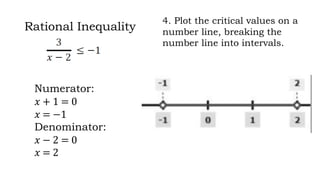
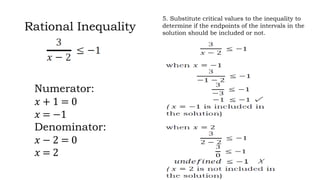
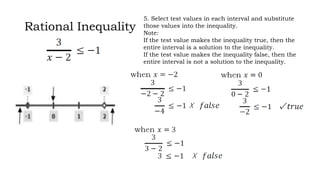
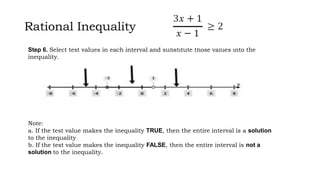
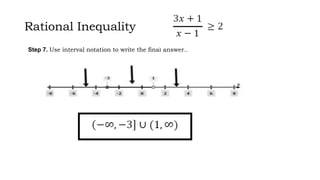
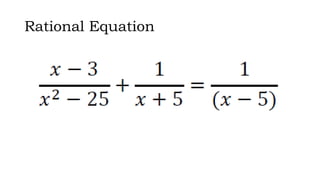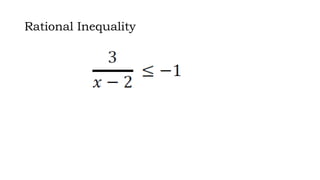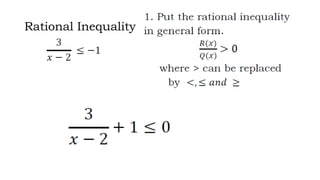This document discusses how to solve rational equations and inequalities. It provides steps for solving rational equations, which include finding the least common denominator, multiplying both sides by the LCD, applying the distributive property, and checking solutions. It also outlines six steps for solving rational inequalities: writing the inequality as a single rational expression, setting the numerator and denominator equal to zero to find critical values, plotting critical values on a number line, substituting critical values into the inequality, selecting test values in each interval, and using interval notation to write the final answer.