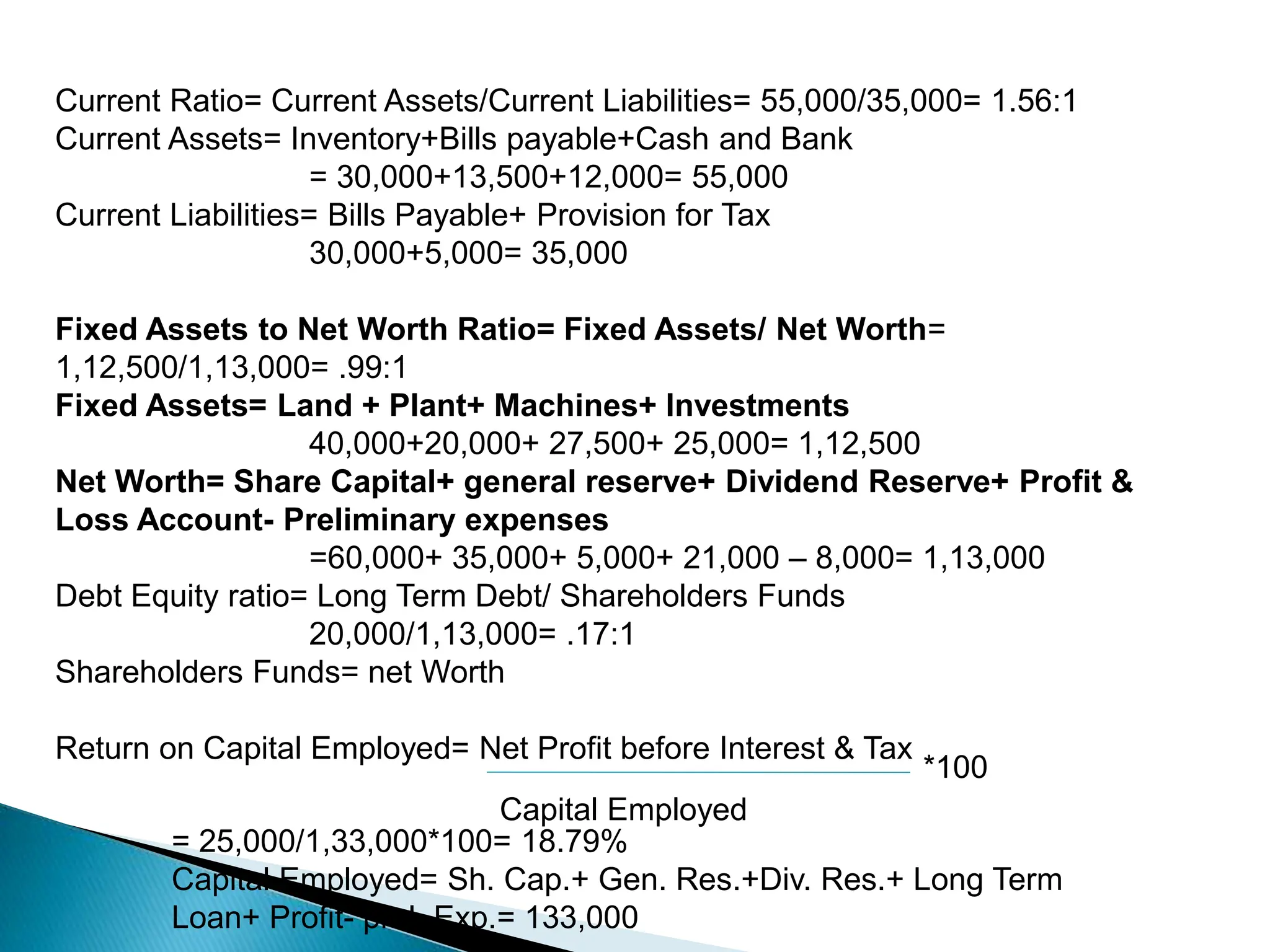
Ratio analysis involves calculating and analyzing financial ratios to evaluate various aspects of a company's performance and financial position. Ratios are calculated using figures from the company's financial statements and can provide insight into areas like profitability, liquidity, asset utilization, debt levels, and investment returns. Common ratio categories include liquidity ratios, capital structure ratios, turnover/activity ratios, and profitability ratios. Ratio analysis allows comparison of a company's performance over time and against industry benchmarks to identify trends and areas for improvement.