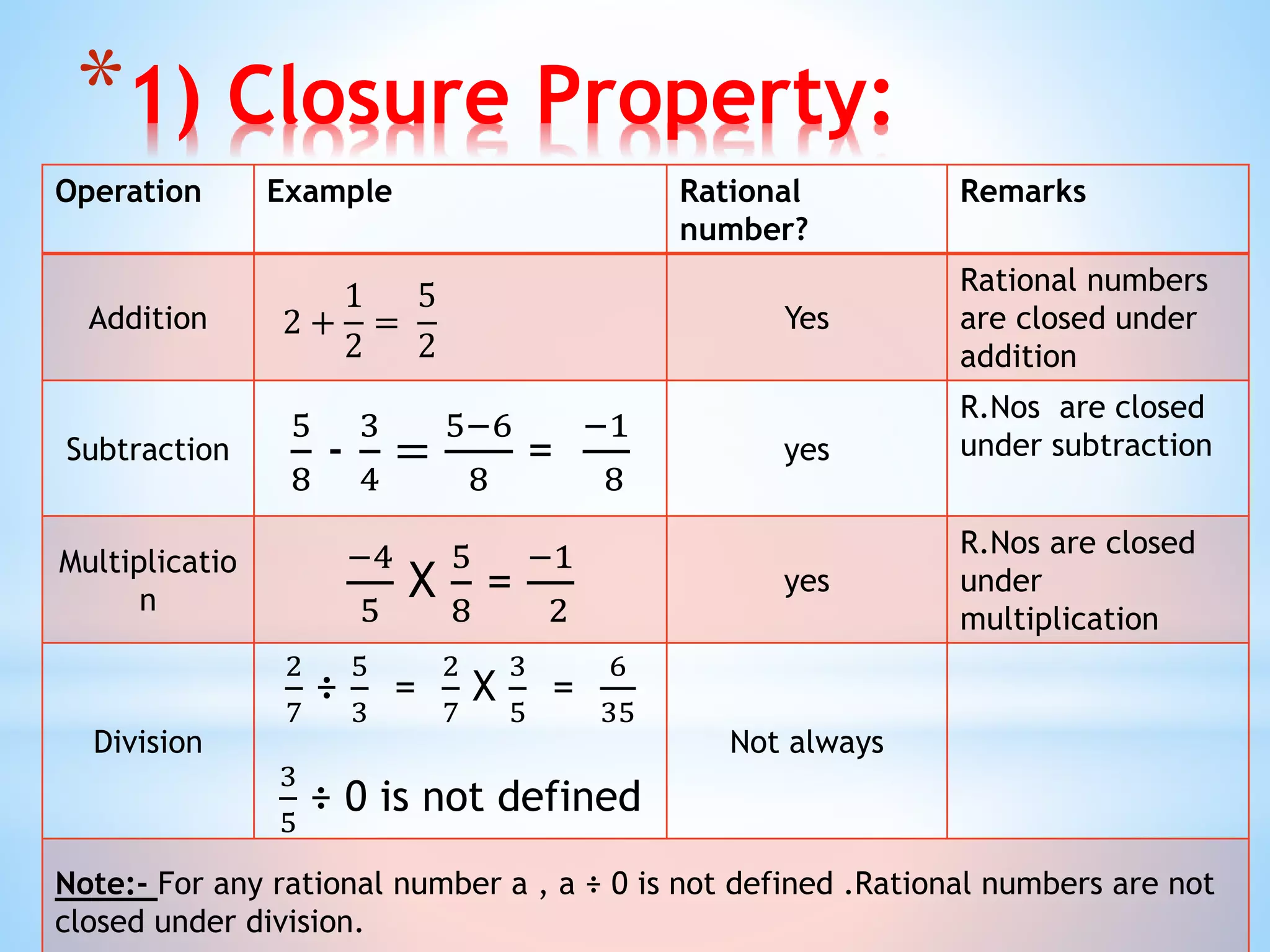
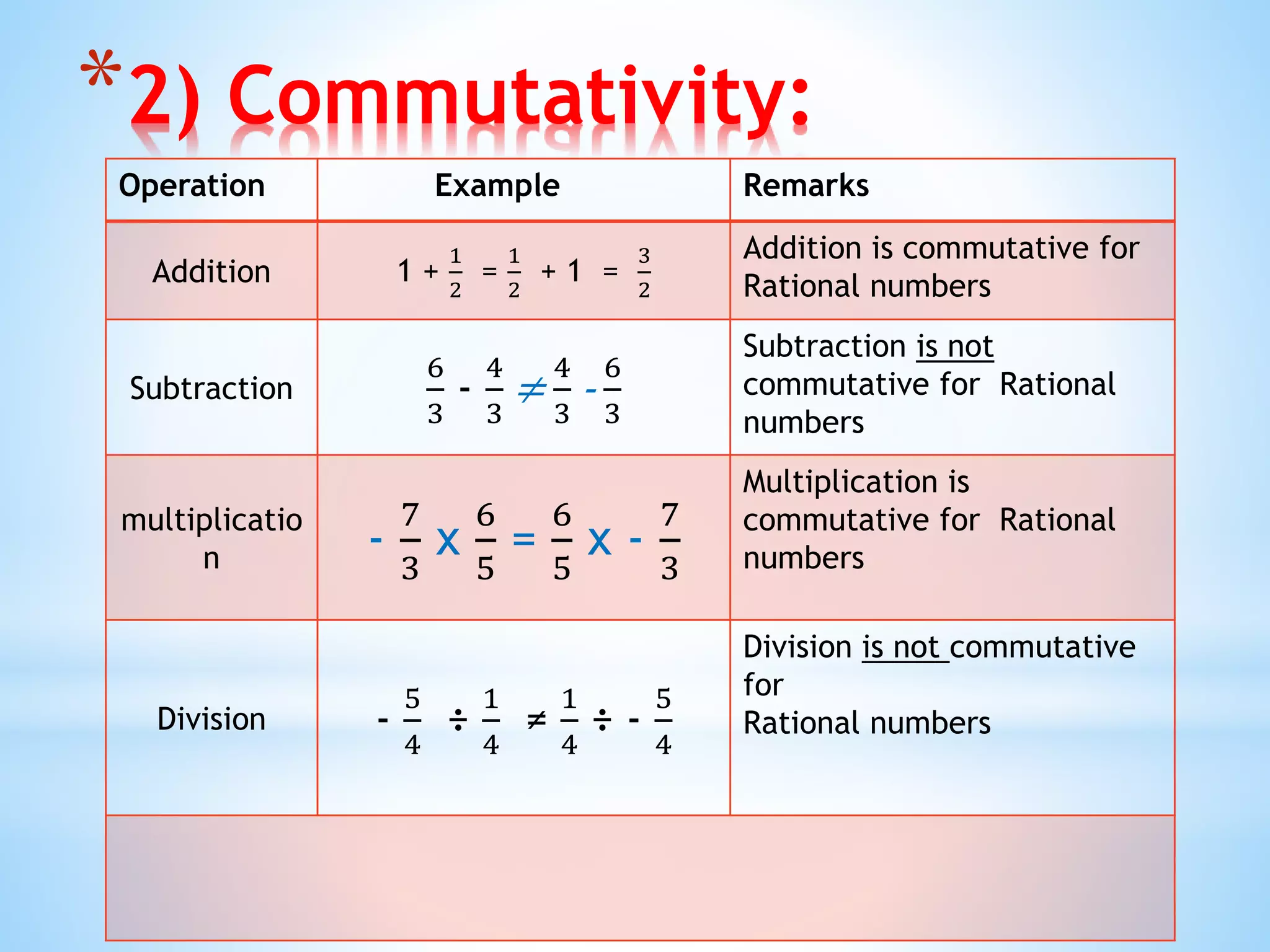
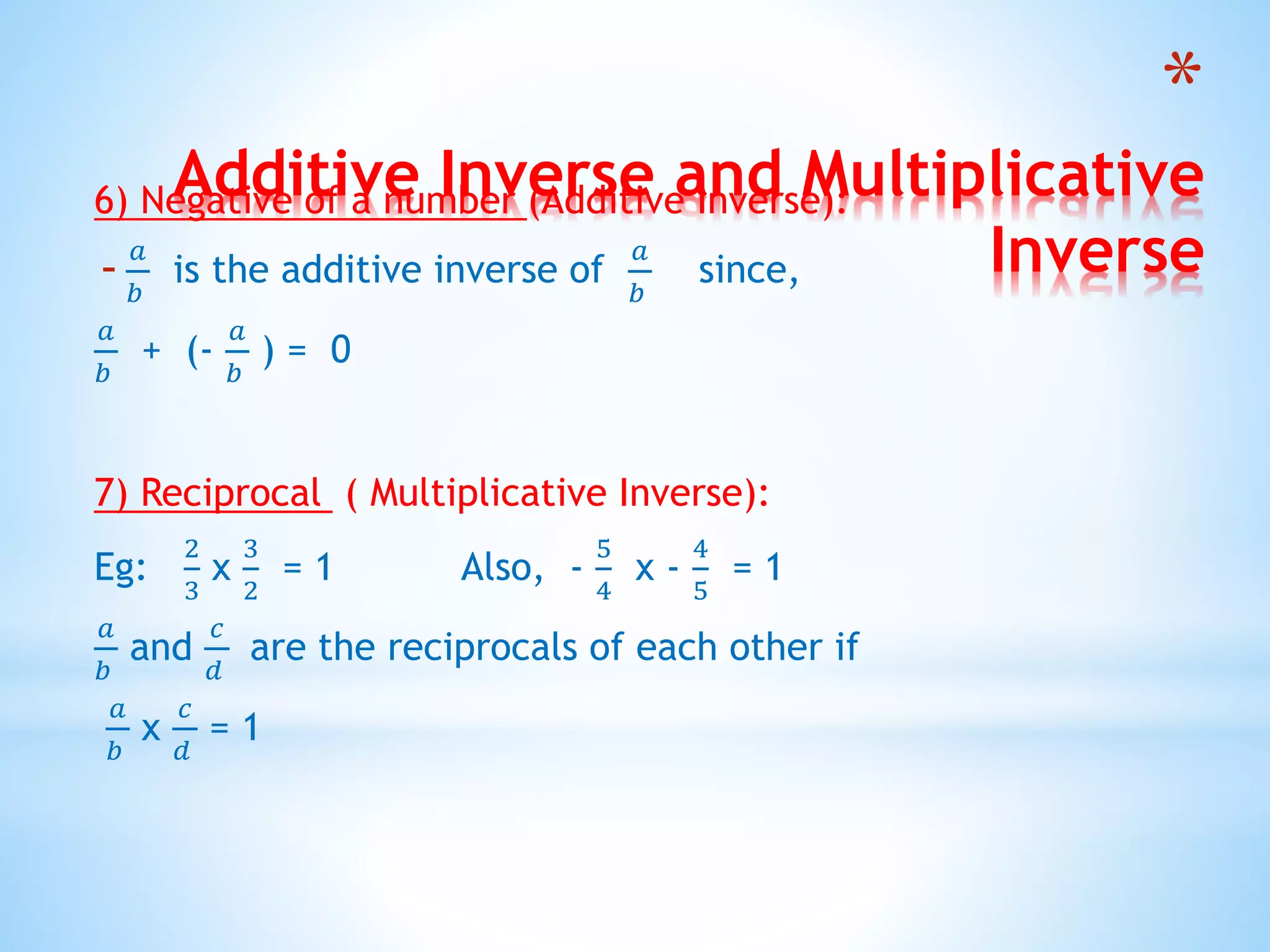
The document outlines the various types of numbers, including natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, and rational numbers, emphasizing their properties and behaviors. It explains operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division in relation to rational numbers and highlights properties like closure, commutativity, and associativity. Additionally, it covers concepts like identity elements, inverses, and how to identify rational numbers within a specified range.