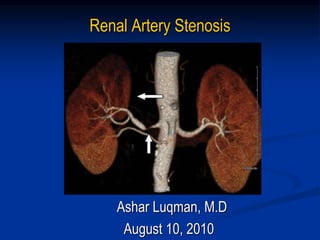
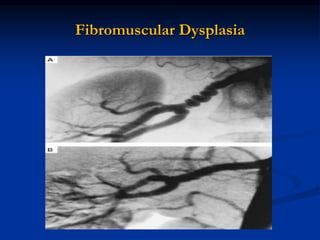
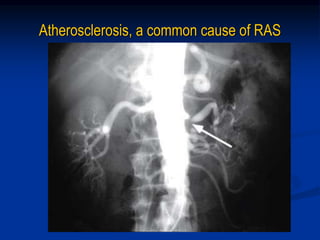
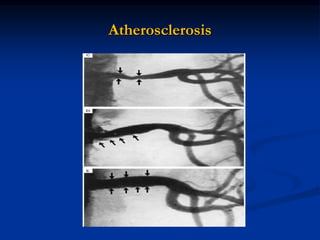
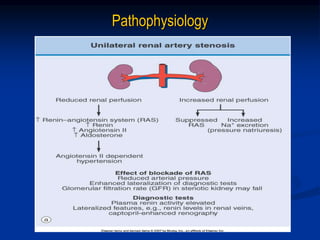
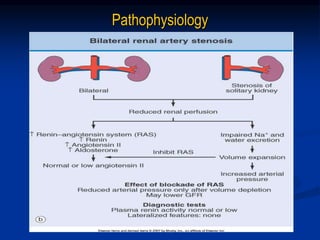
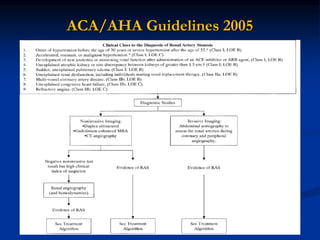
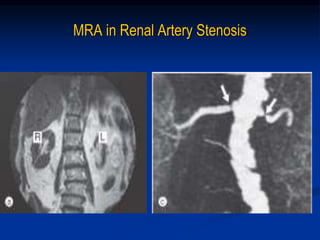
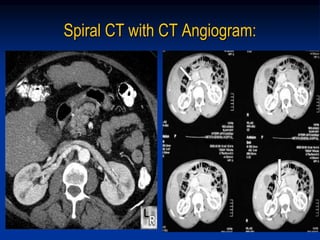
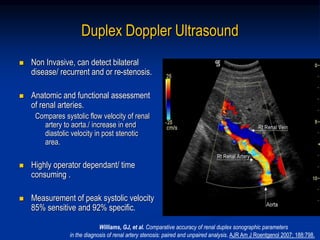
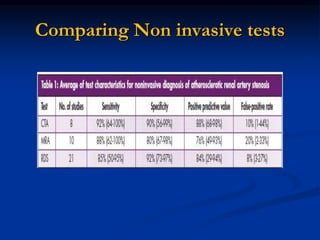
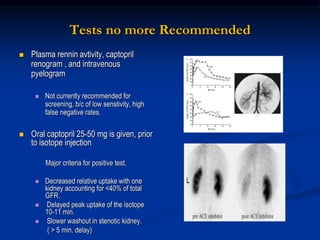
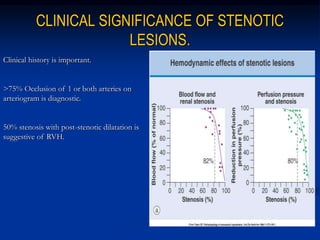
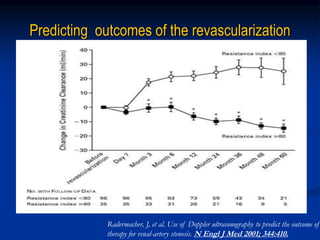
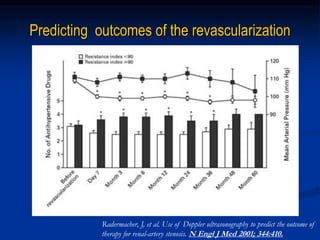
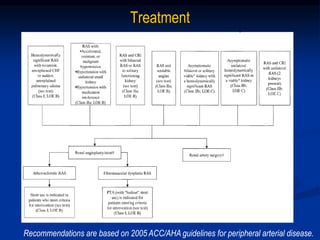
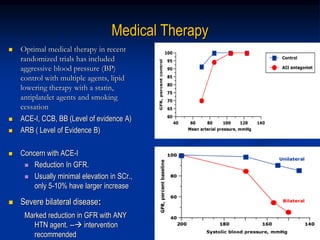
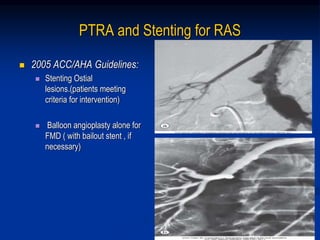
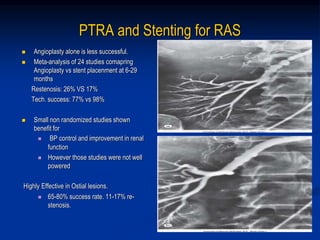
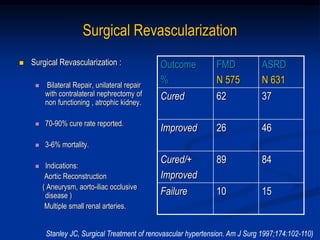
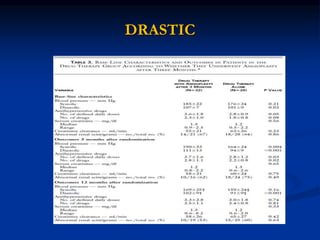
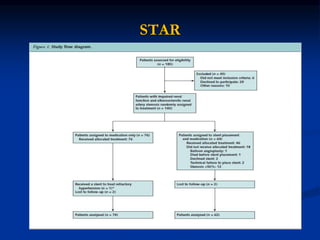
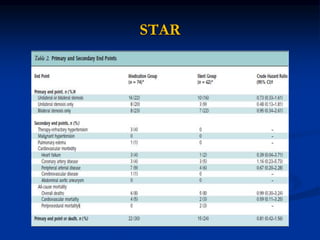
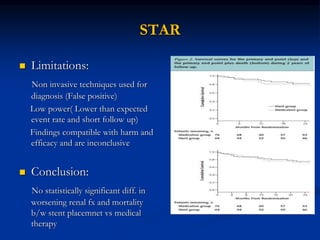
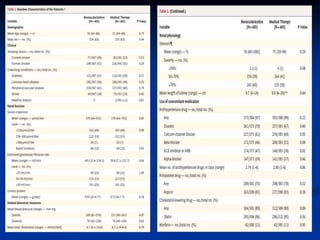
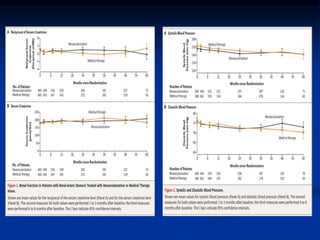
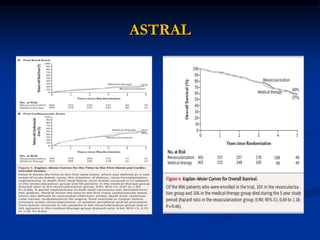
This document discusses renal artery stenosis, including its definition, epidemiology, causes, pathophysiology, clinical findings, and screening/diagnostic tests. Renal artery stenosis is the narrowing of the renal artery, often caused by atherosclerosis or fibromuscular dysplasia. It can lead to hypertension and renal failure if not treated. Screening is recommended for patients with difficult to control or resistant hypertension. Non-invasive tests like MRA, CTA, and duplex Doppler ultrasound can detect renal artery stenosis with varying accuracy compared to the gold standard angiography. The clinical significance and outcomes of revascularization may be predicted using resistive indices on duplex Doppler ultrasound.