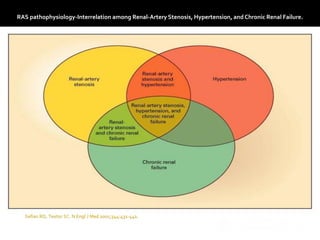
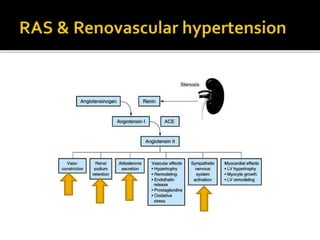
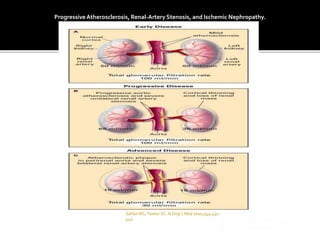
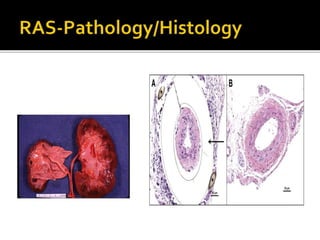
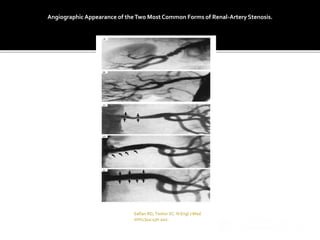
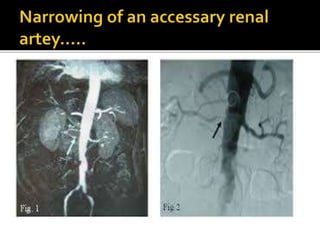
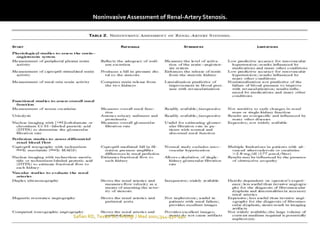
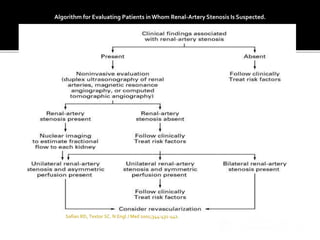
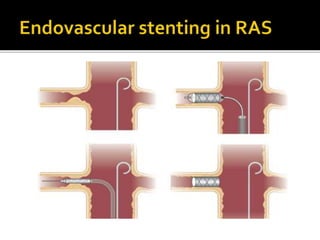
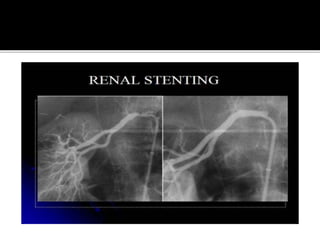
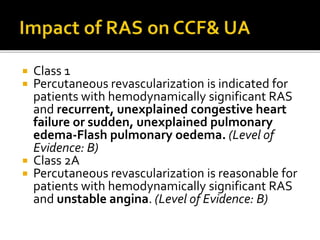
This document provides an overview of renal artery stenosis (RAS), including its pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, and management recommendations. There are two main types of RAS - atherosclerotic renal vascular disease (ARVD) and fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD). RAS can cause hypertension and ischemic nephropathy. Evaluation involves assessing renal function and imaging modalities like duplex ultrasound, MRA, CTA, and angiography. Treatment depends on symptoms and includes medications like ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, calcium channel blockers, and beta blockers. Percutaneous or surgical revascularization may be considered for significant bilateral disease or resistant hypertension.