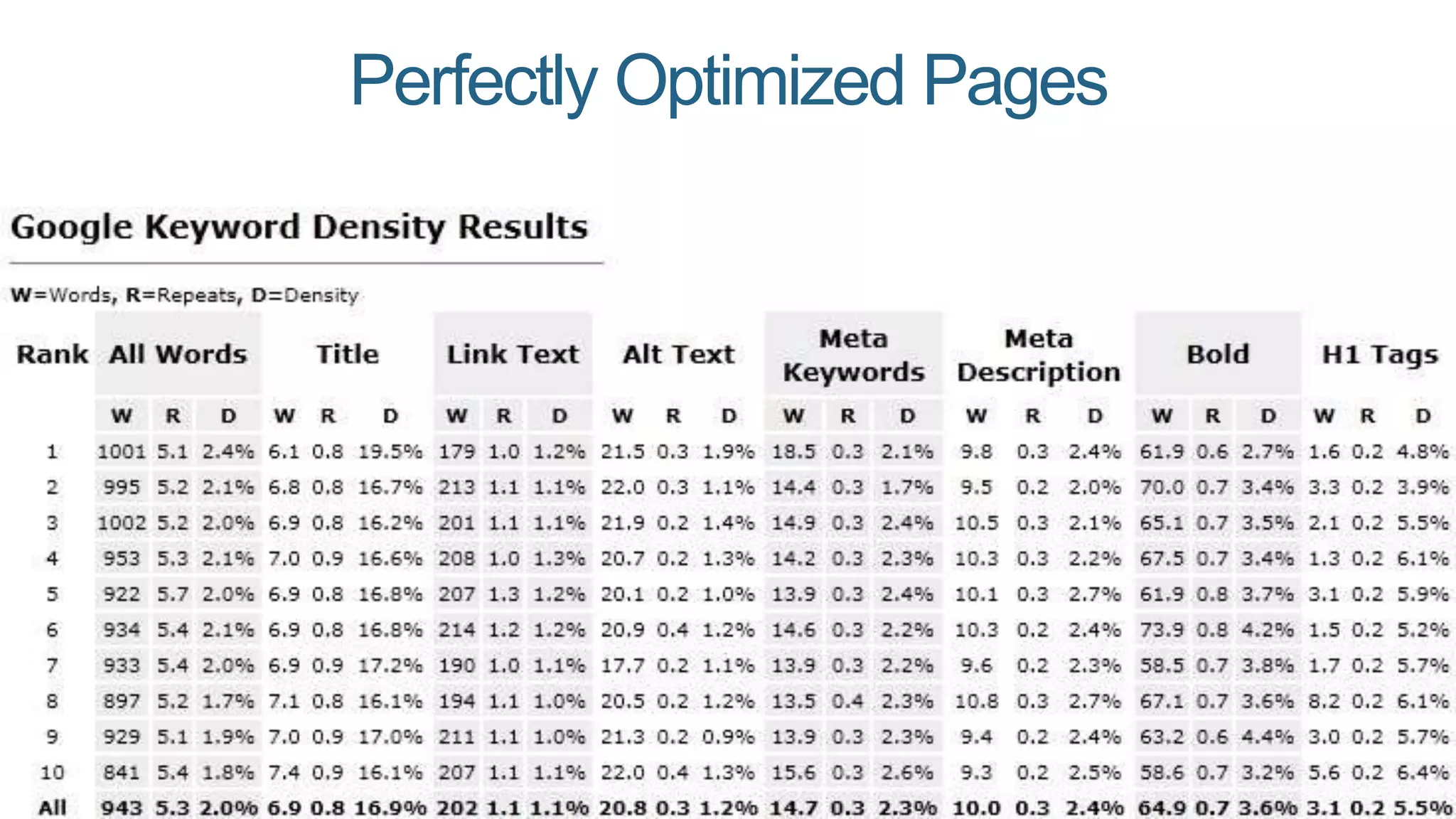
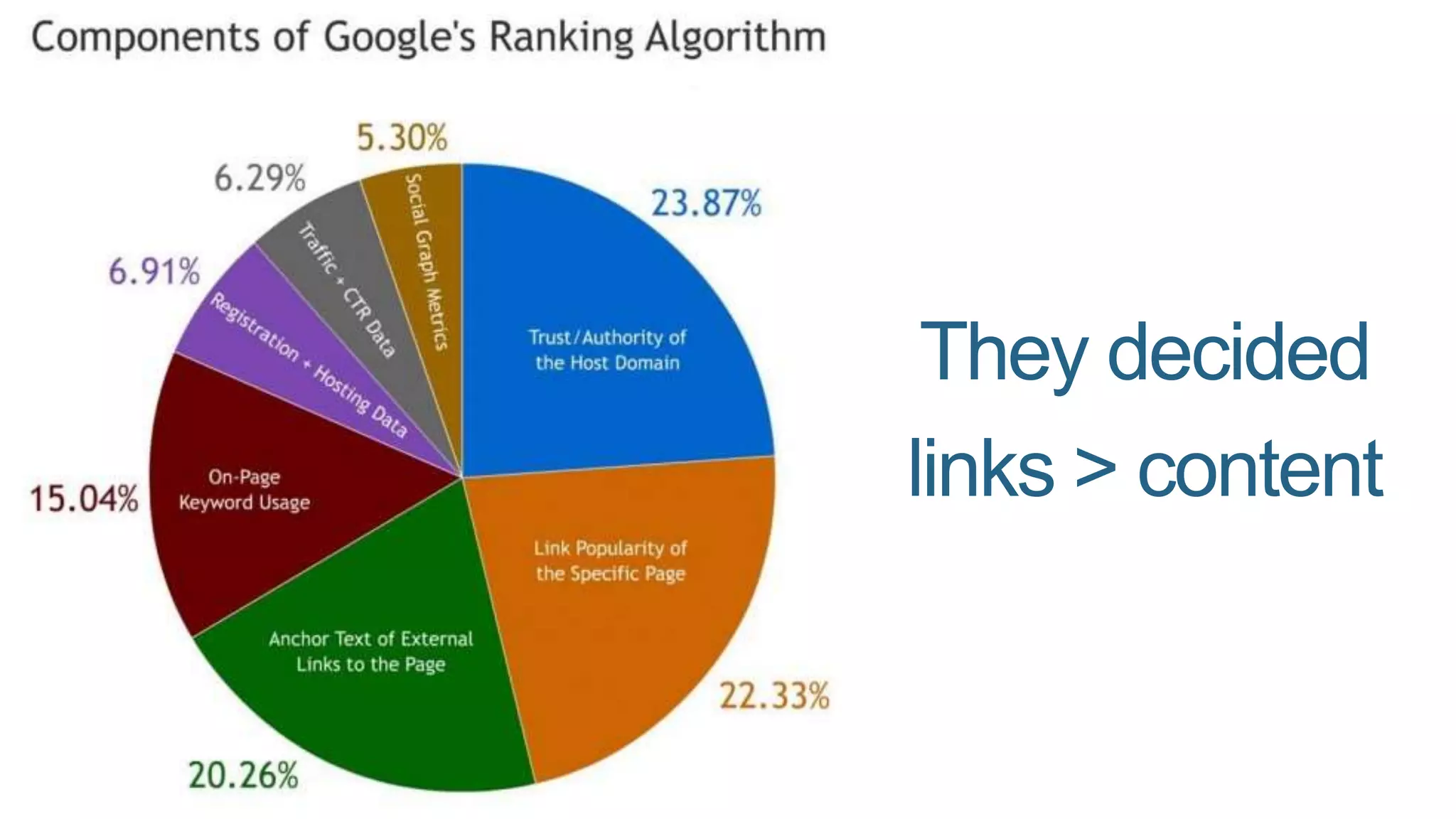
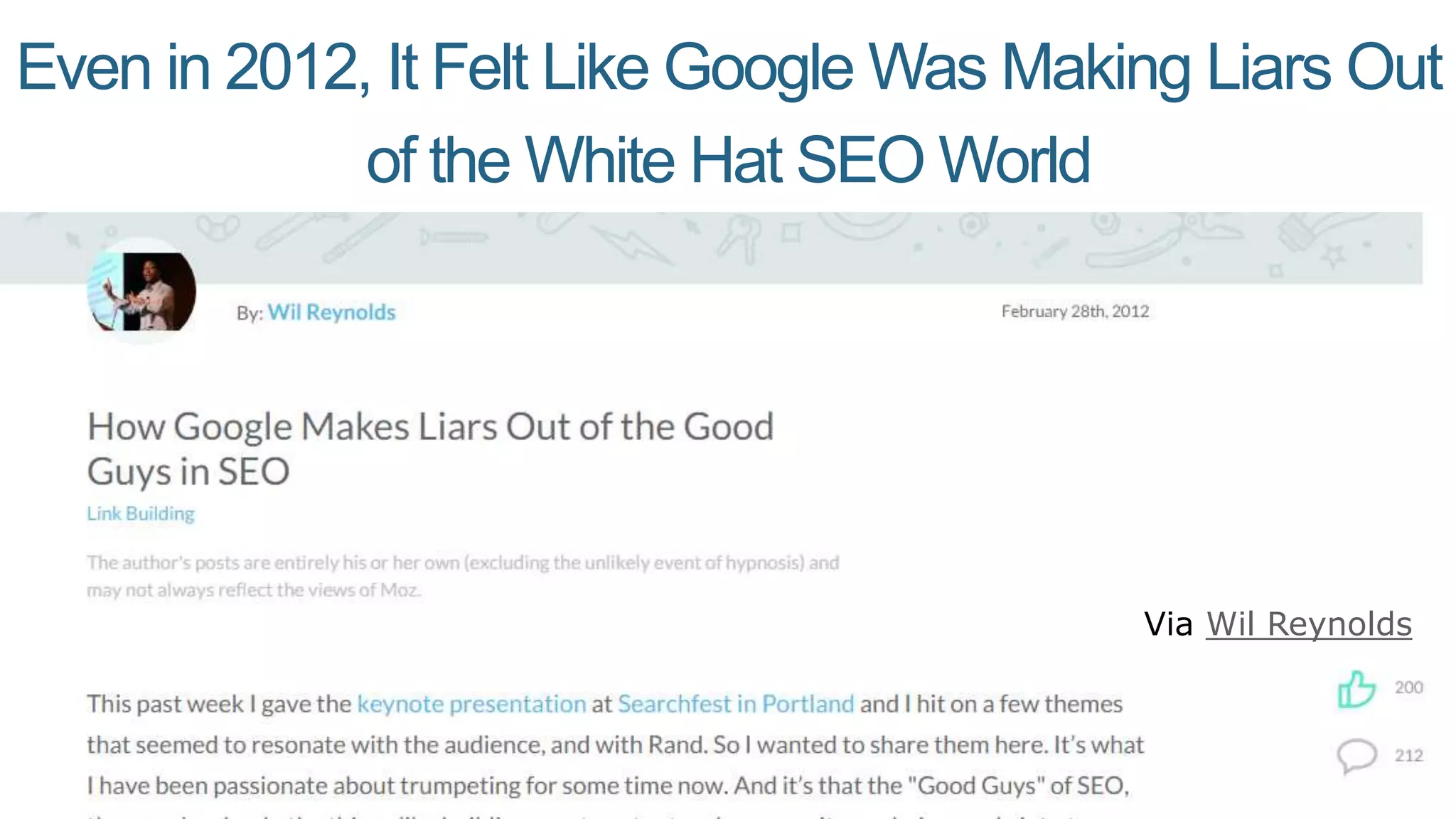
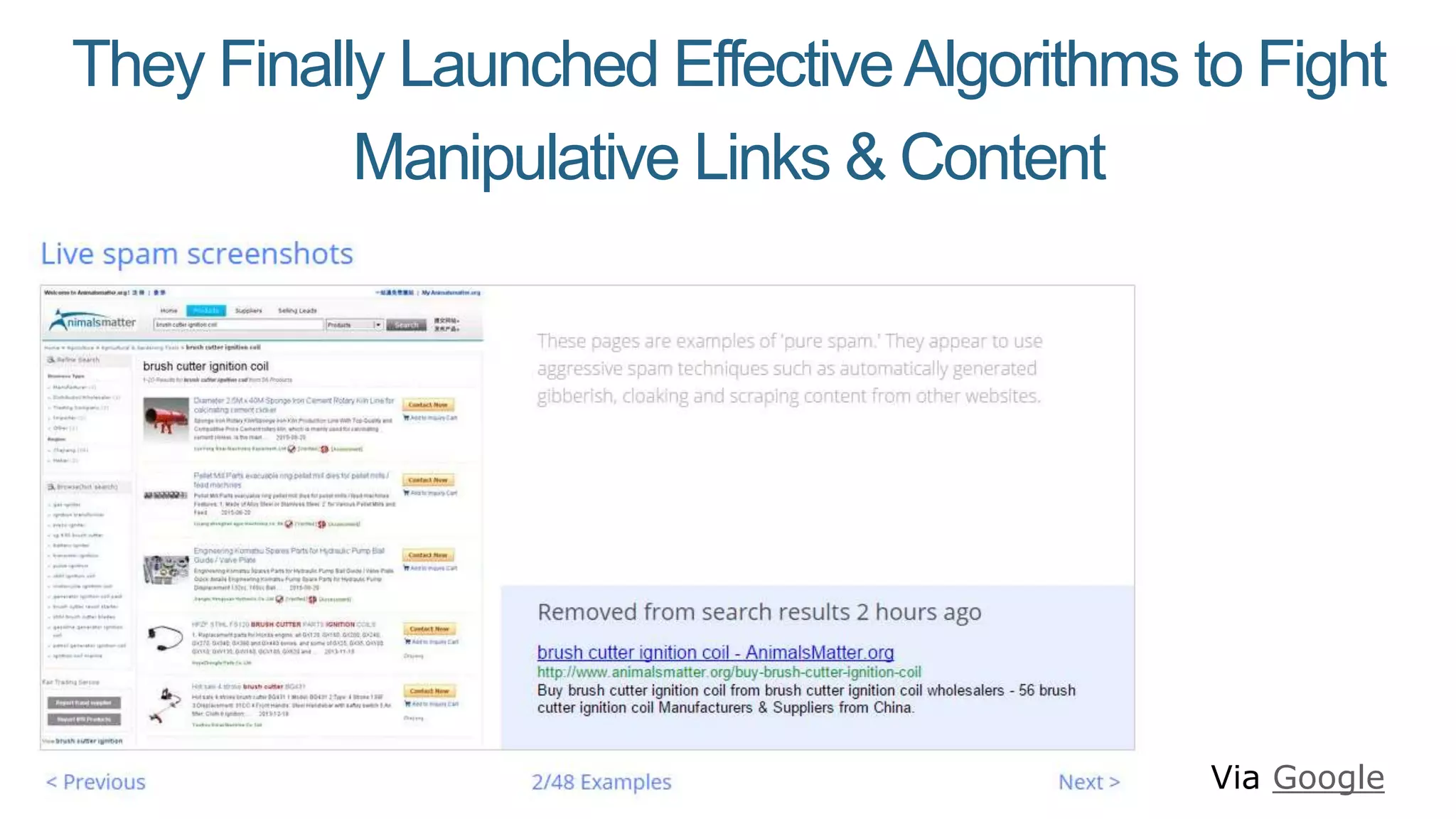
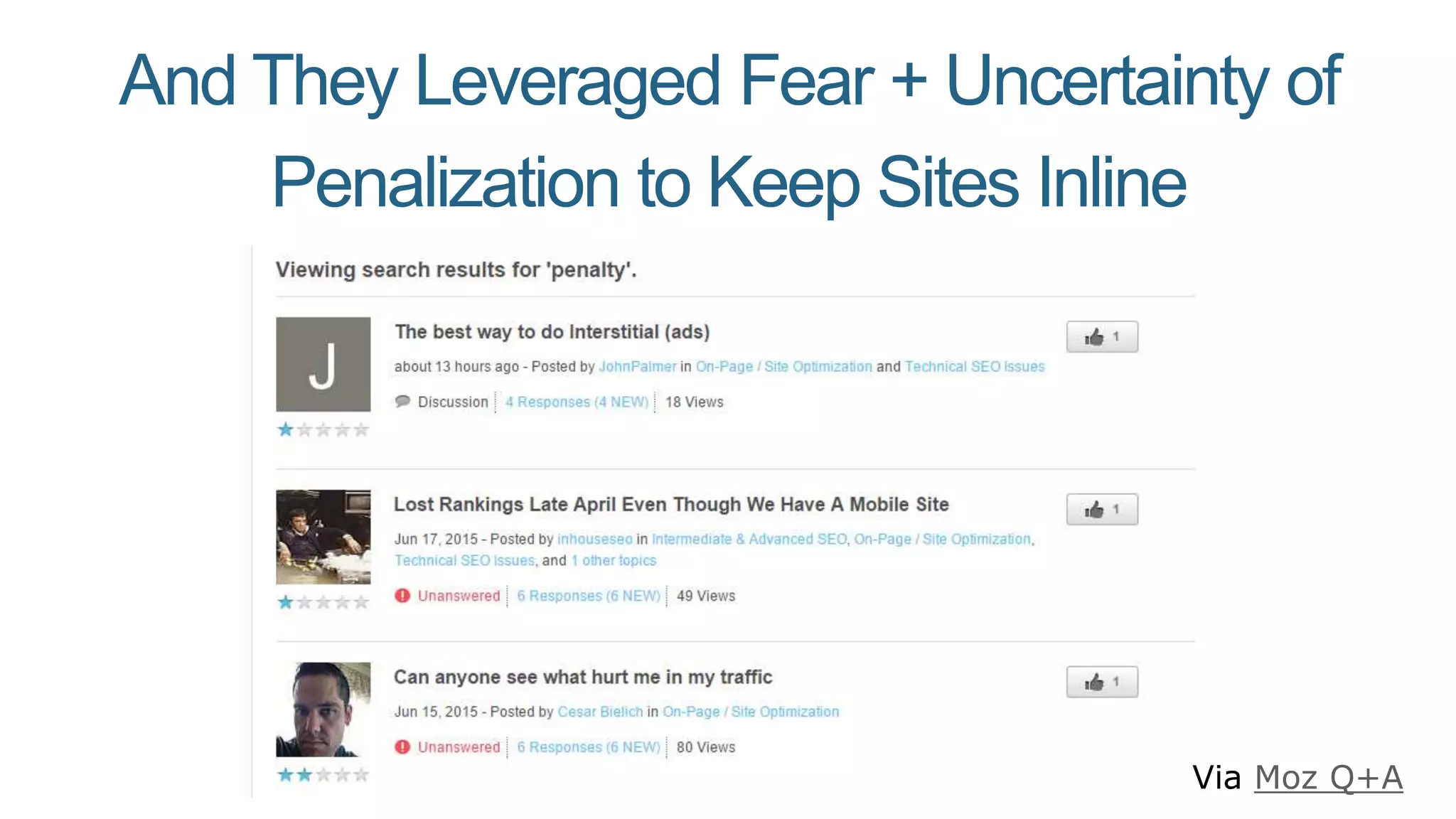
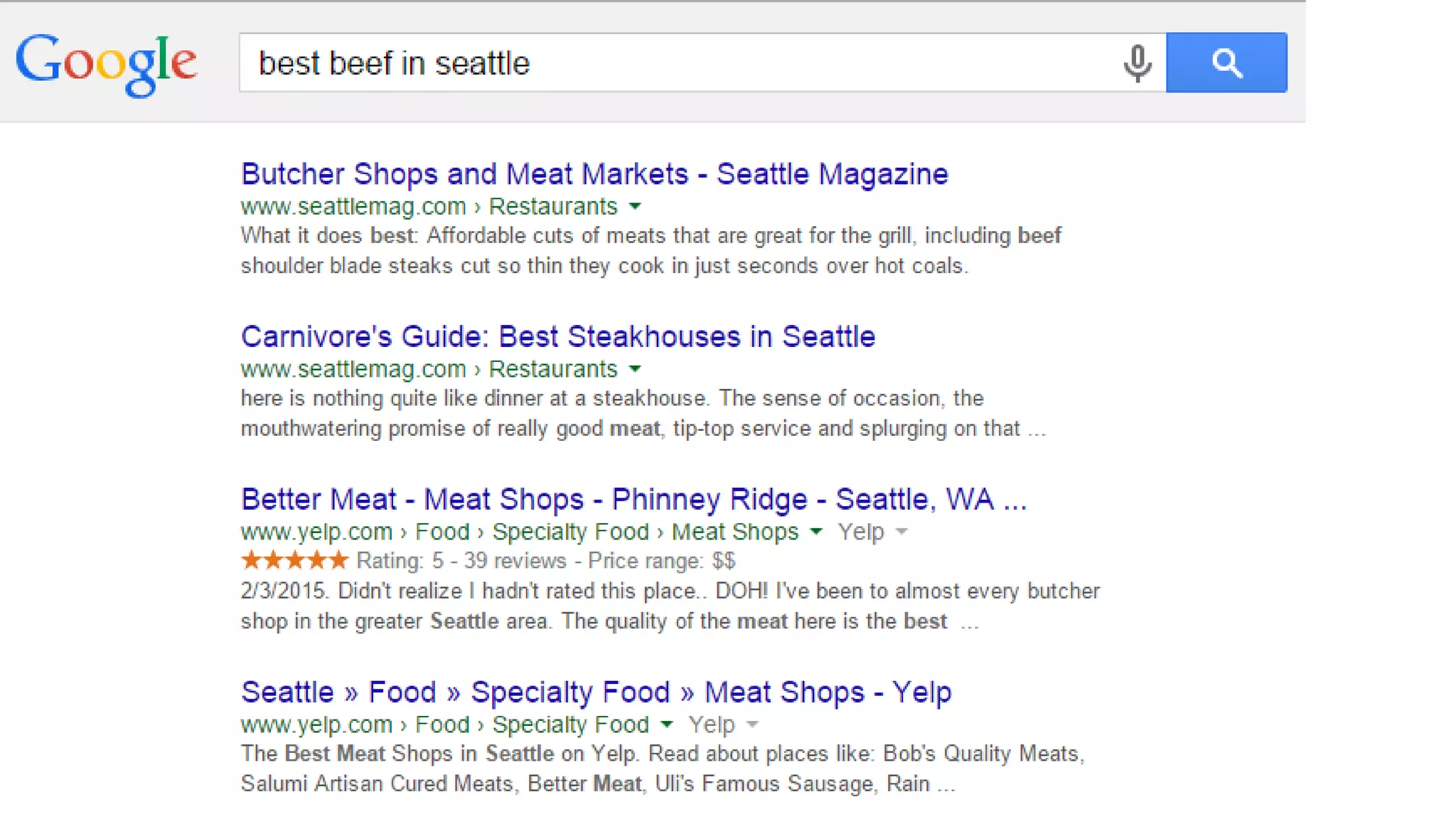
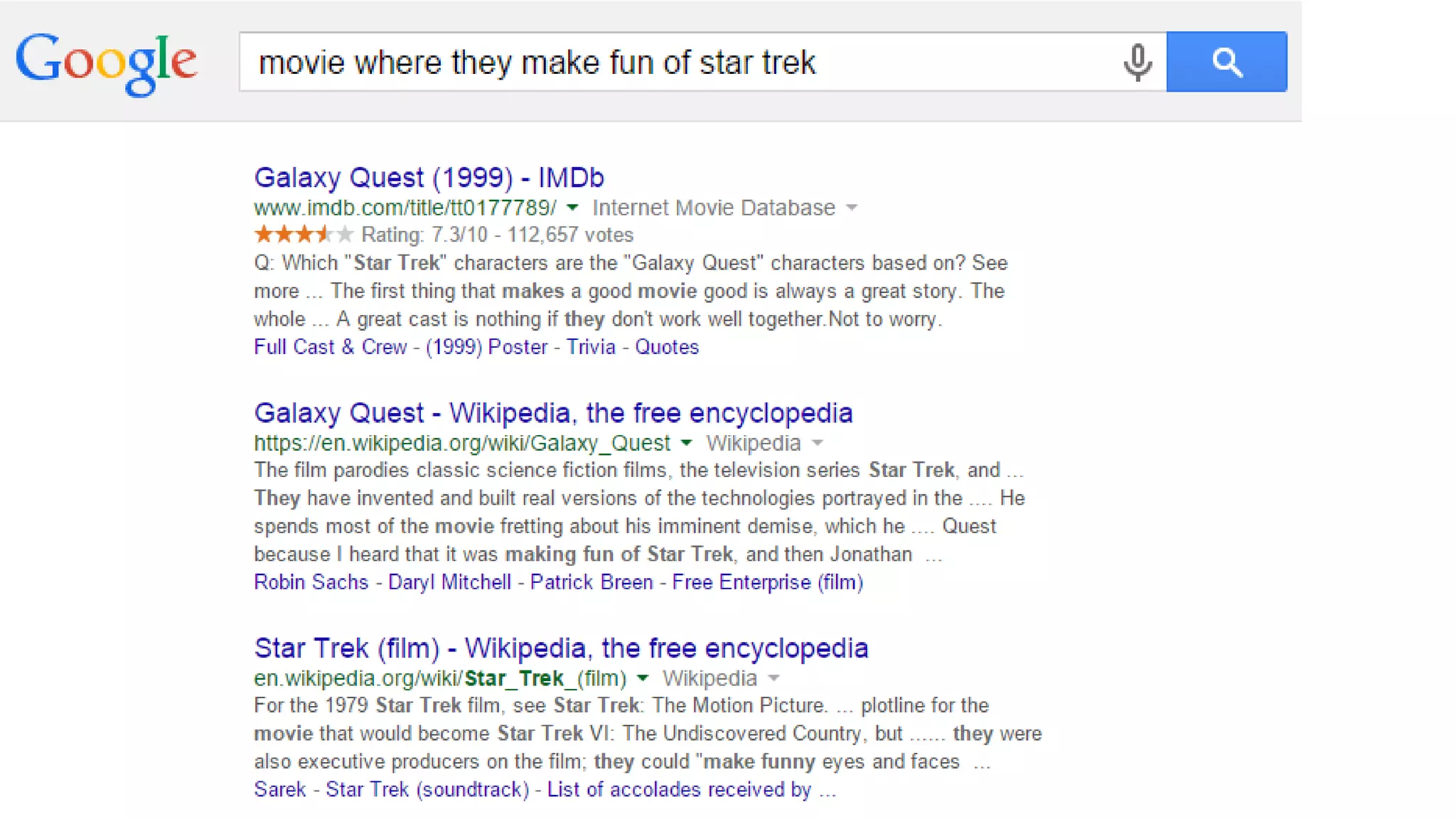
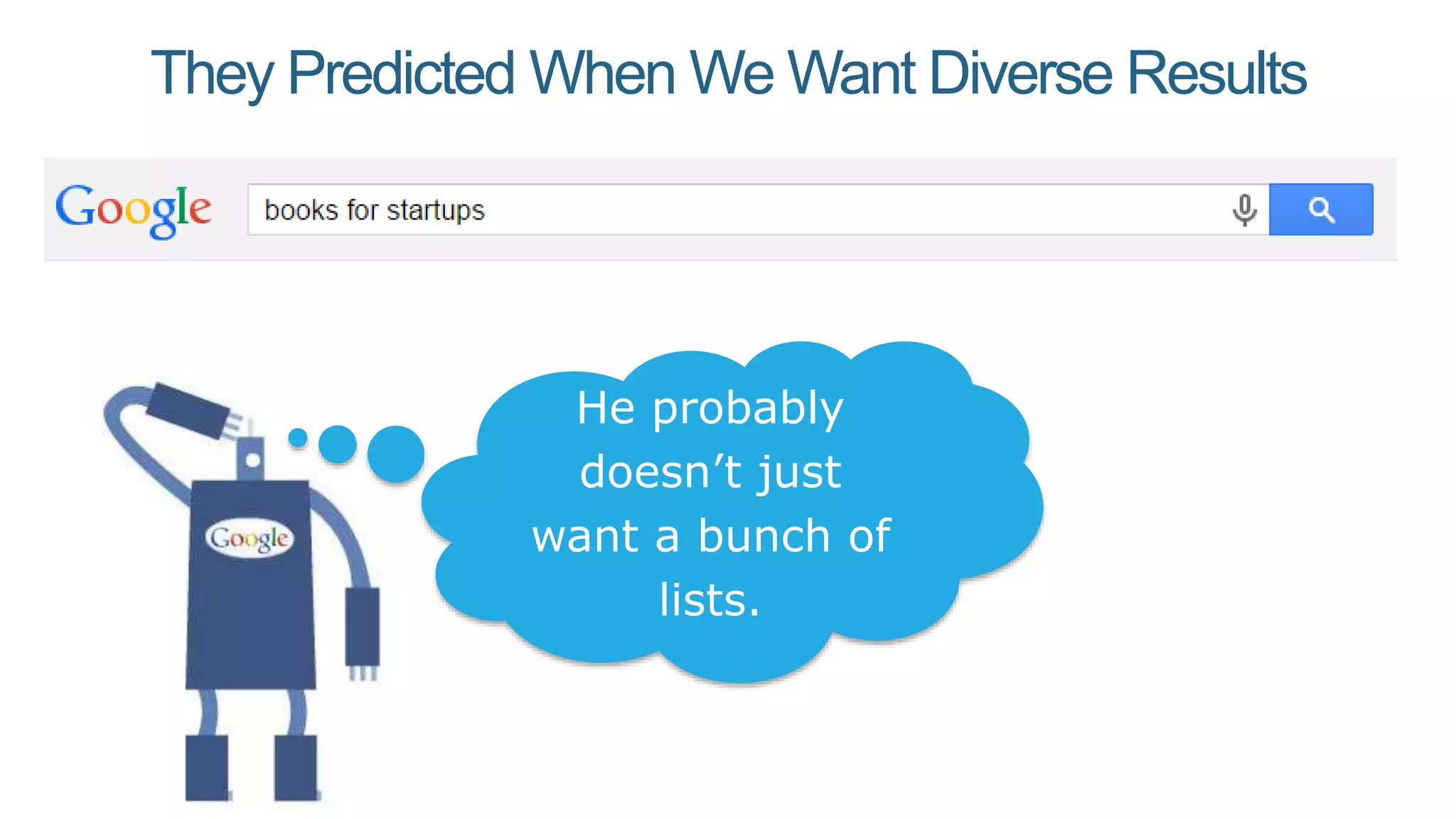
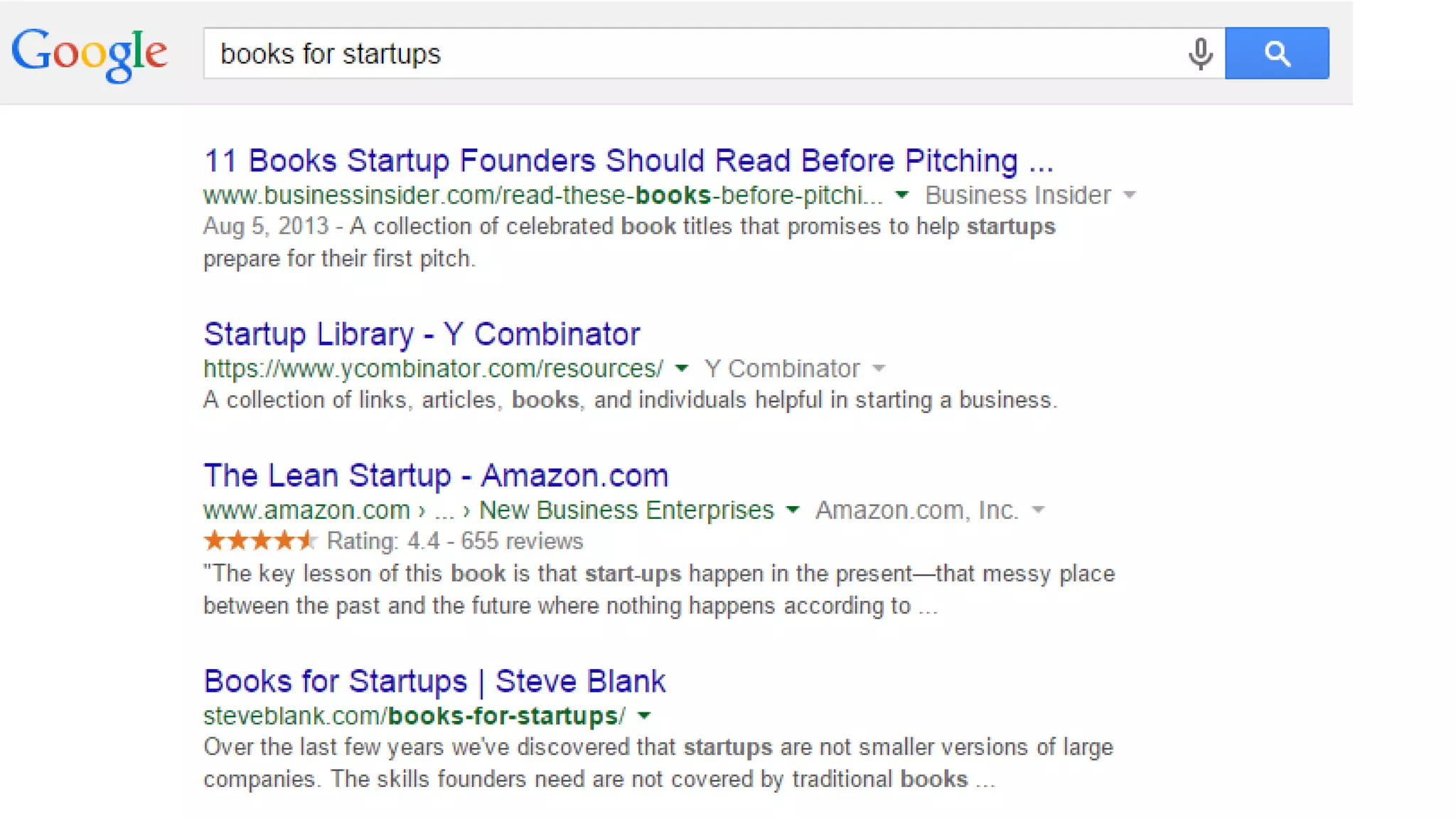
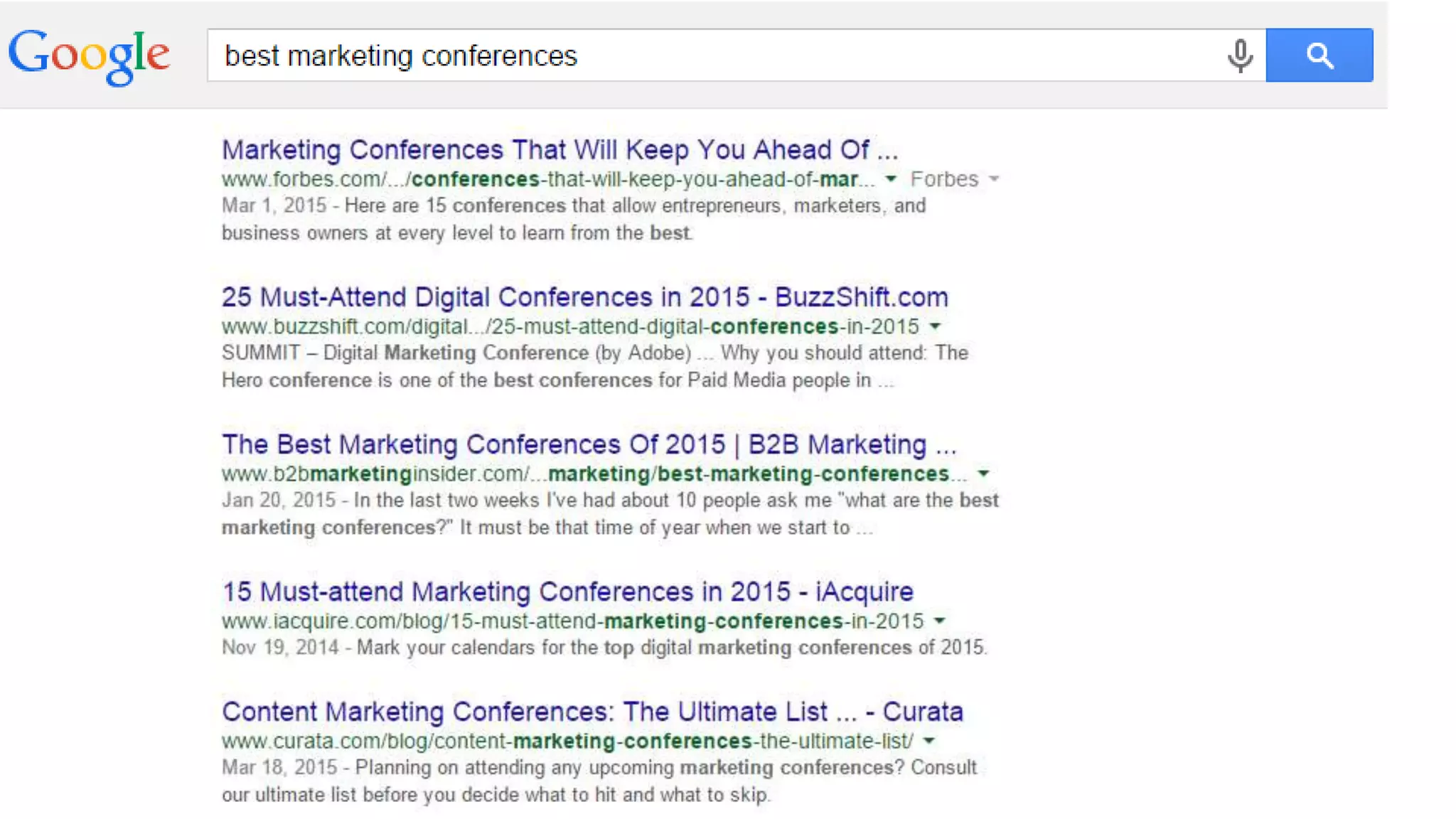
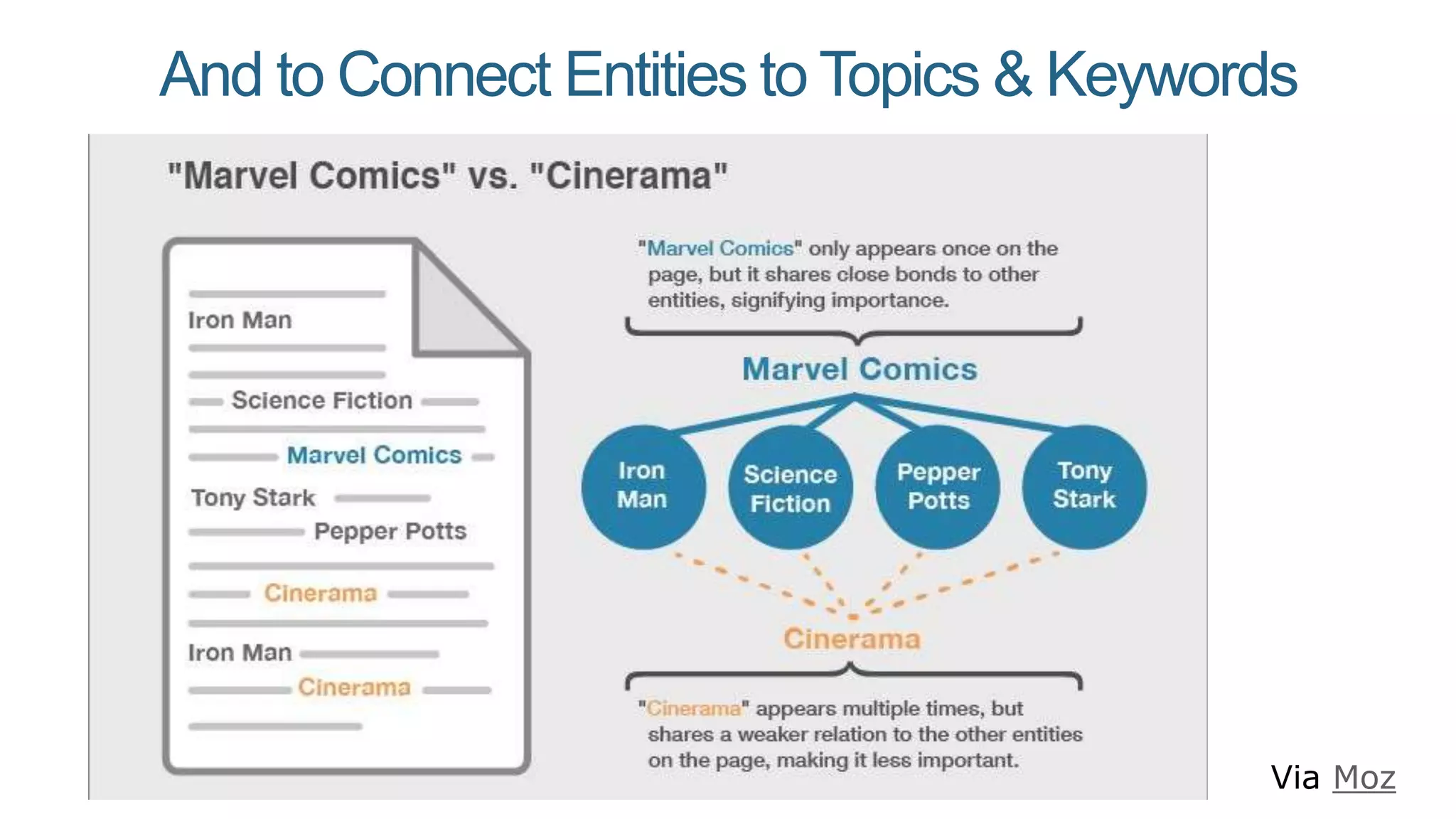
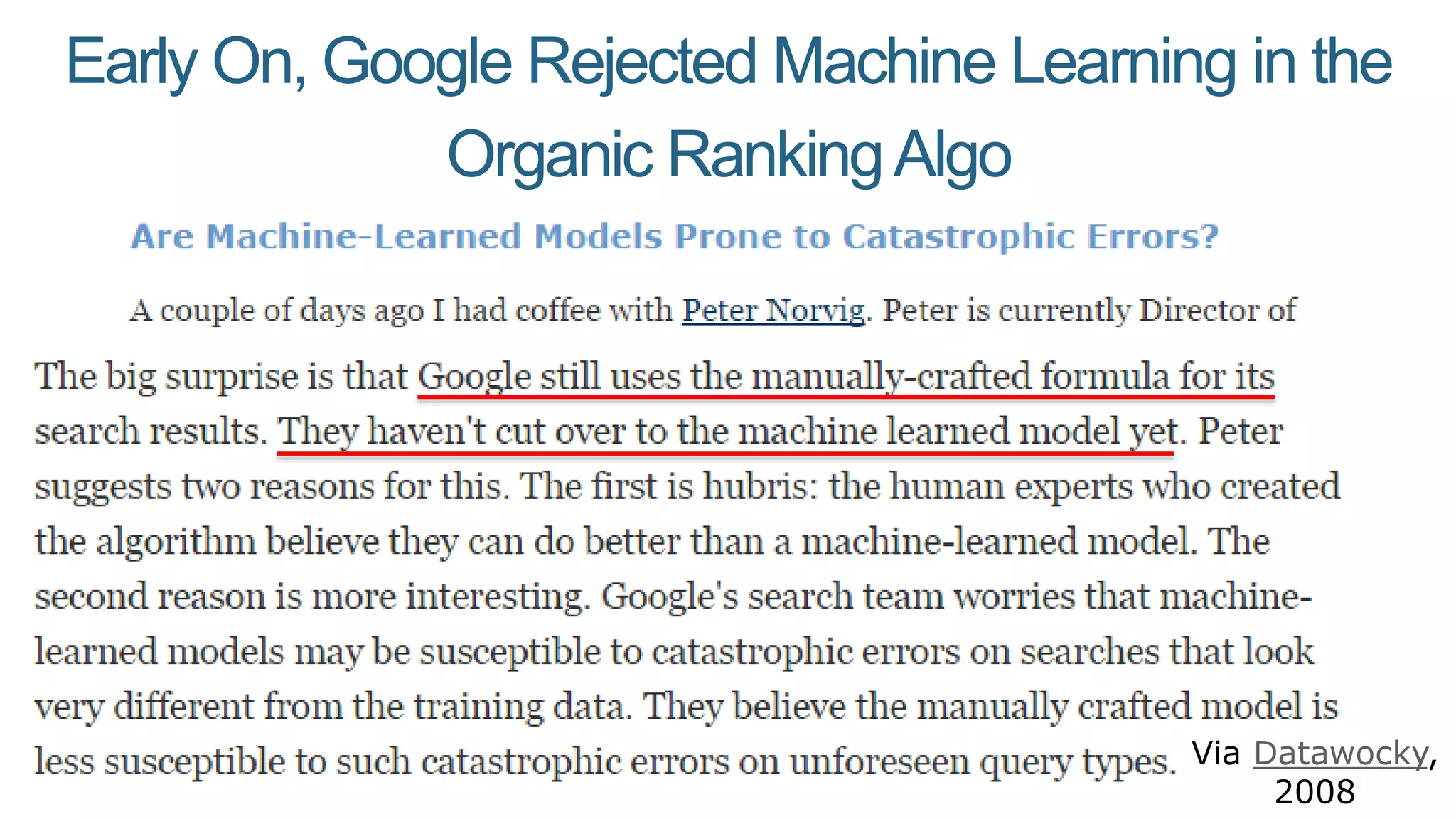
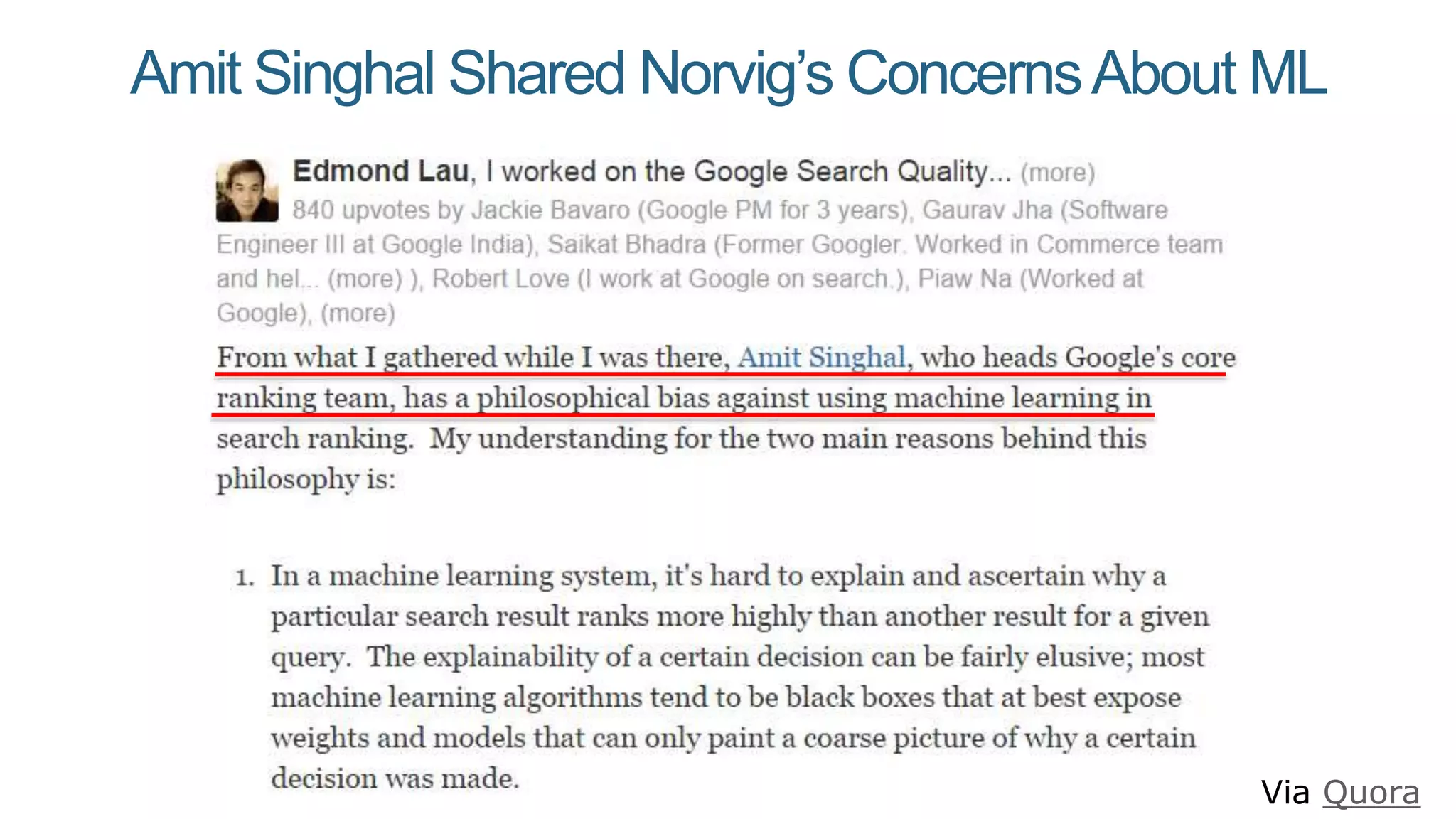
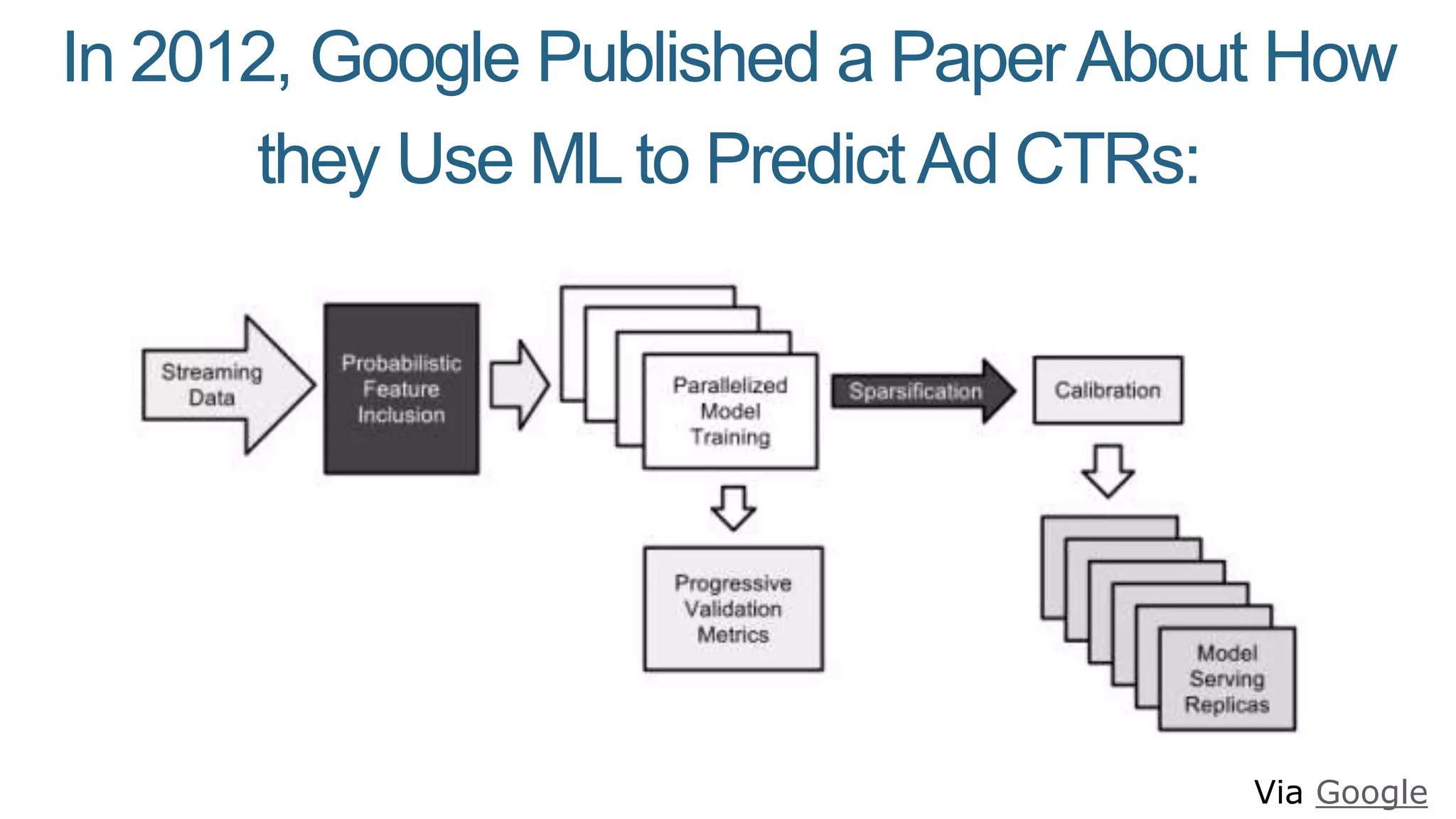
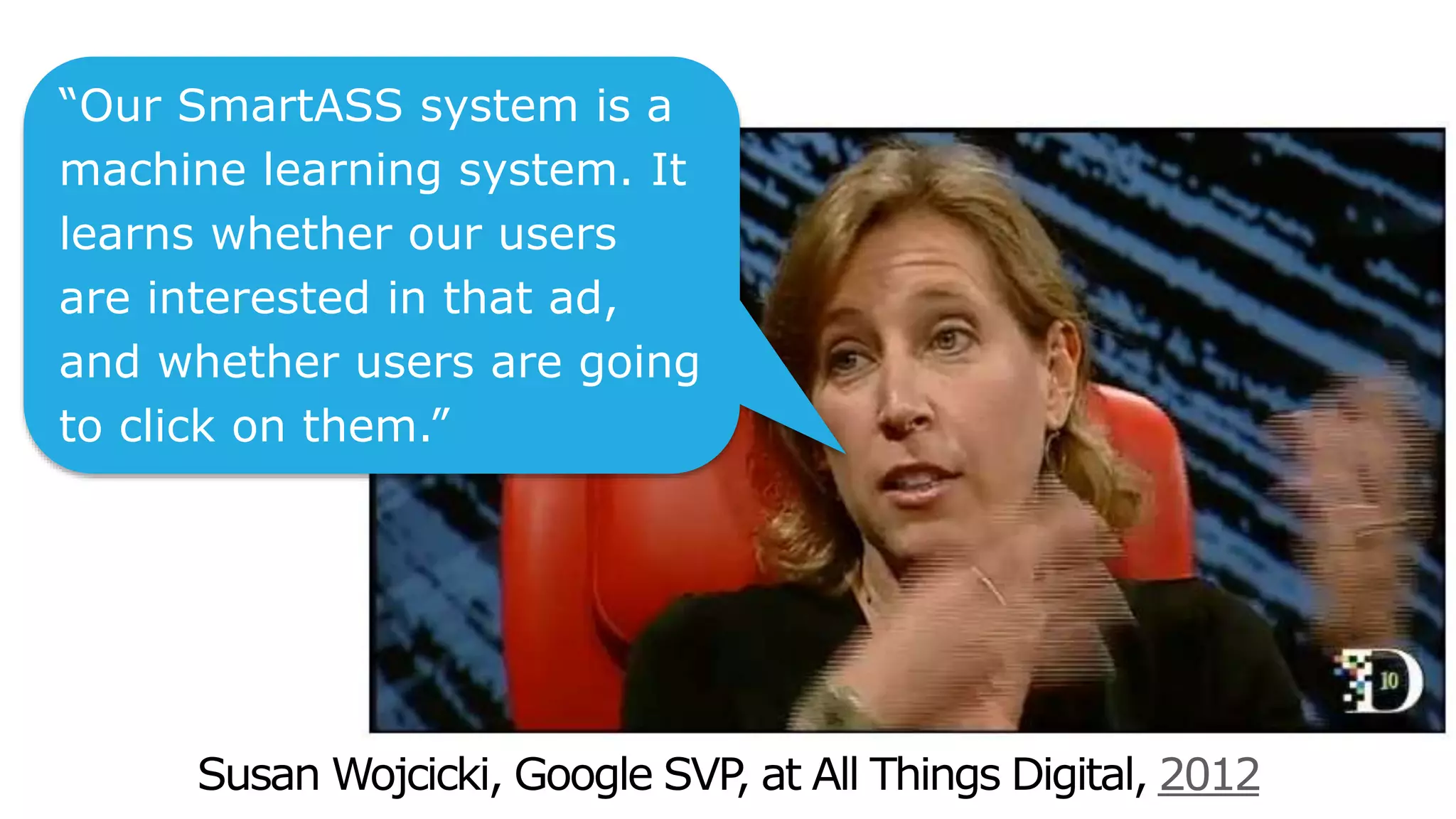
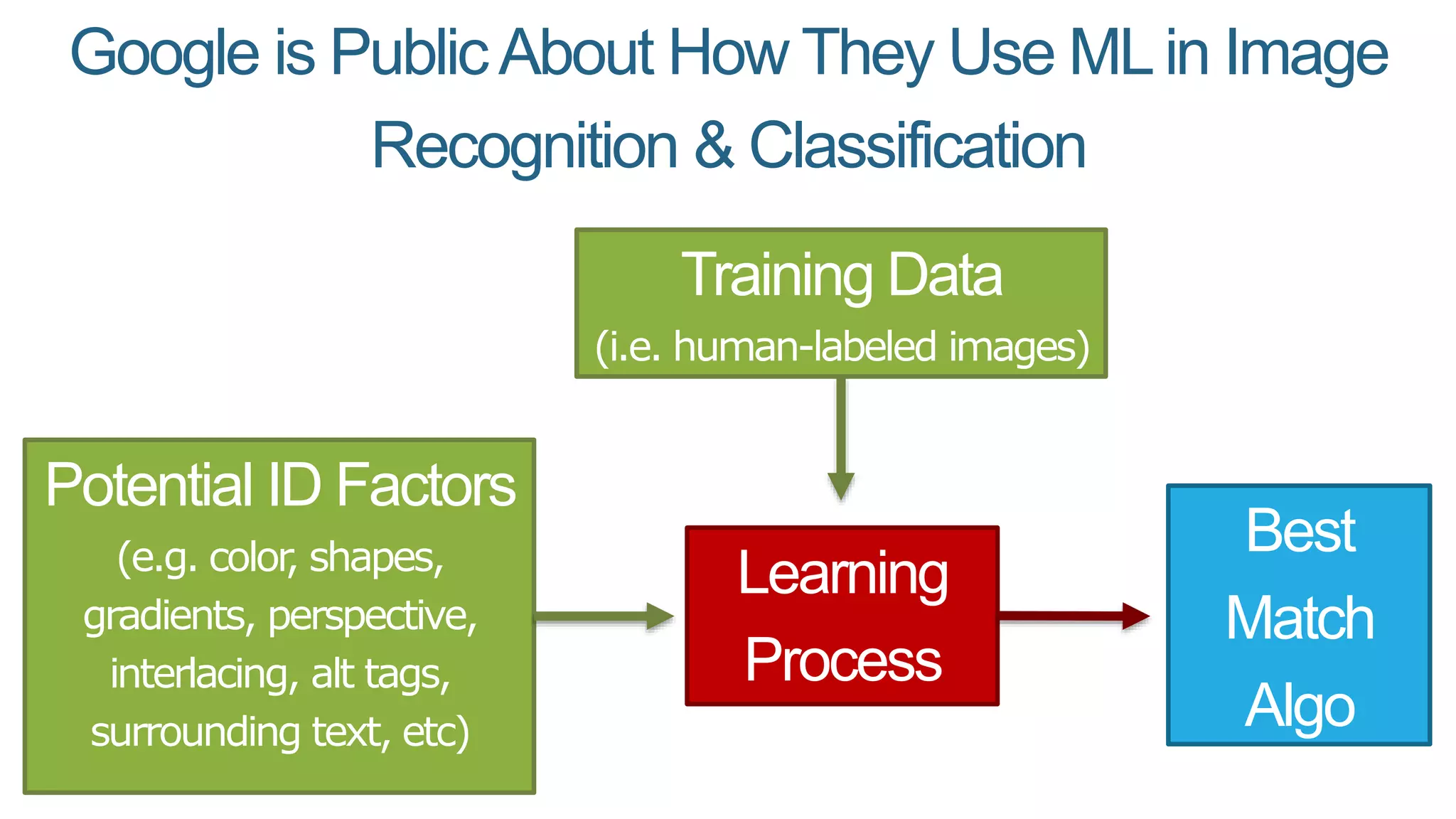
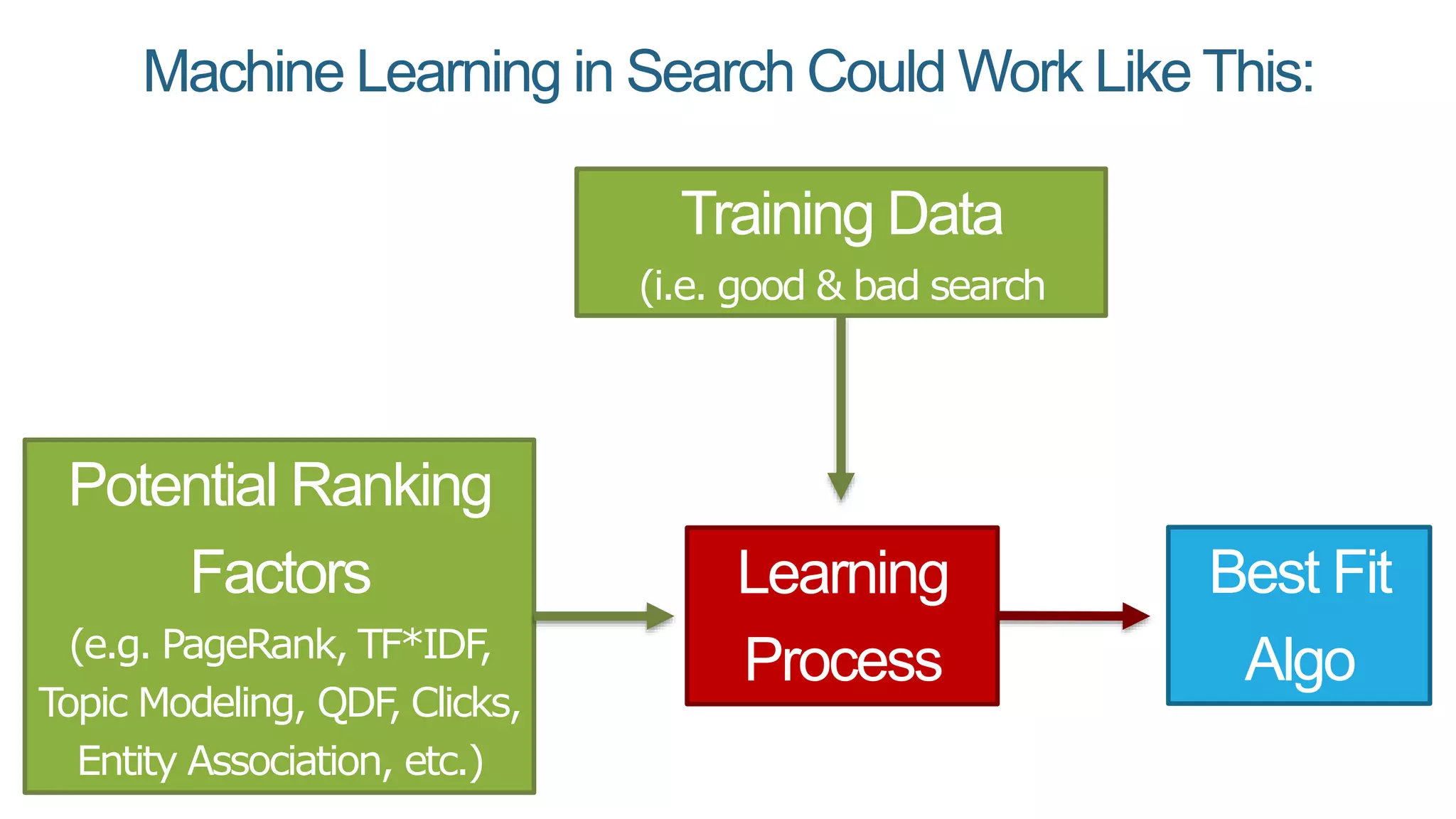
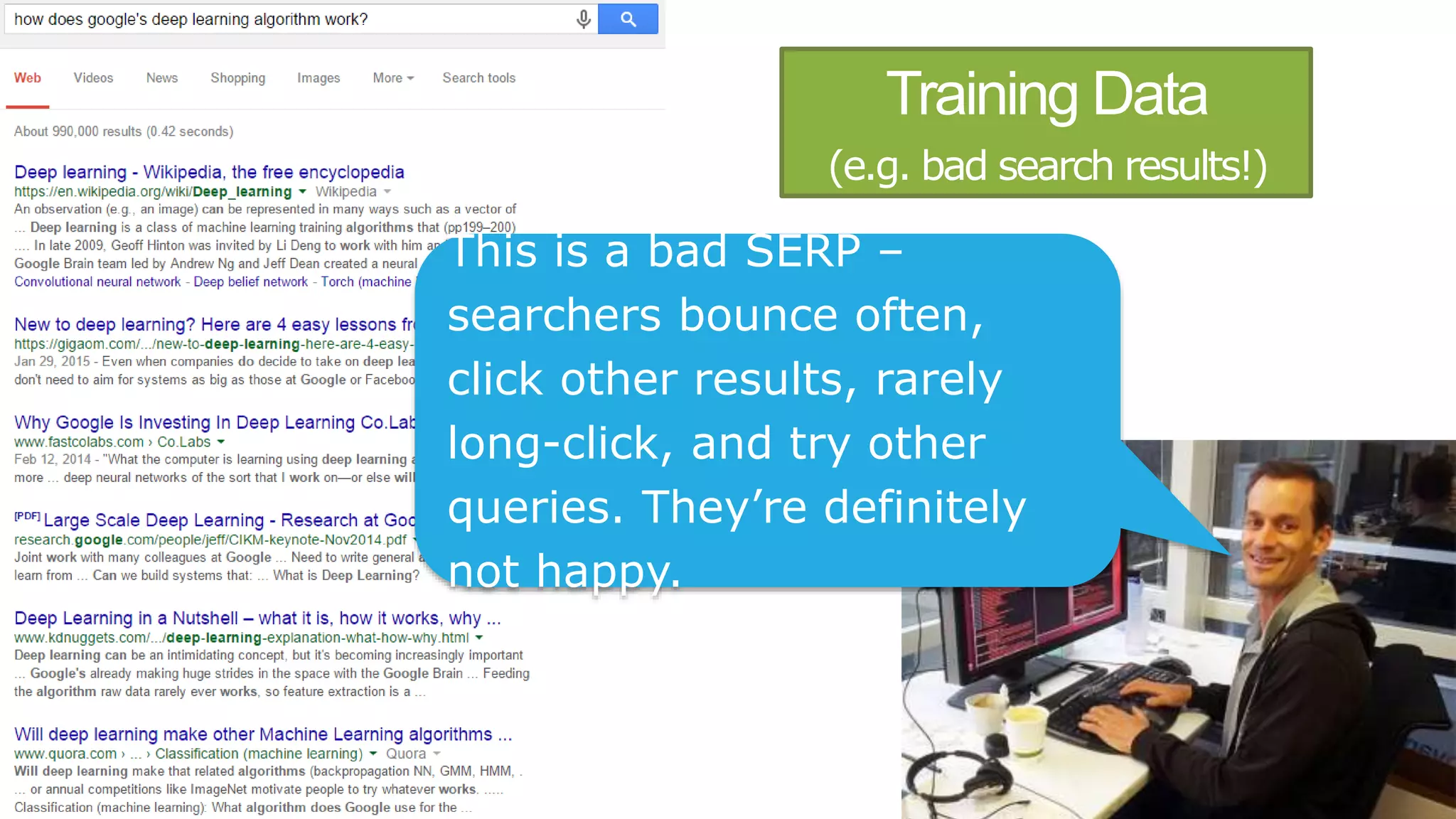
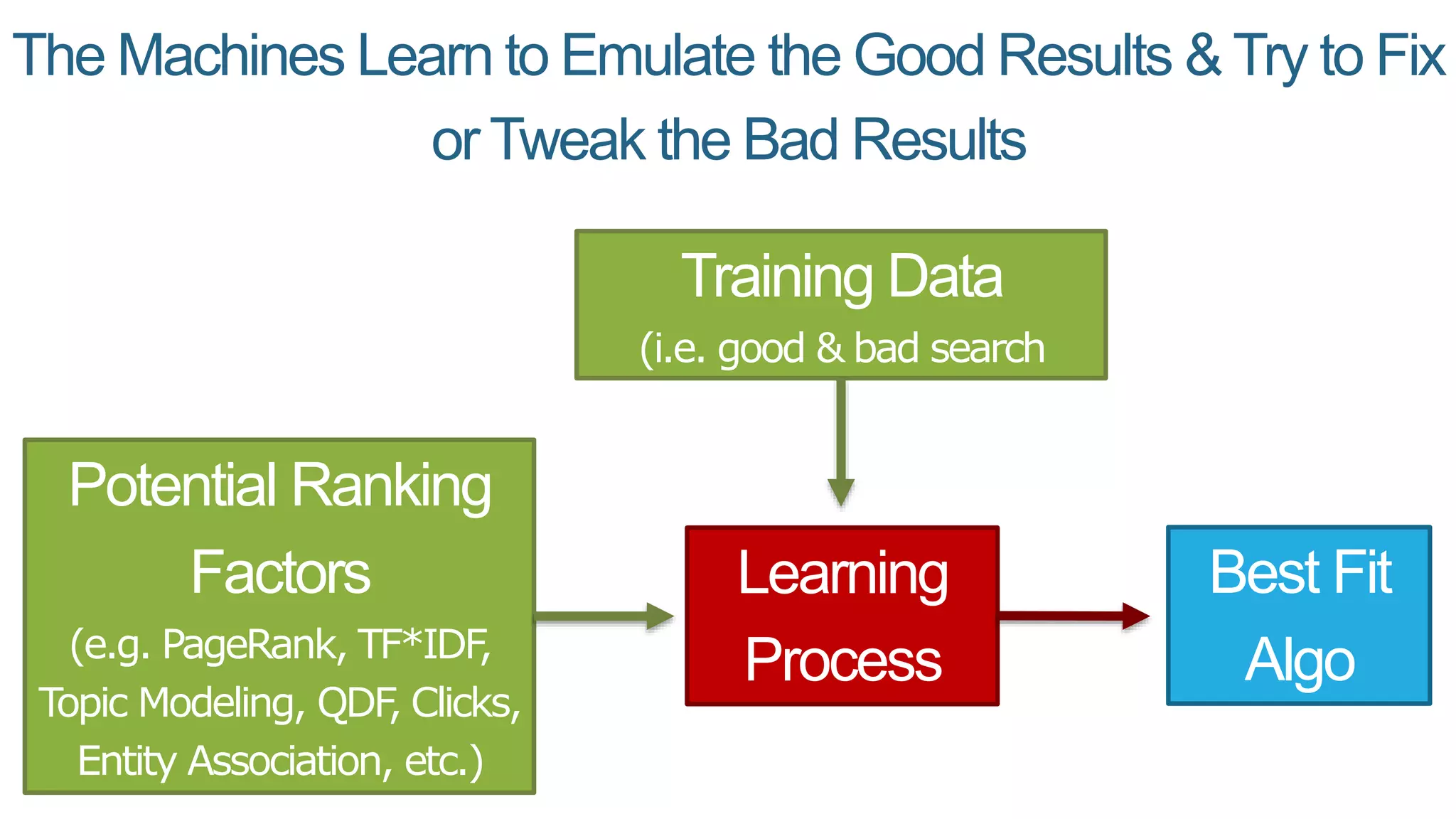
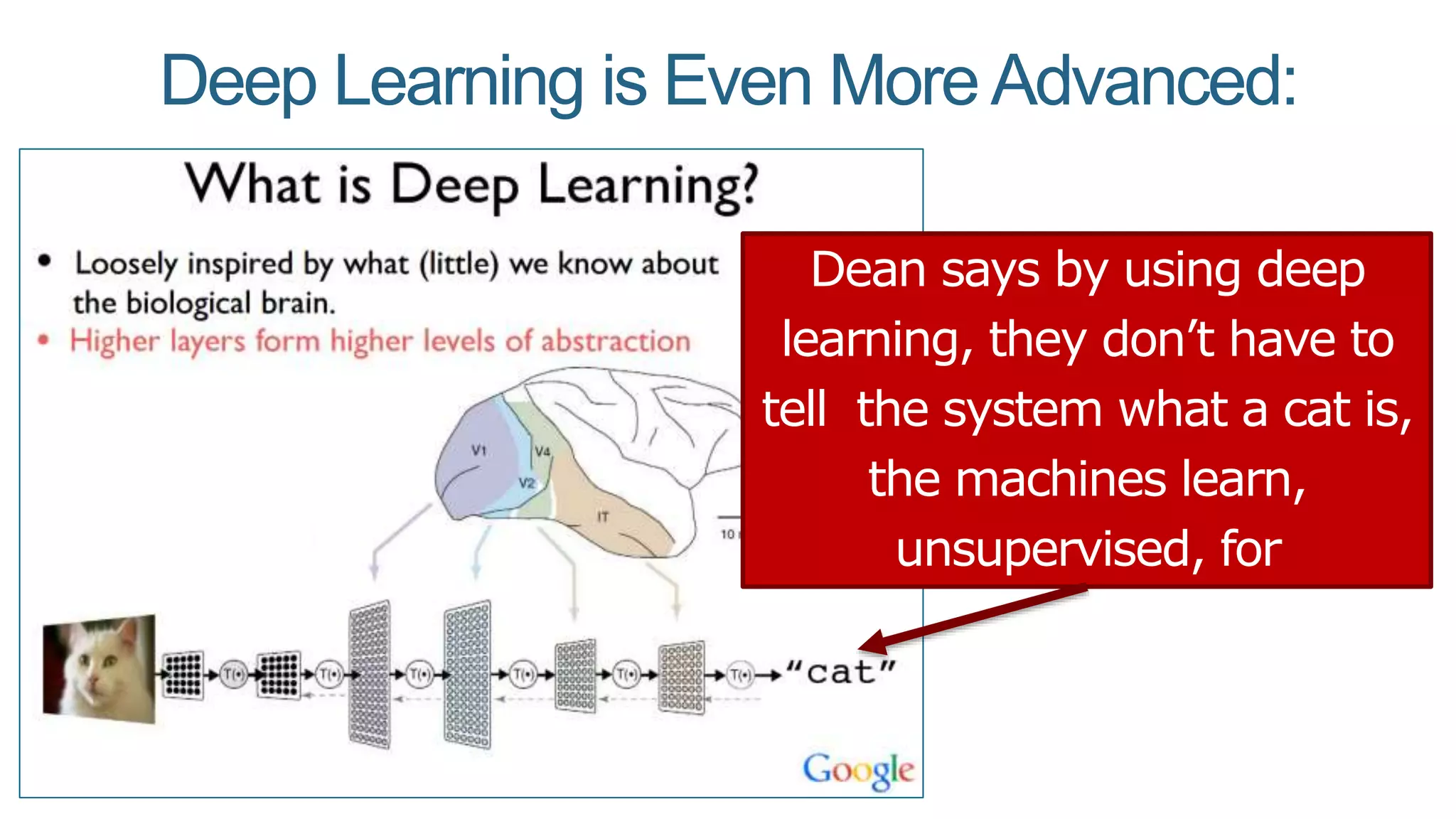
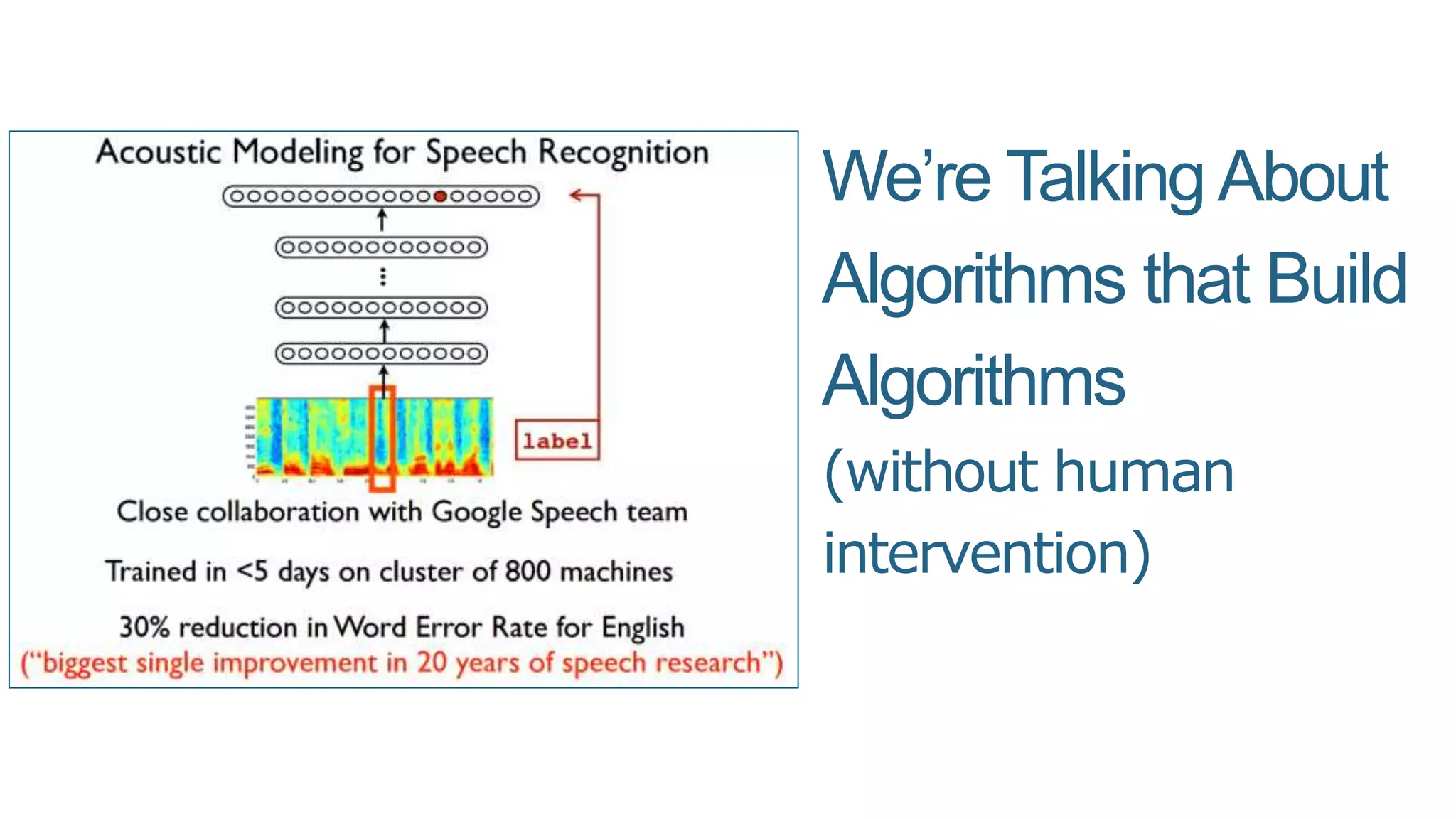
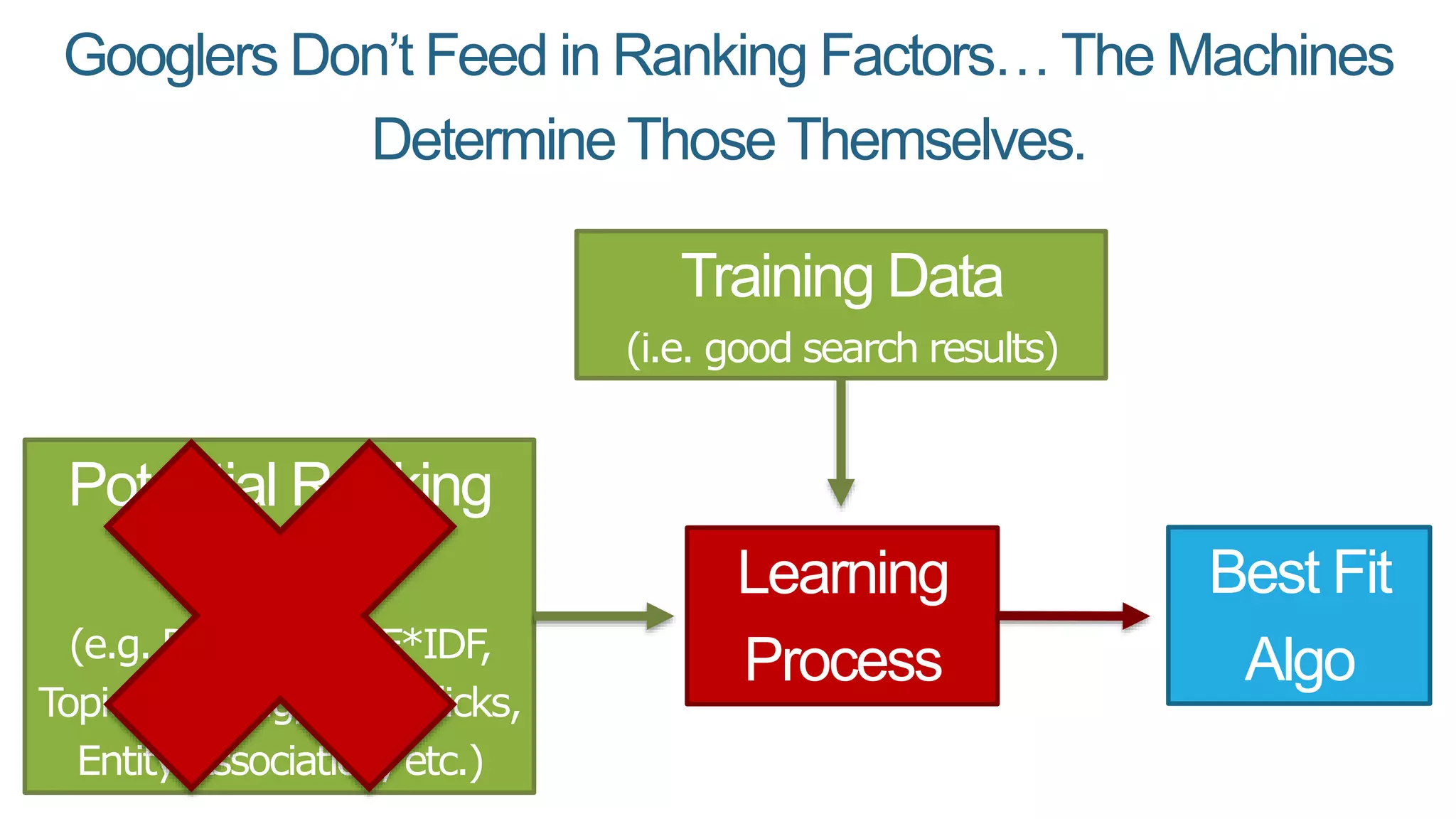
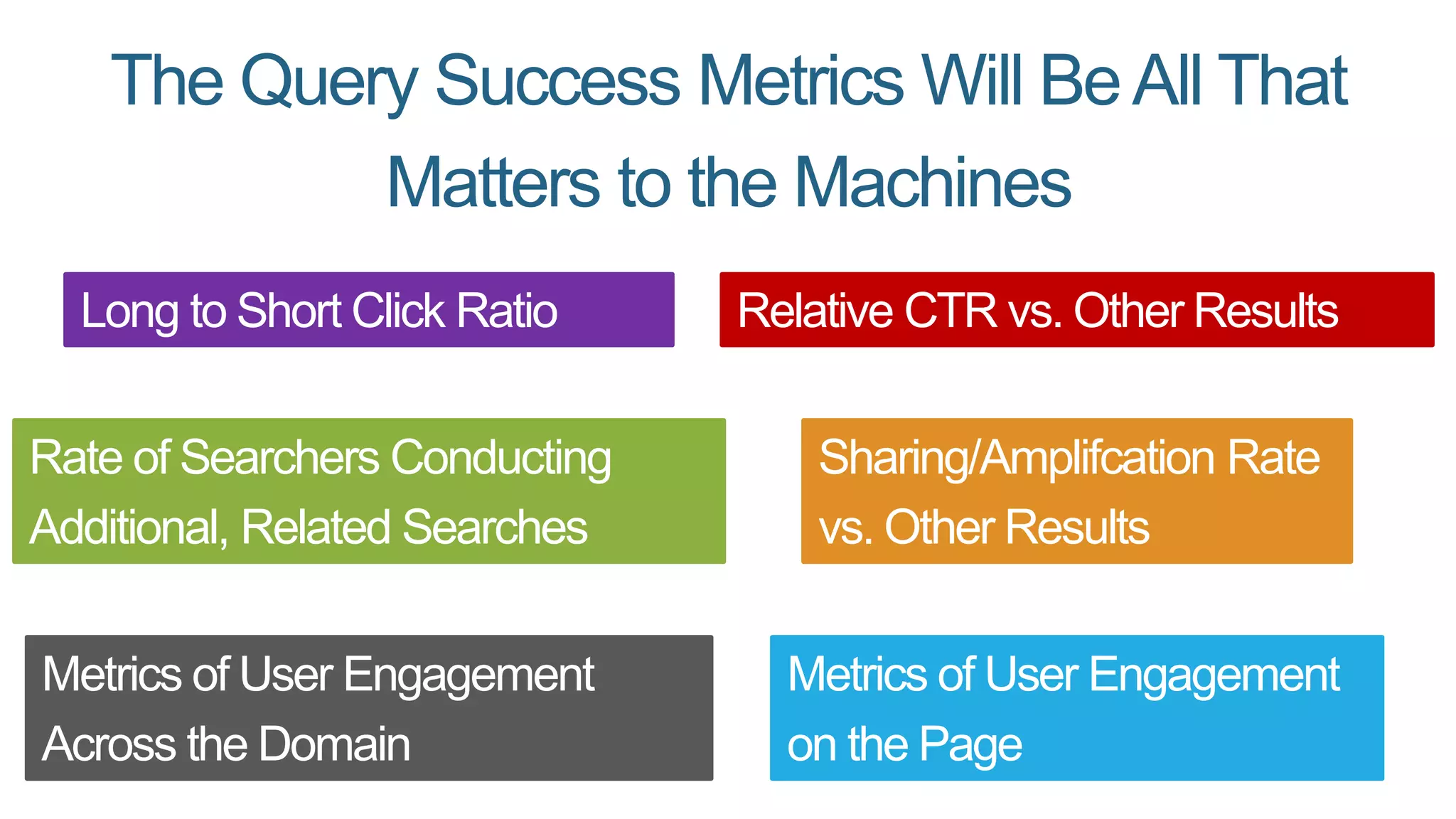
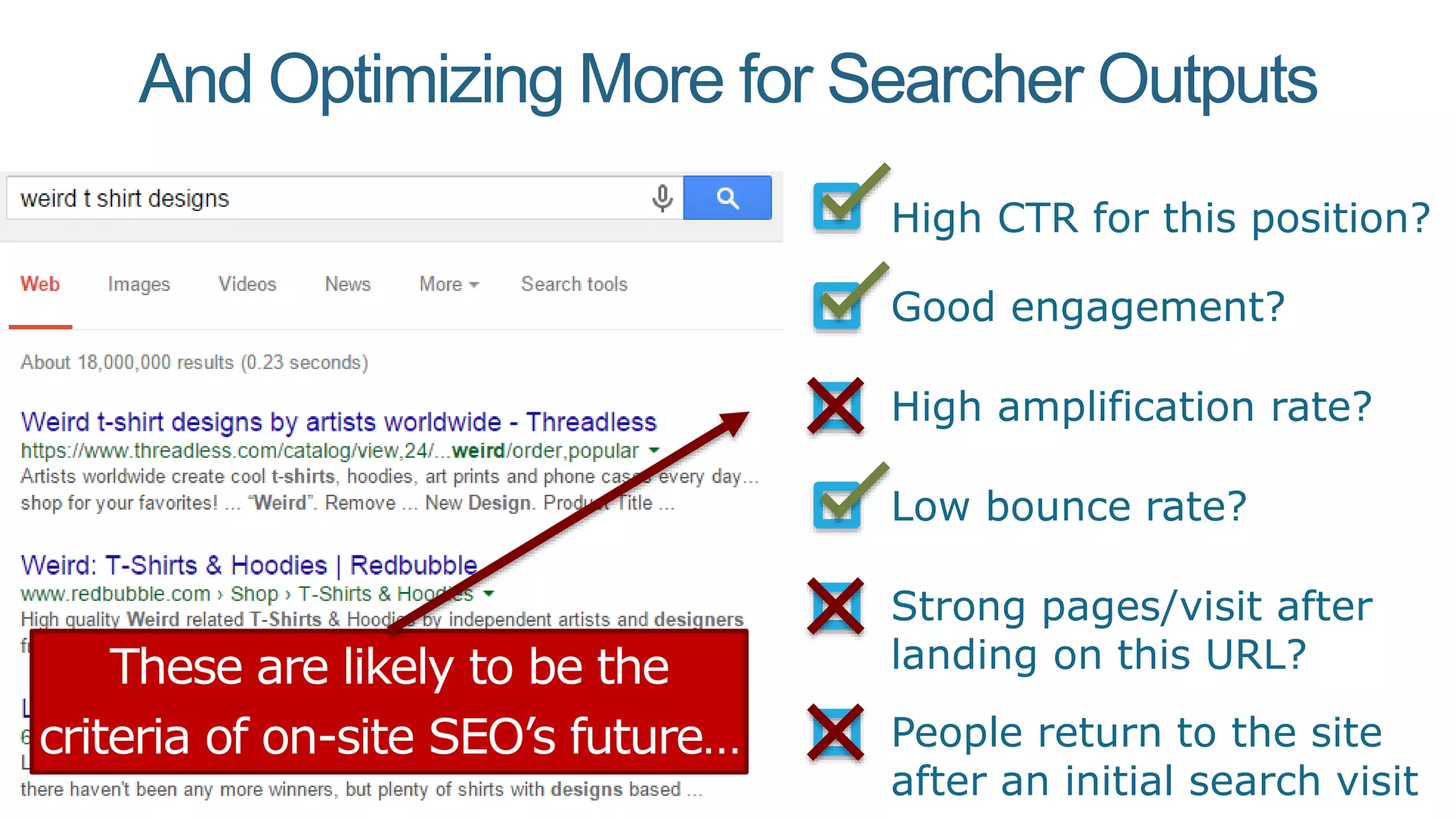
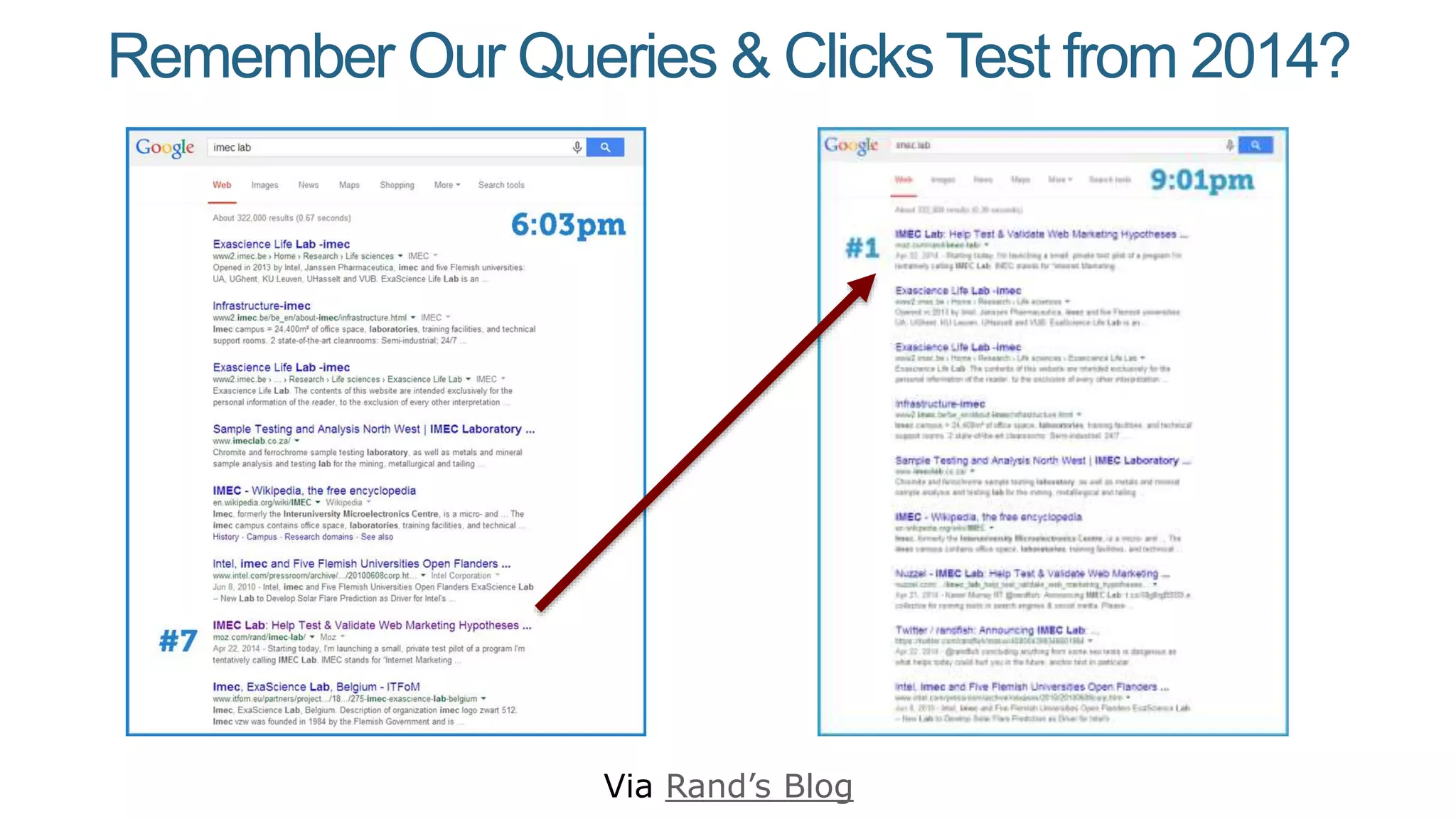
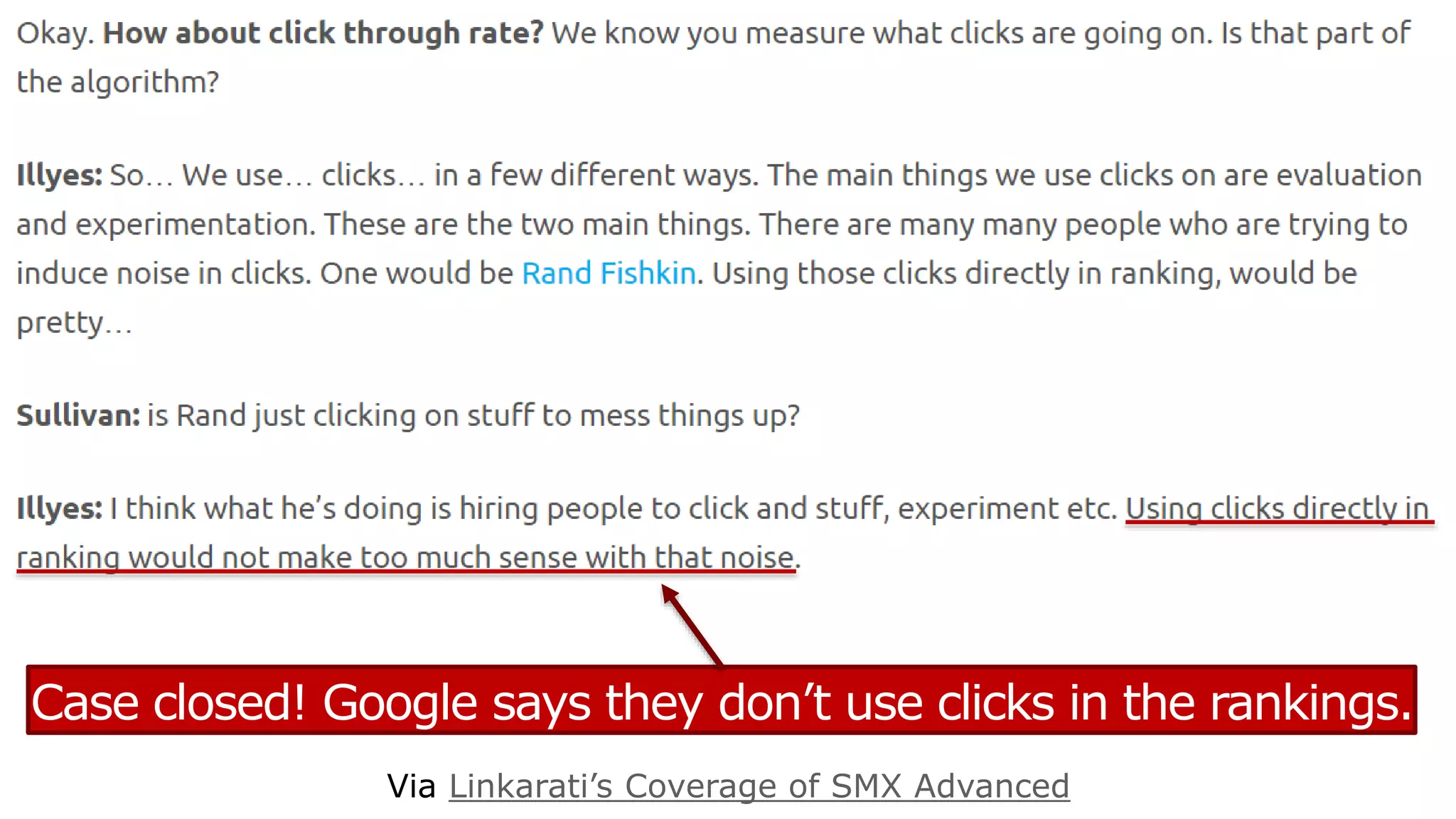
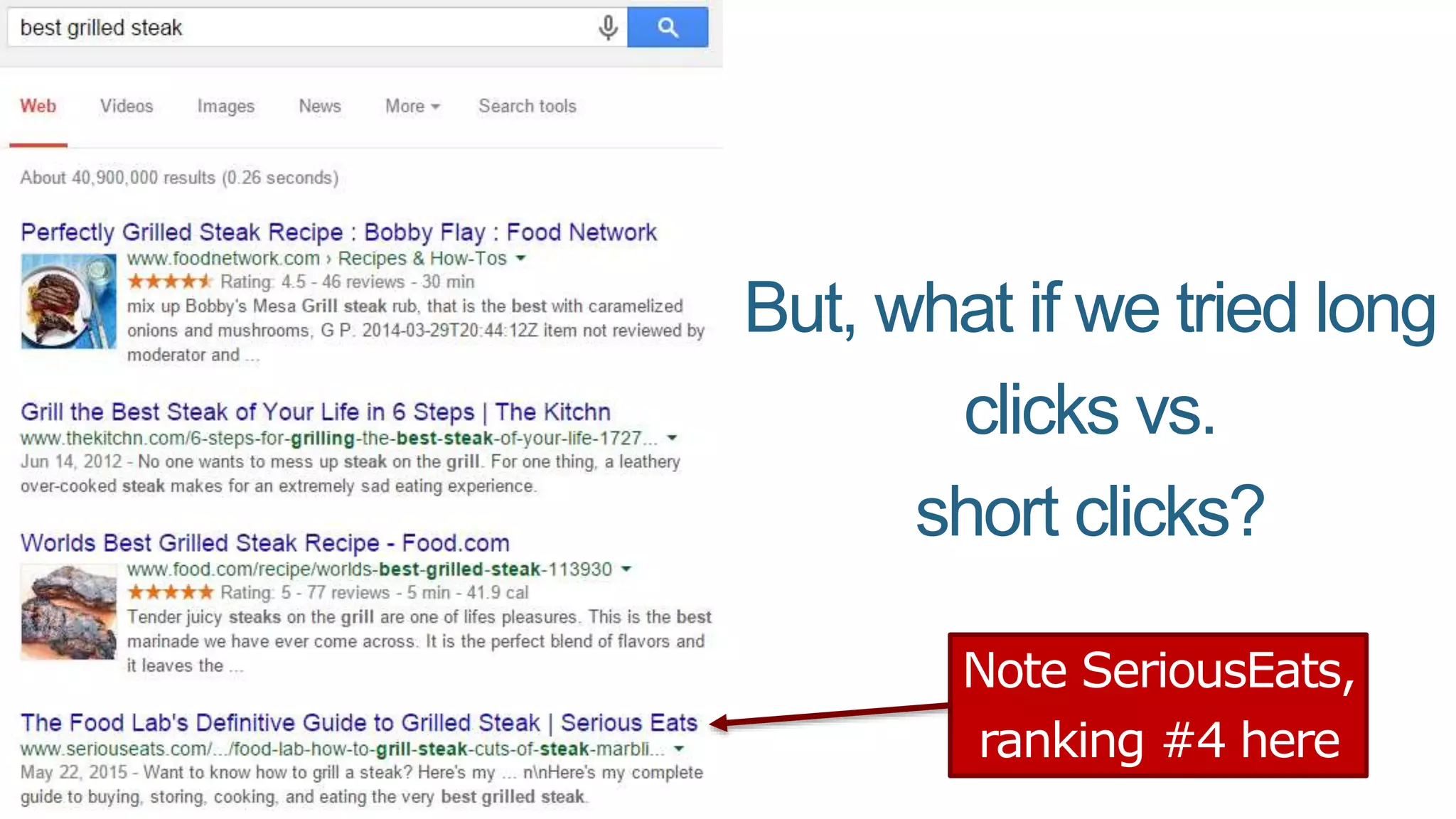
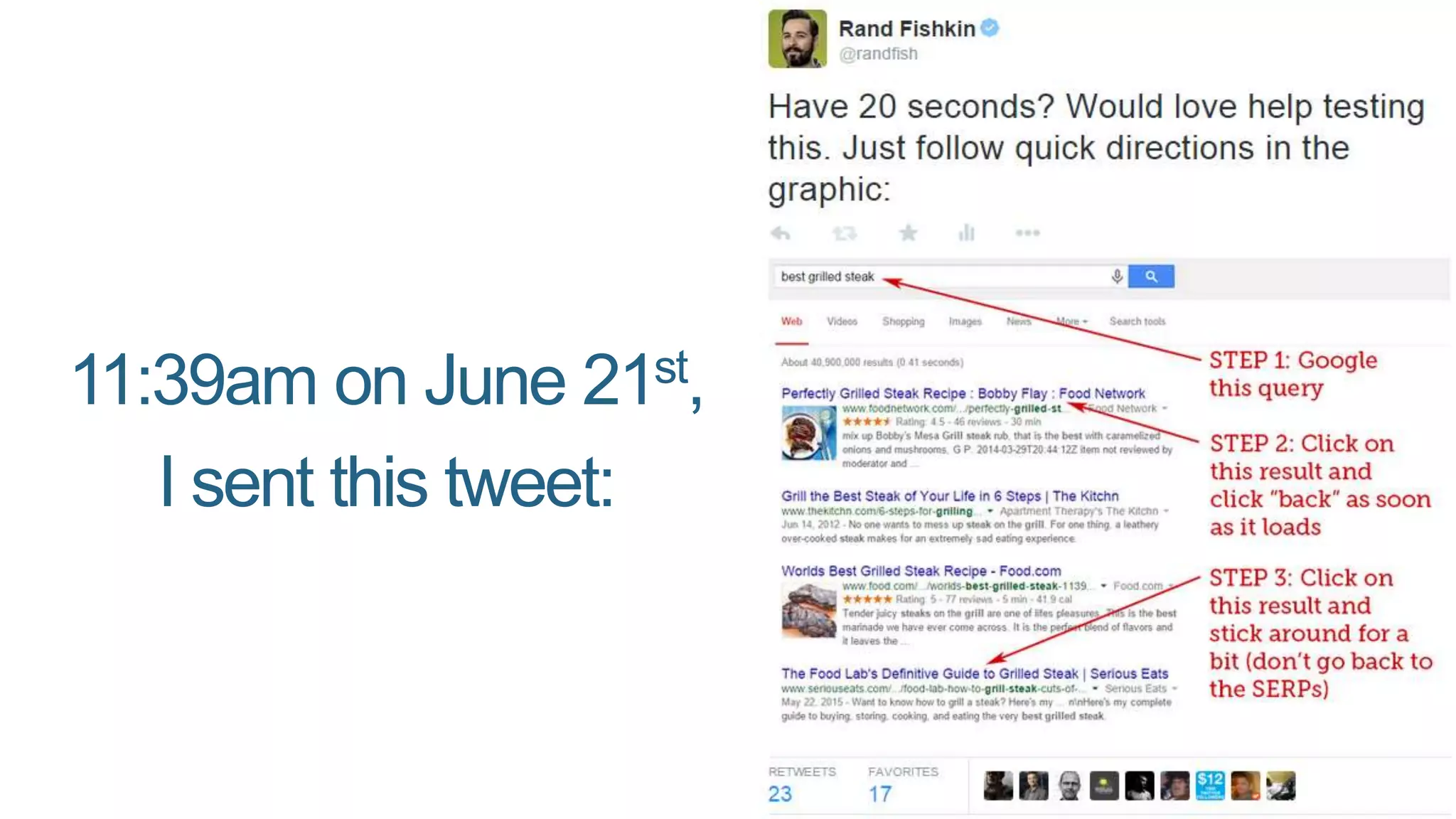
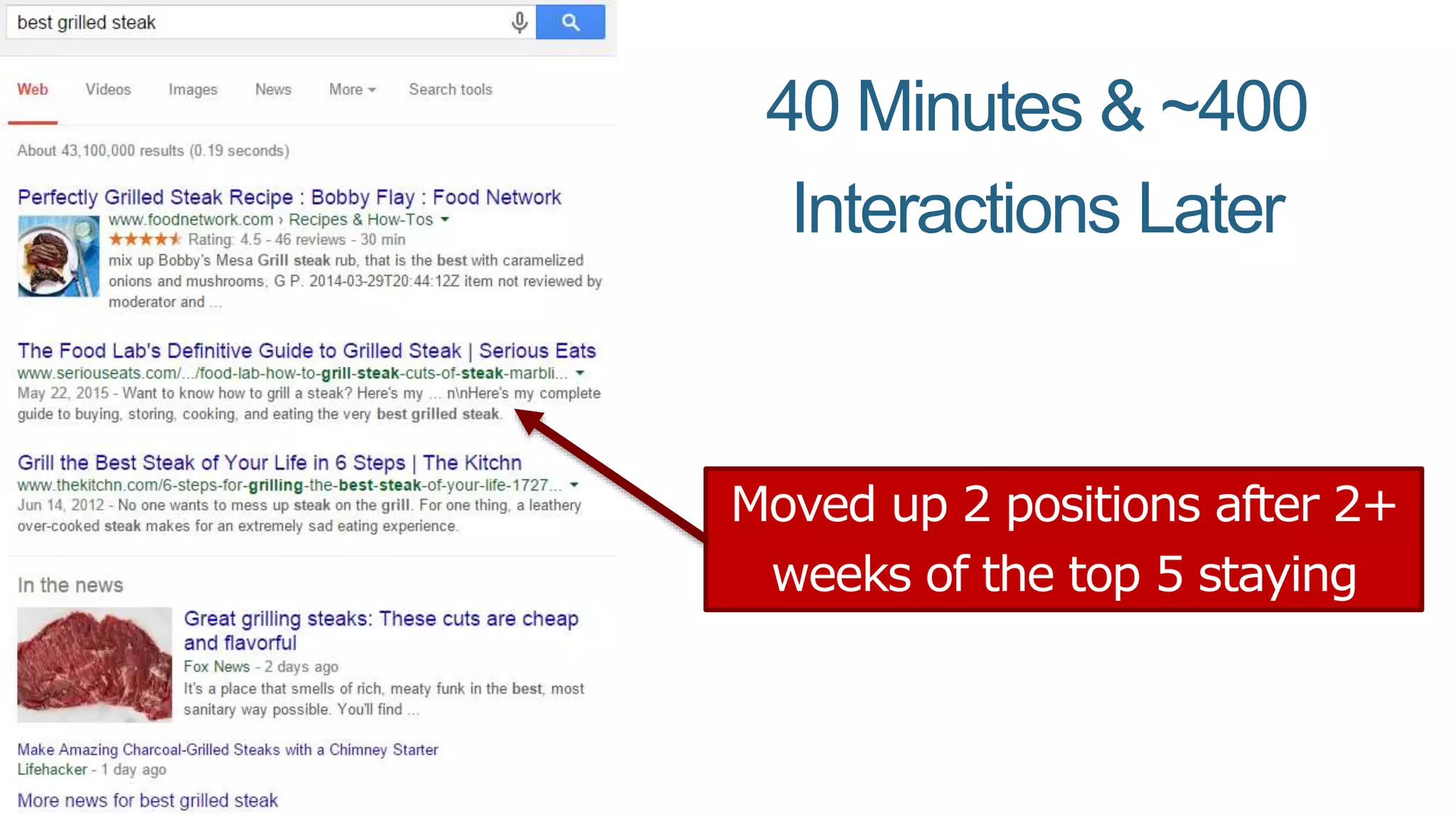
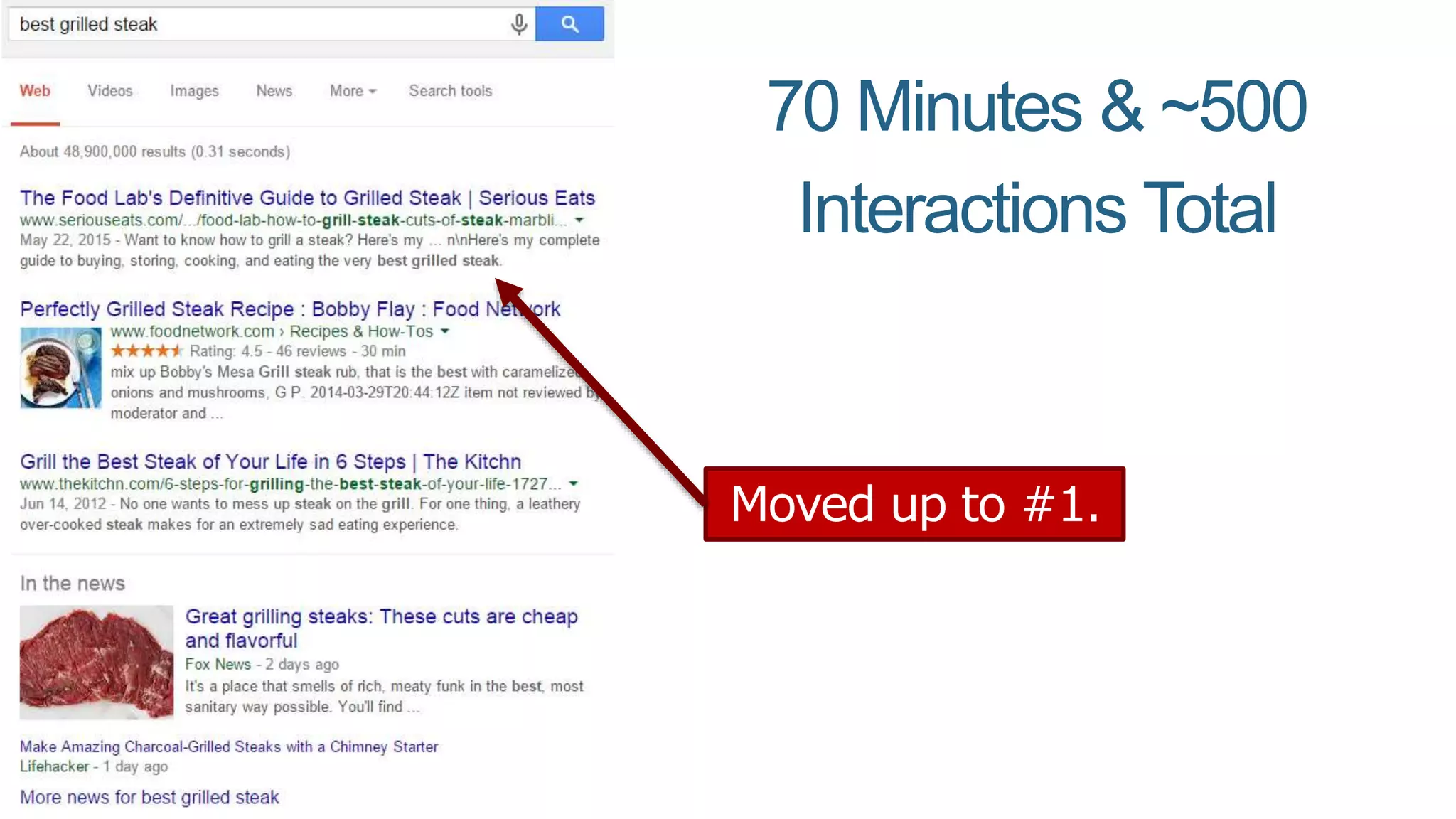
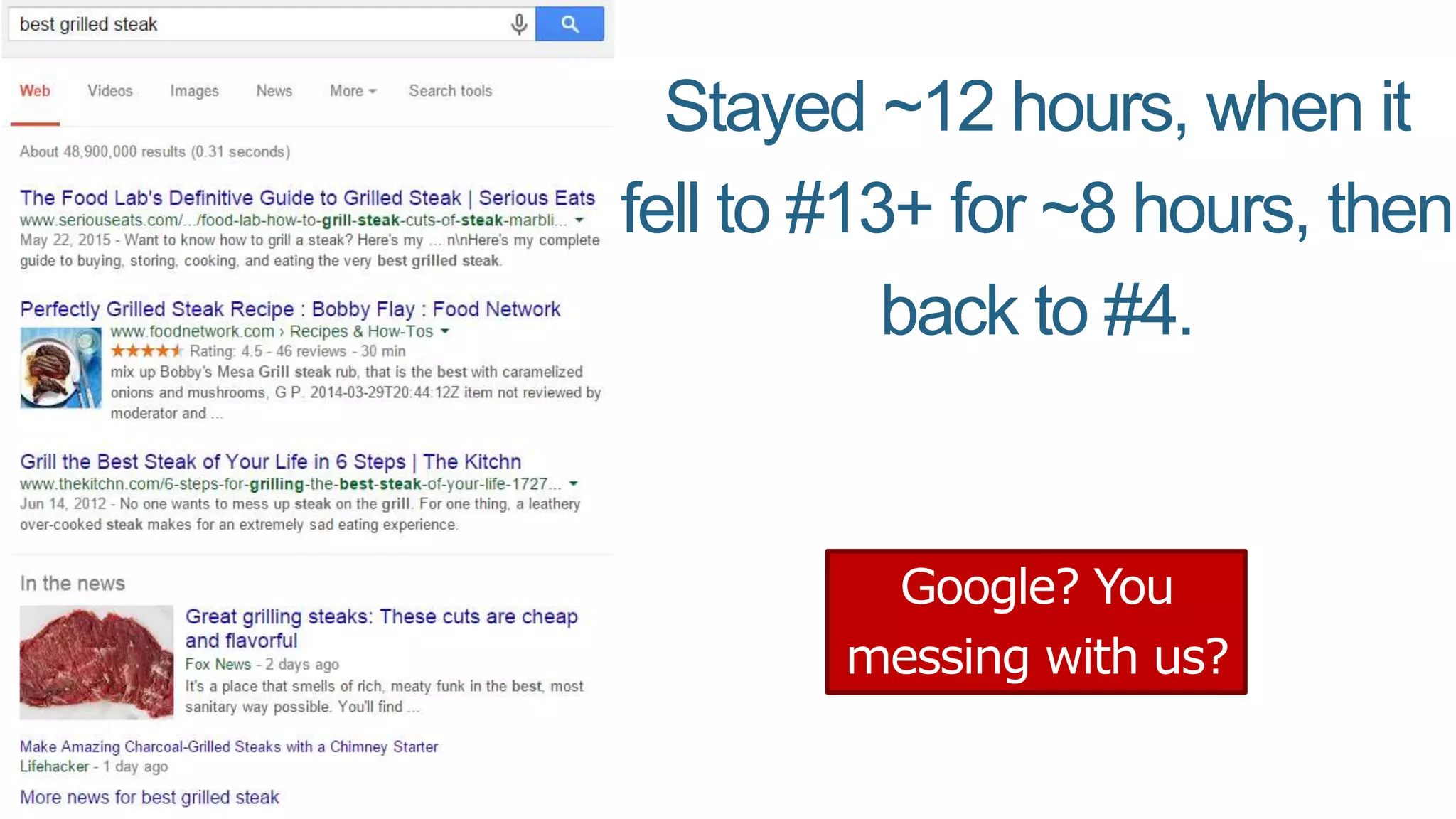
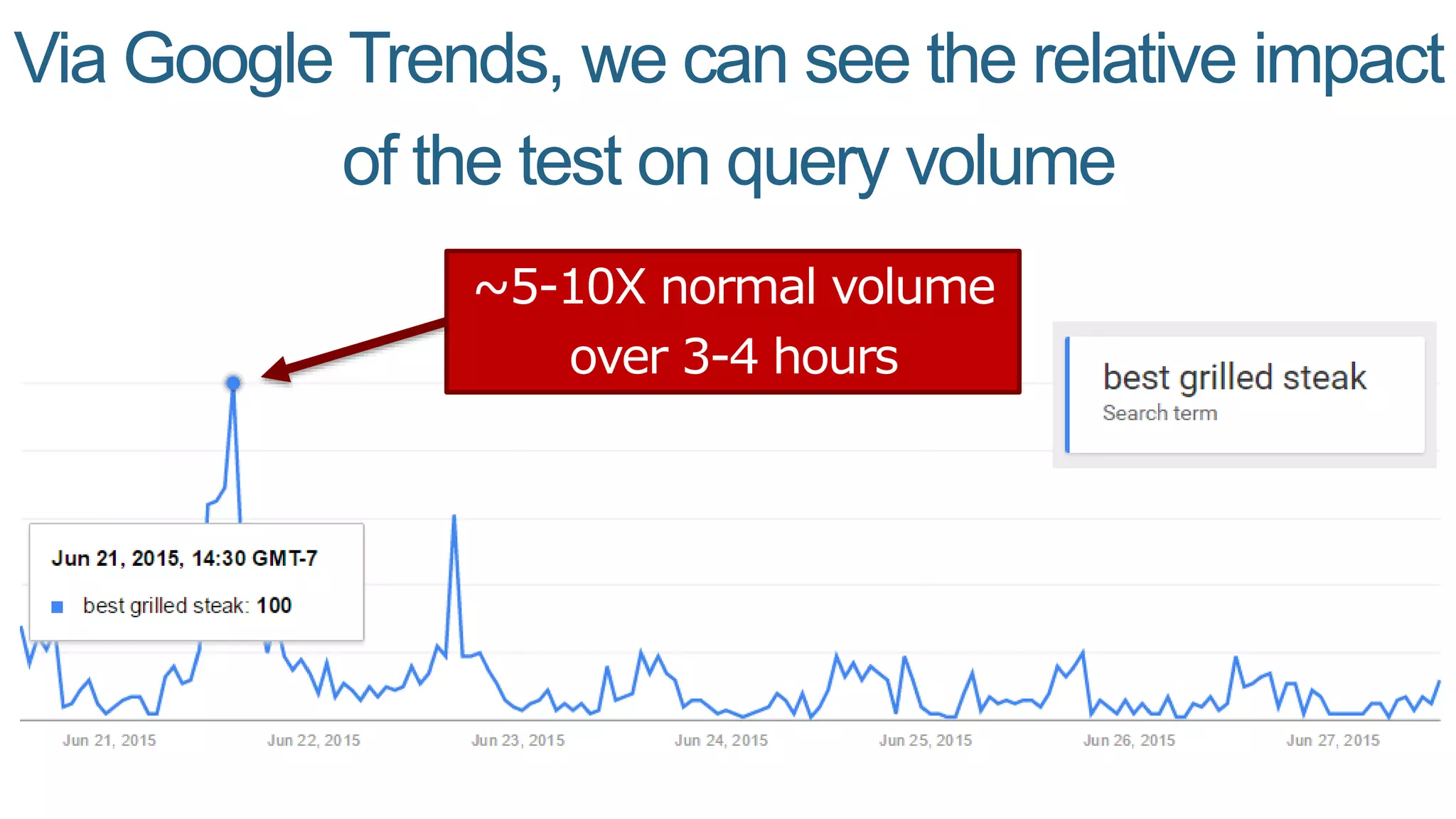
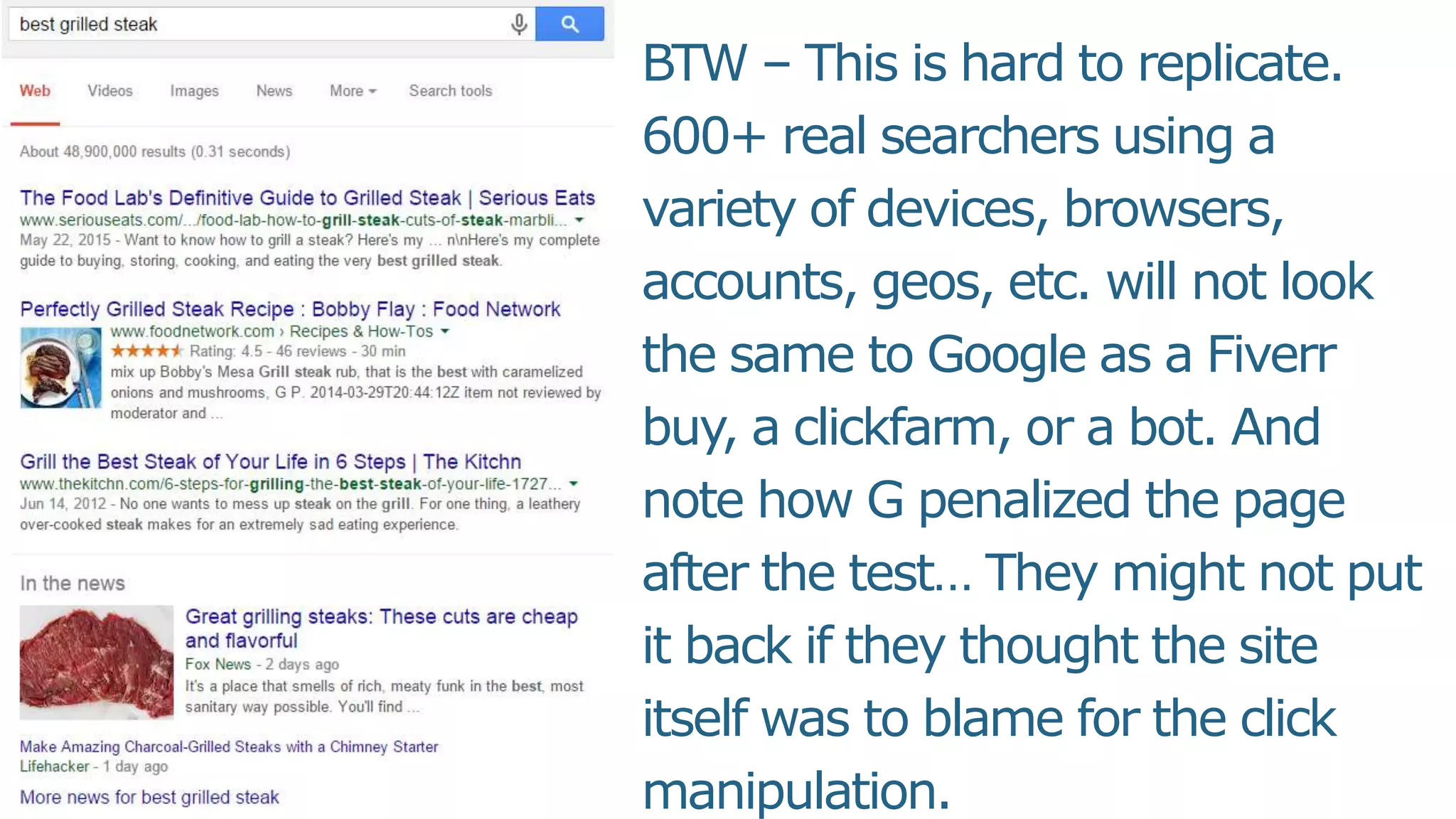
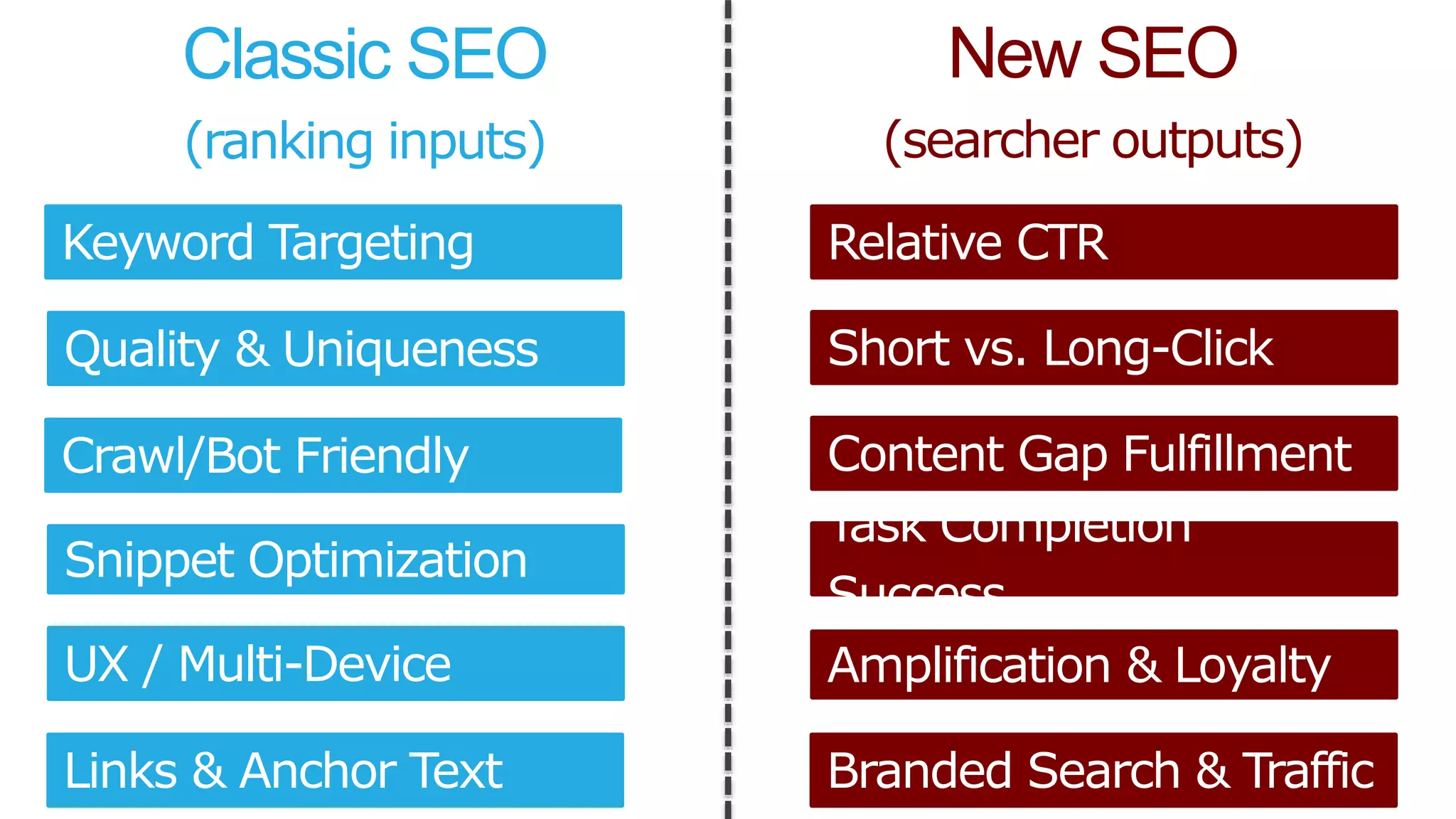
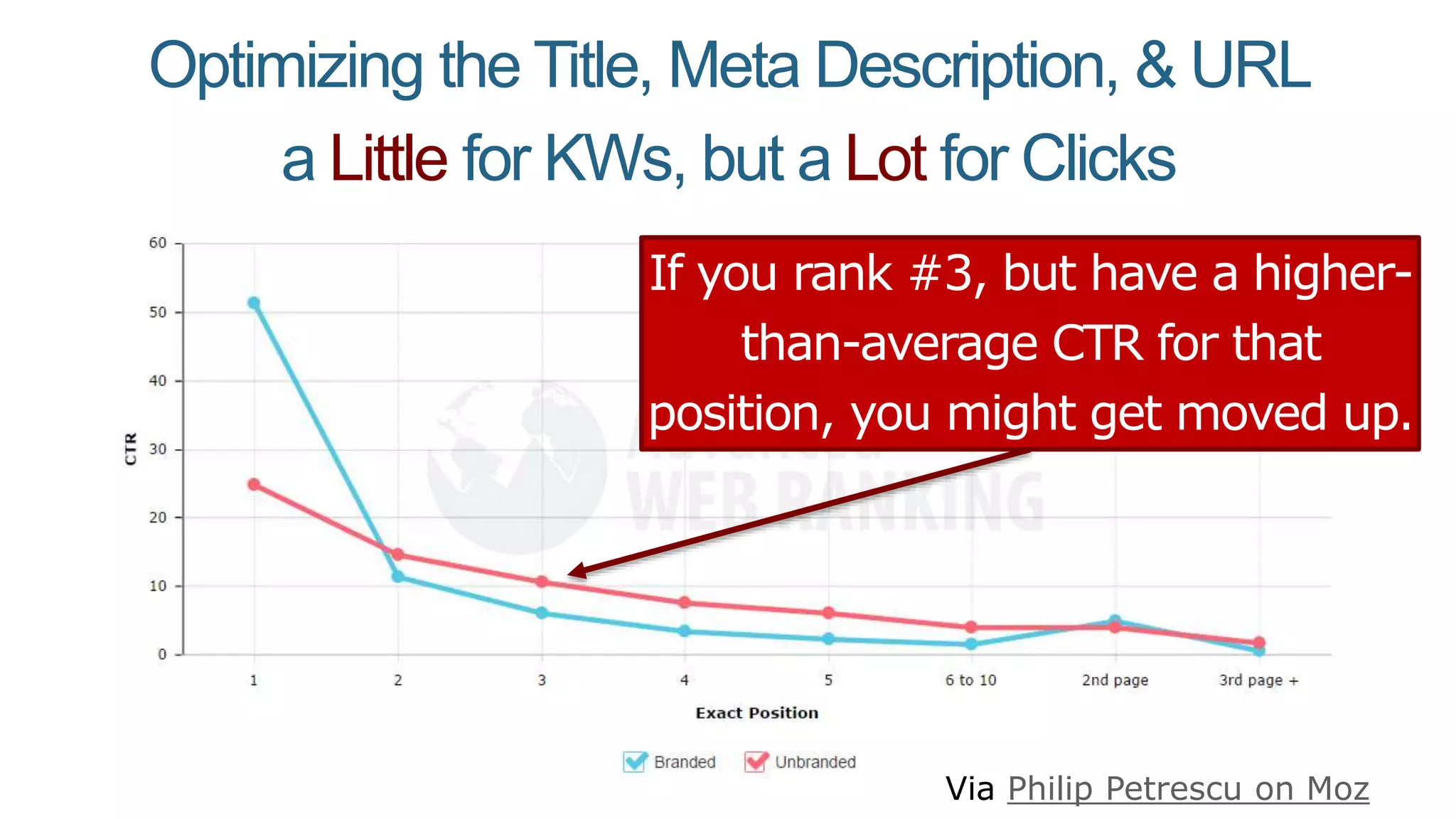
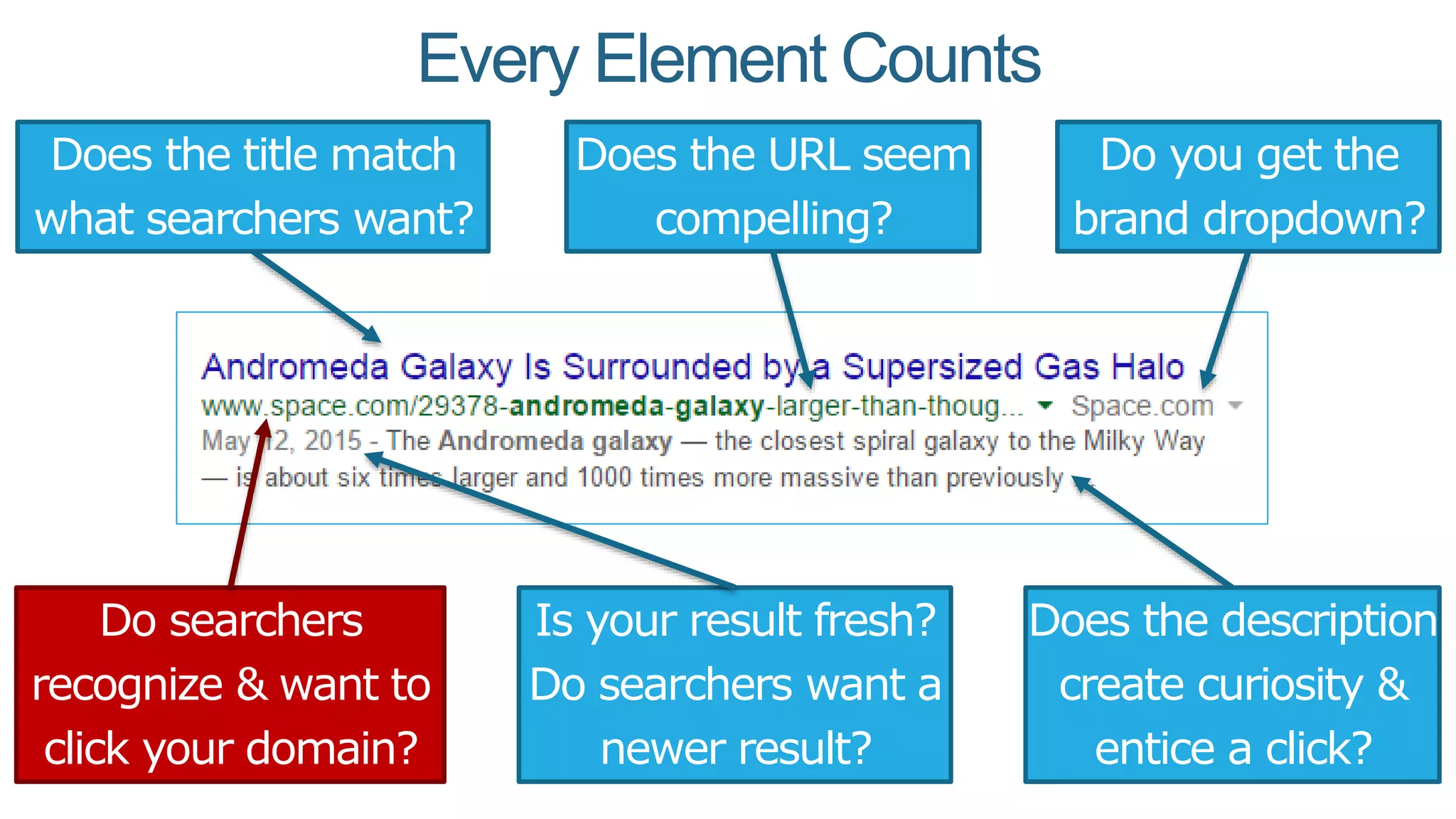
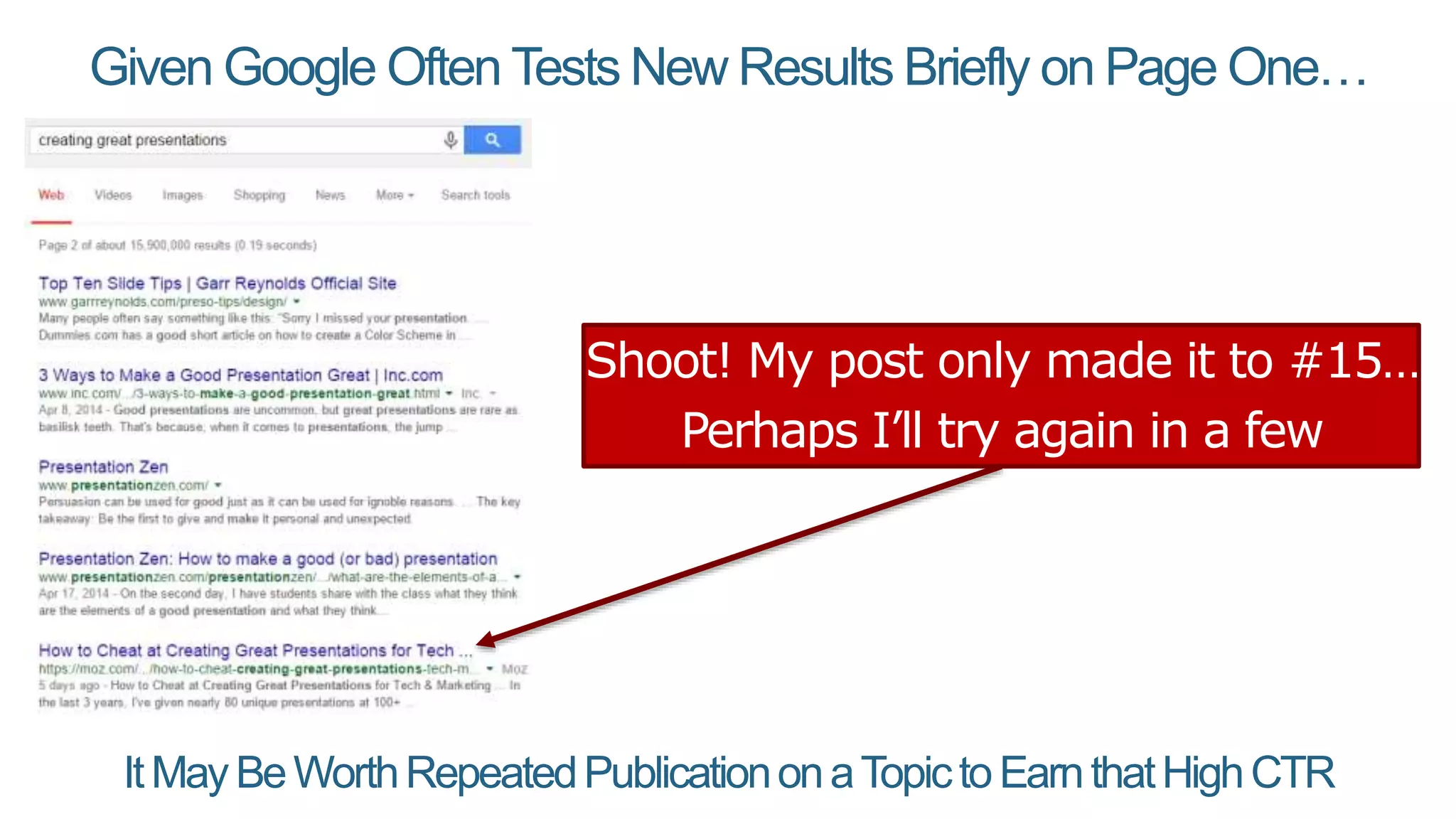
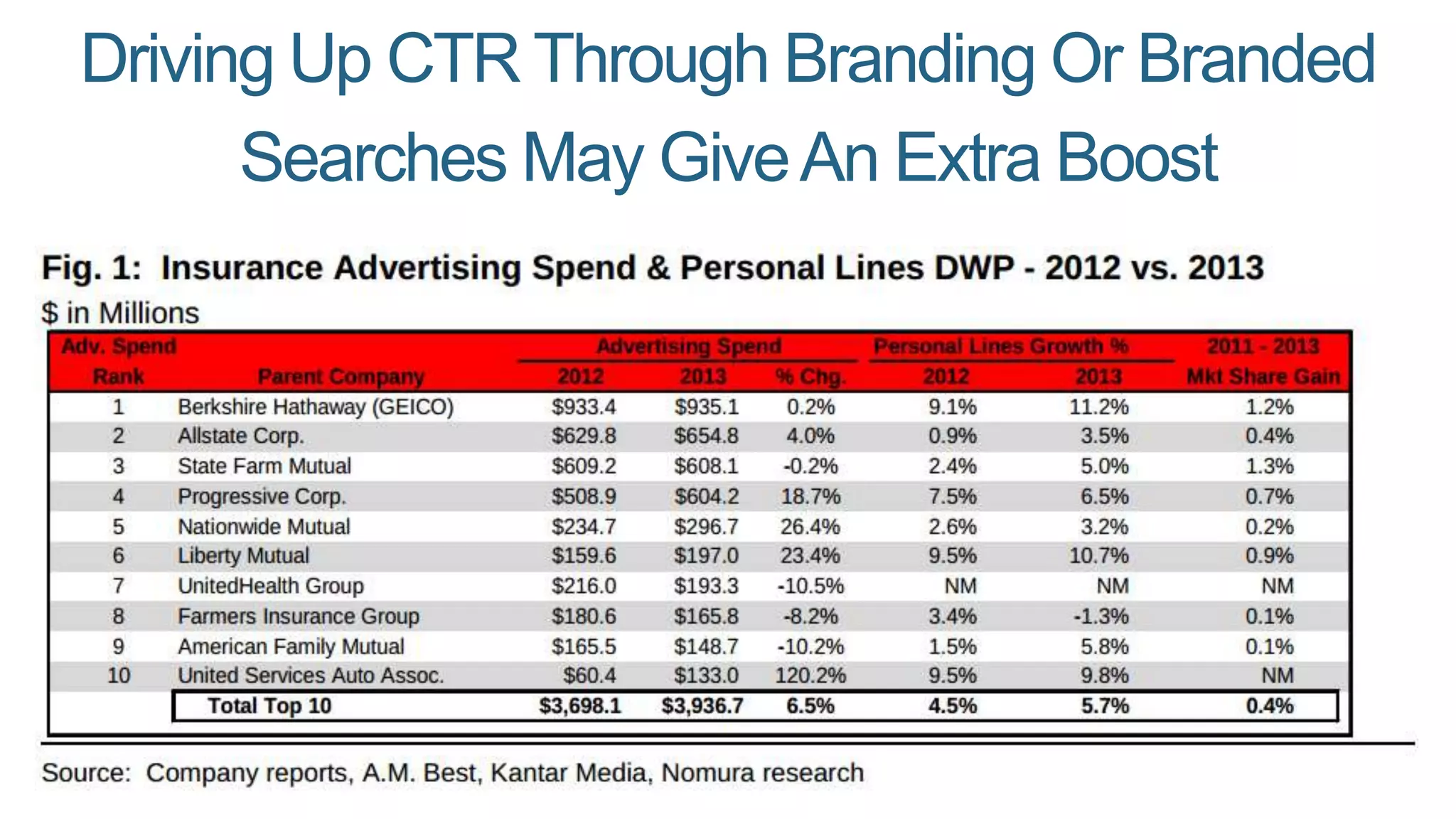
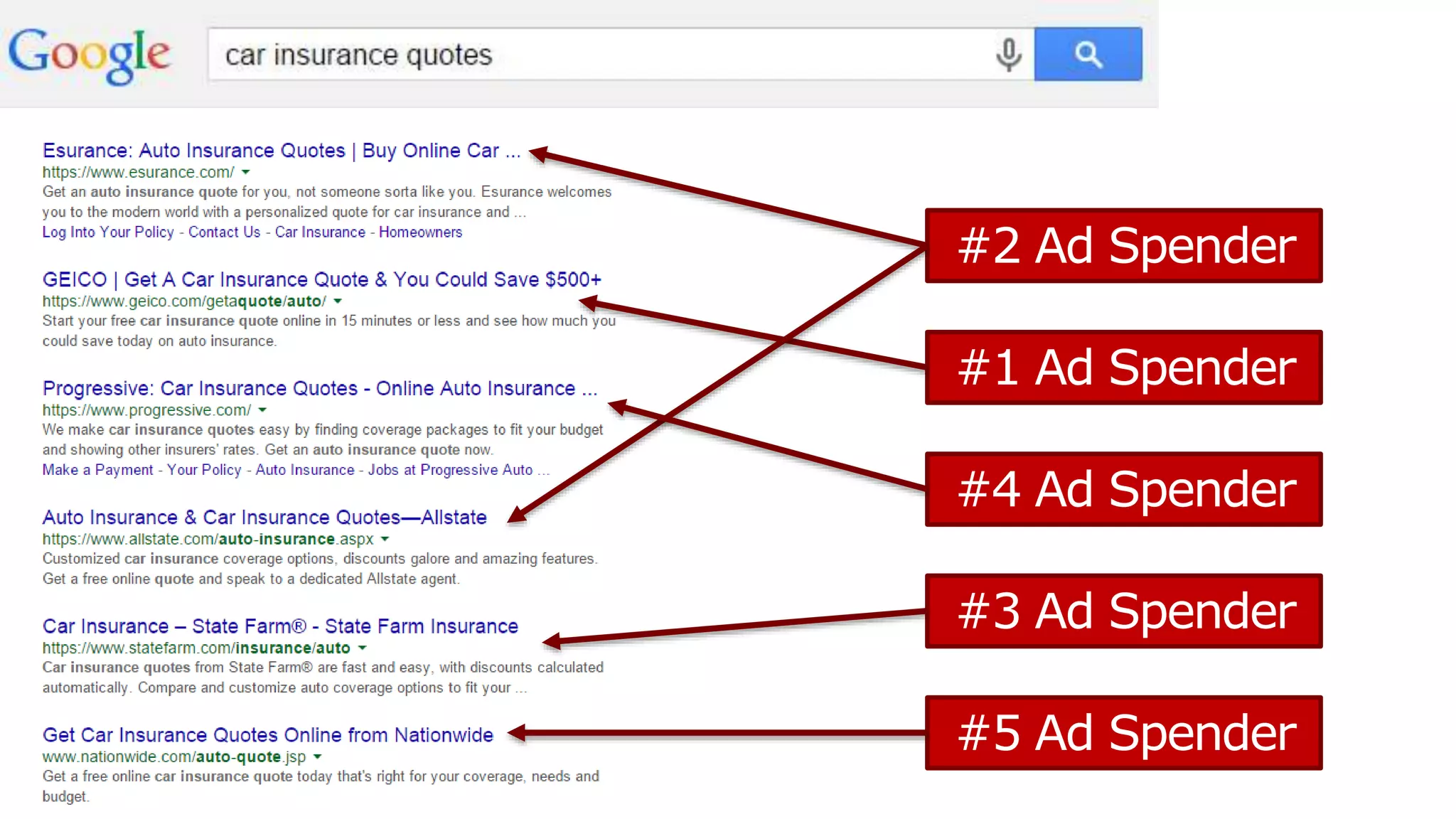
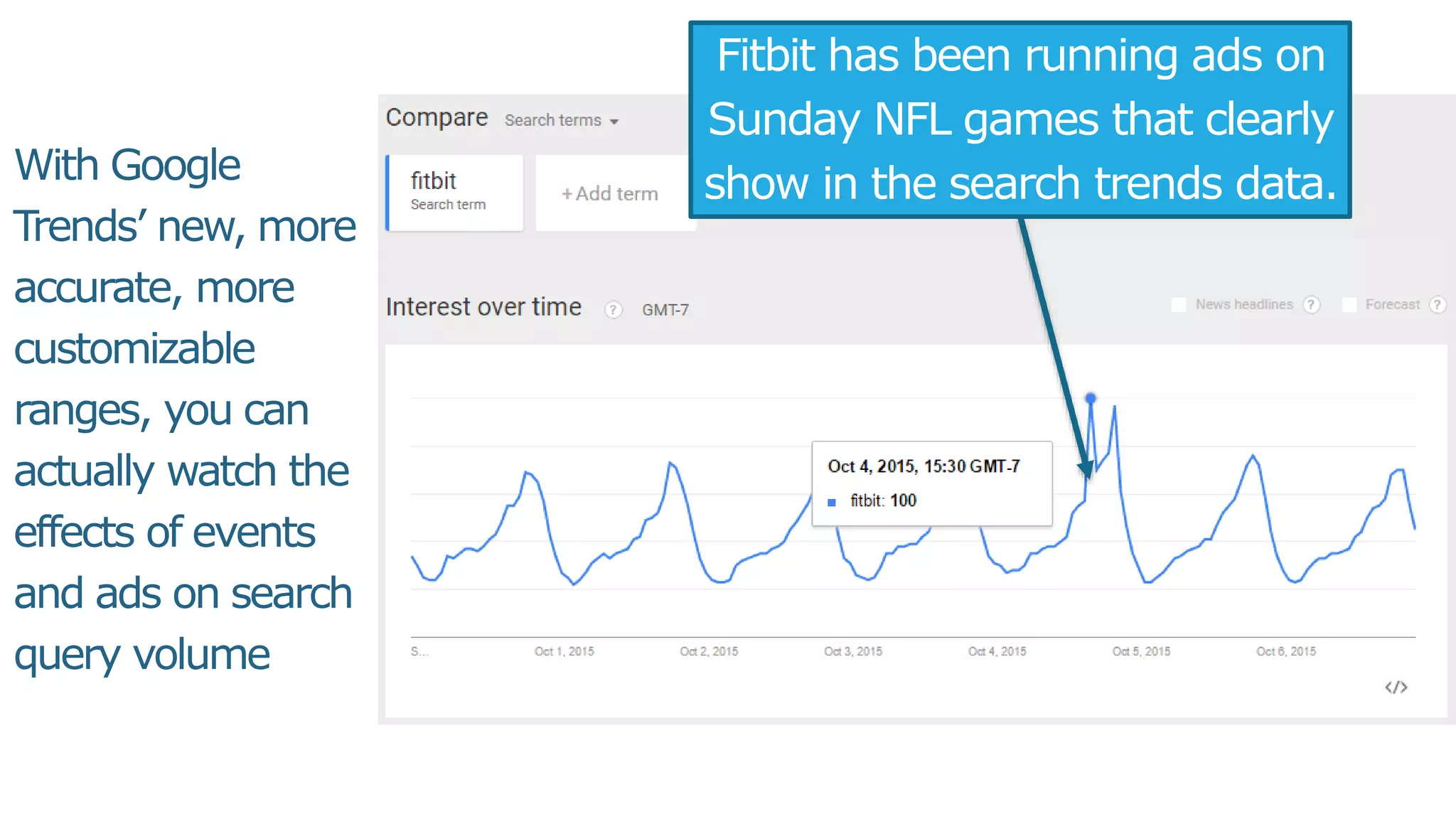
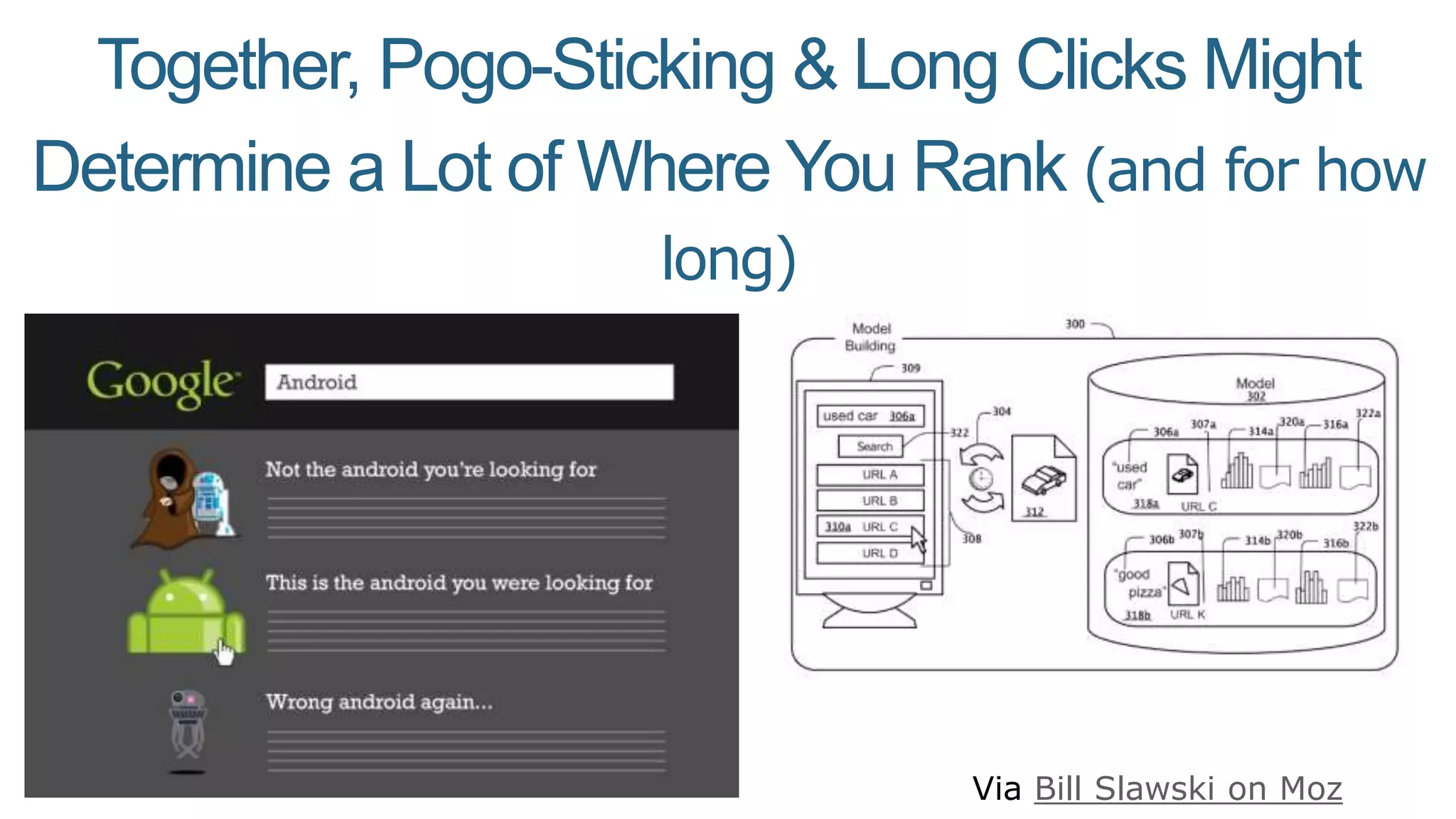
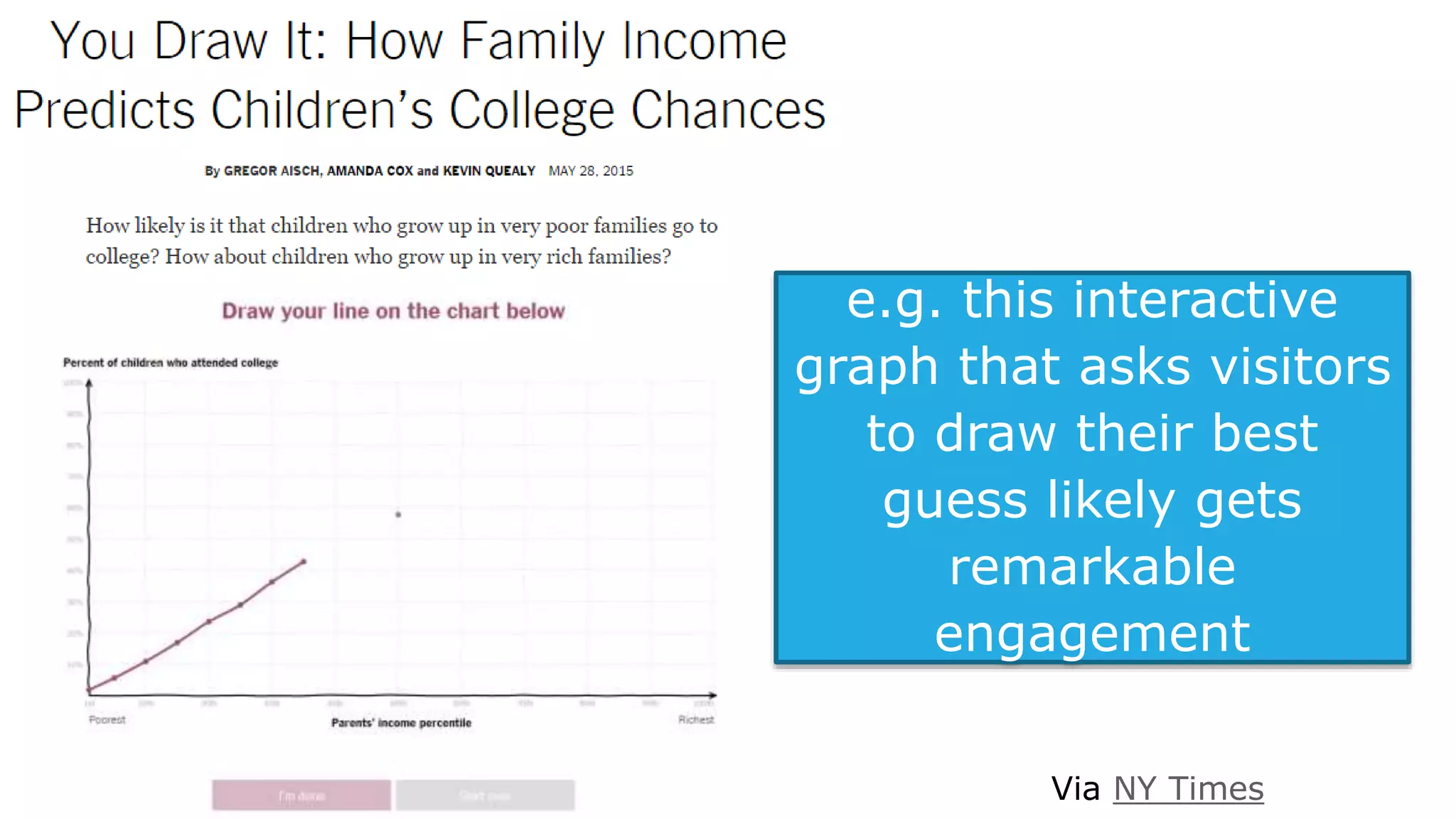
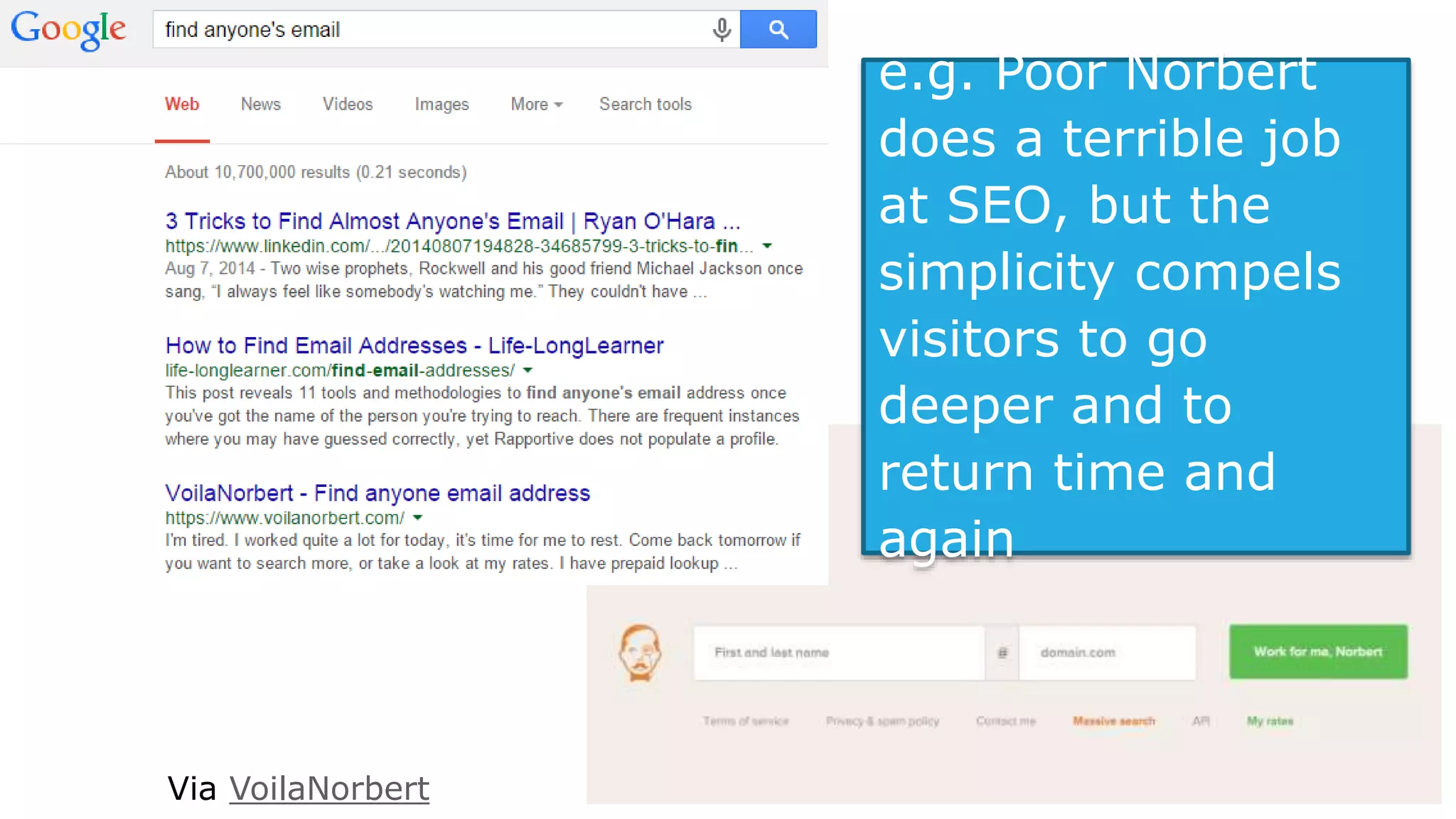
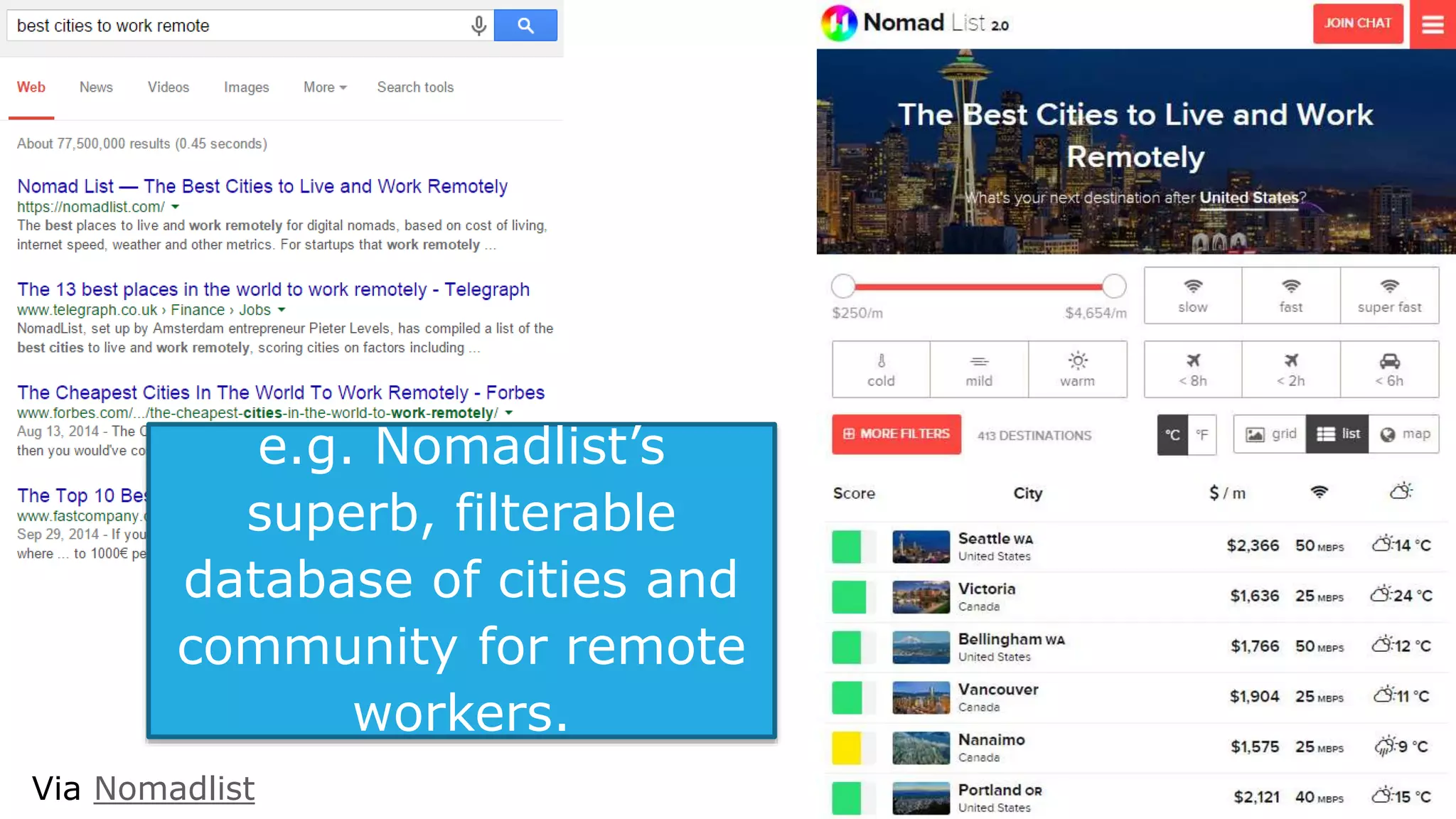
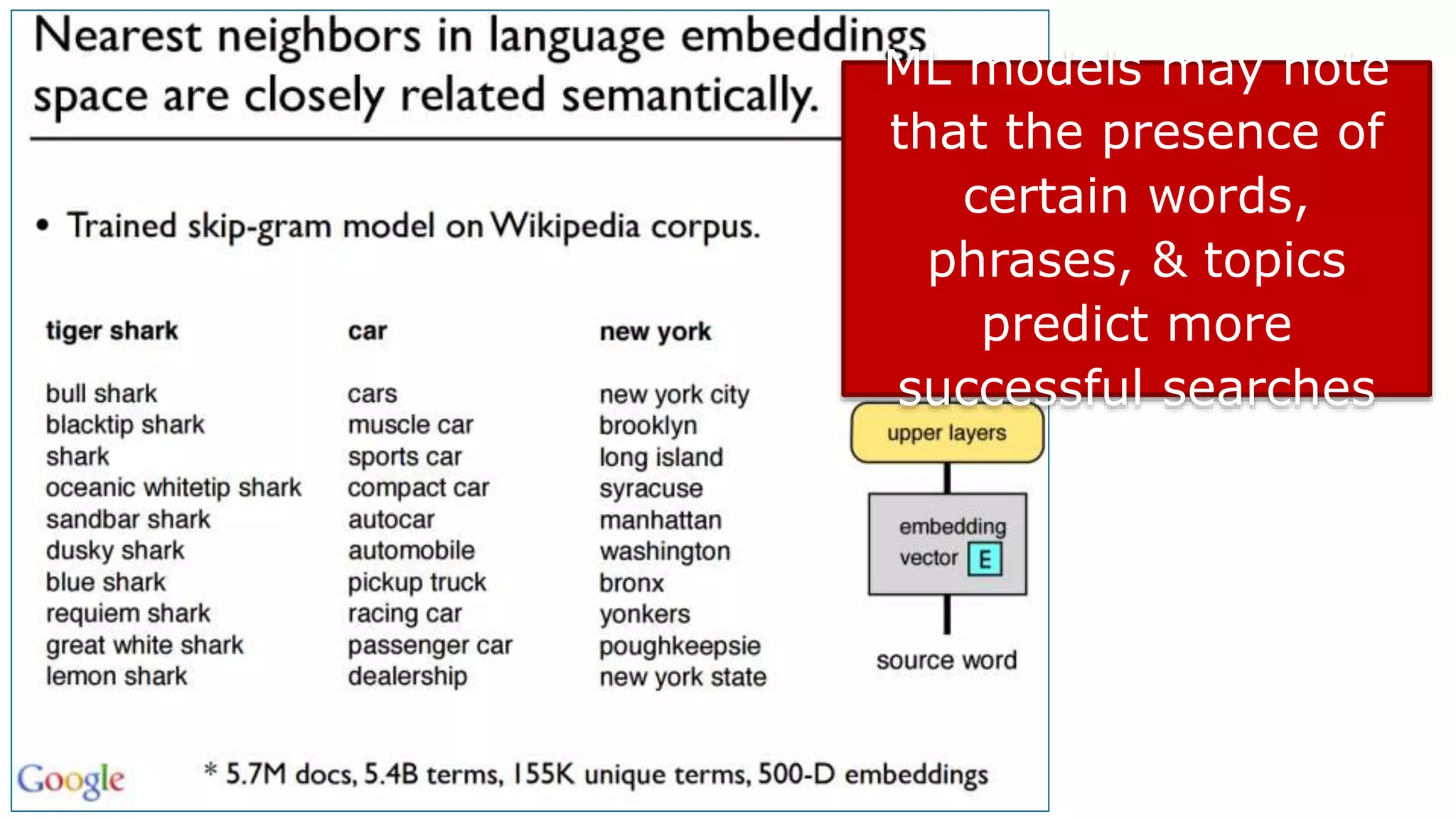
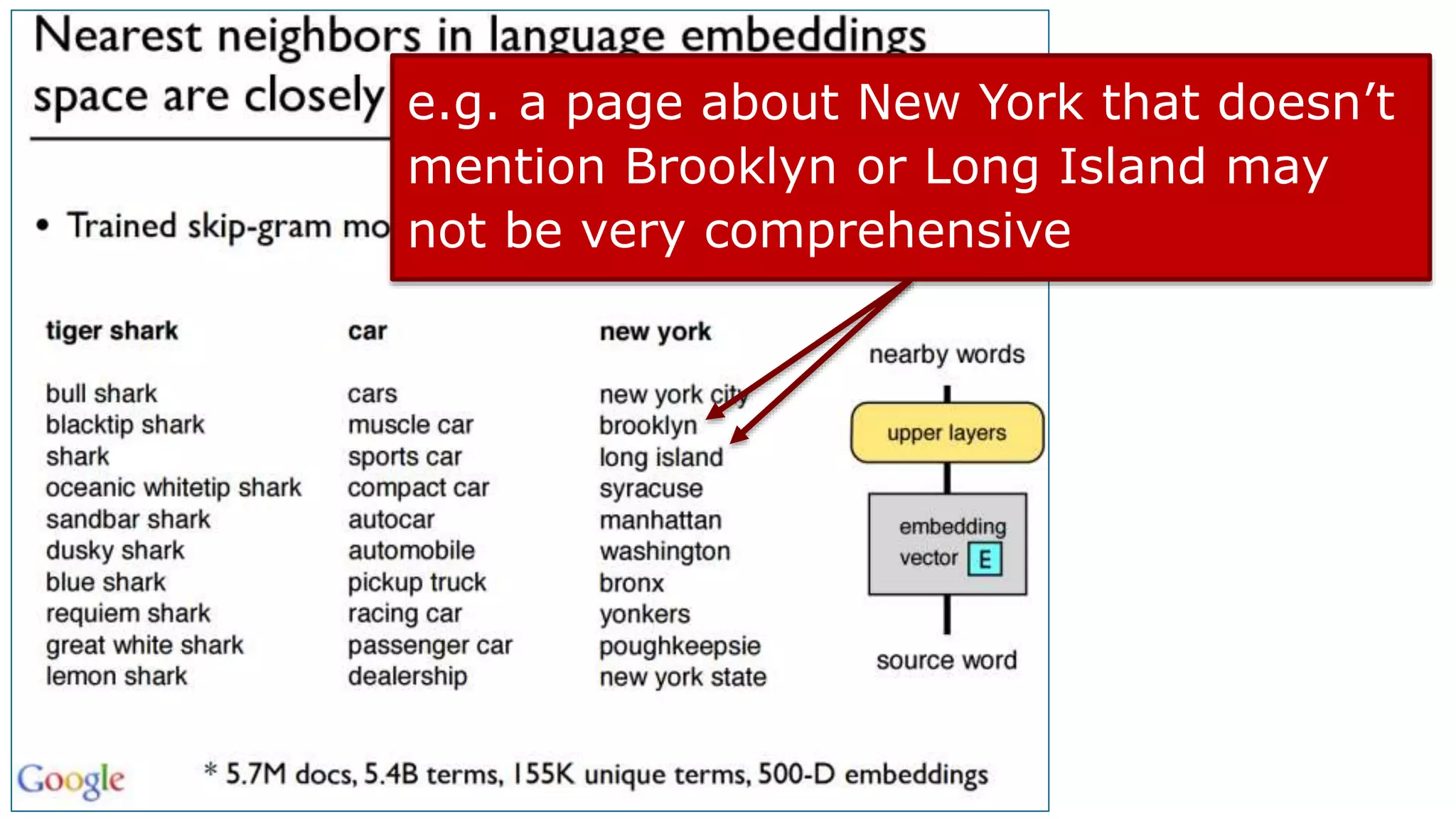
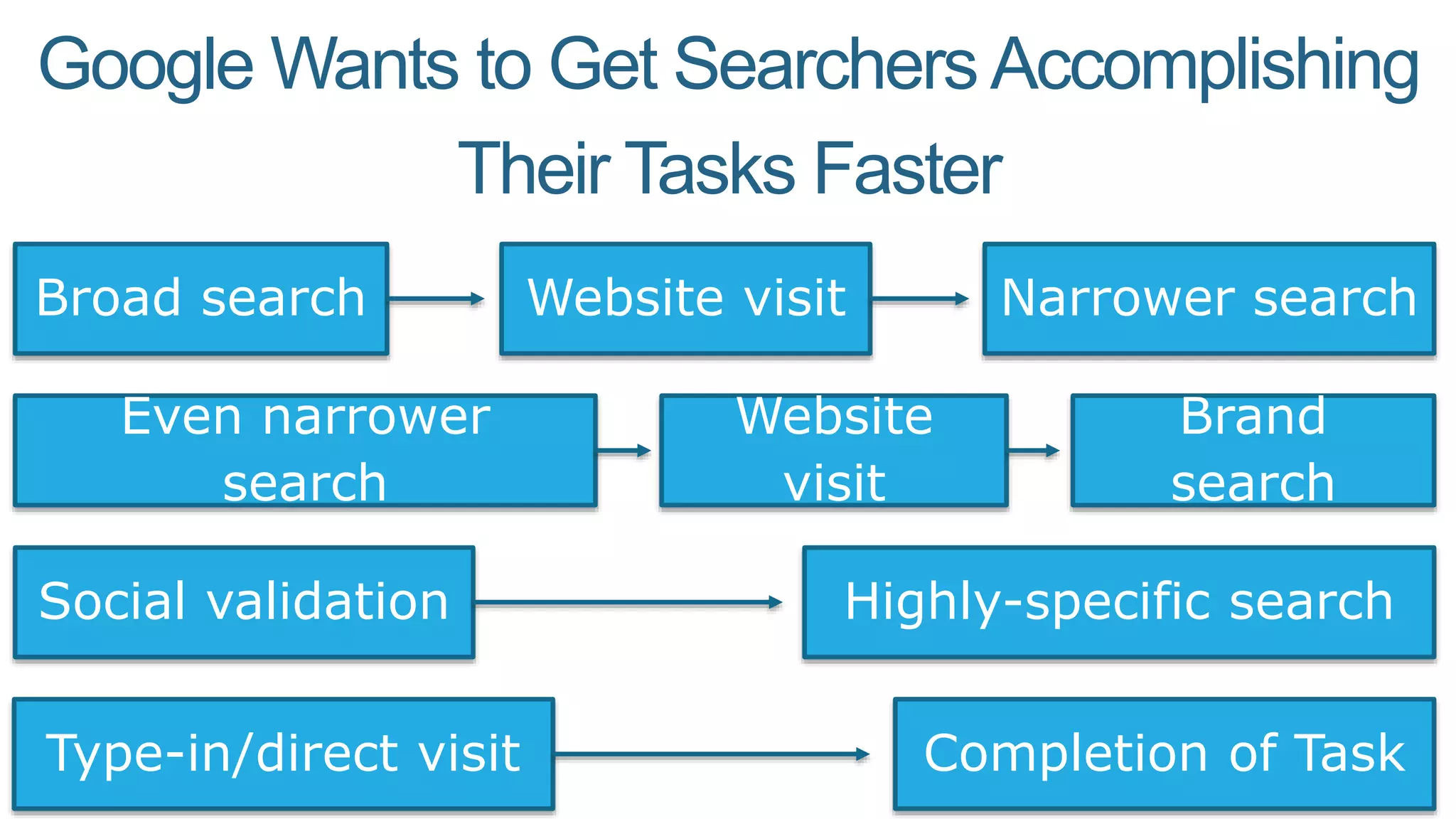
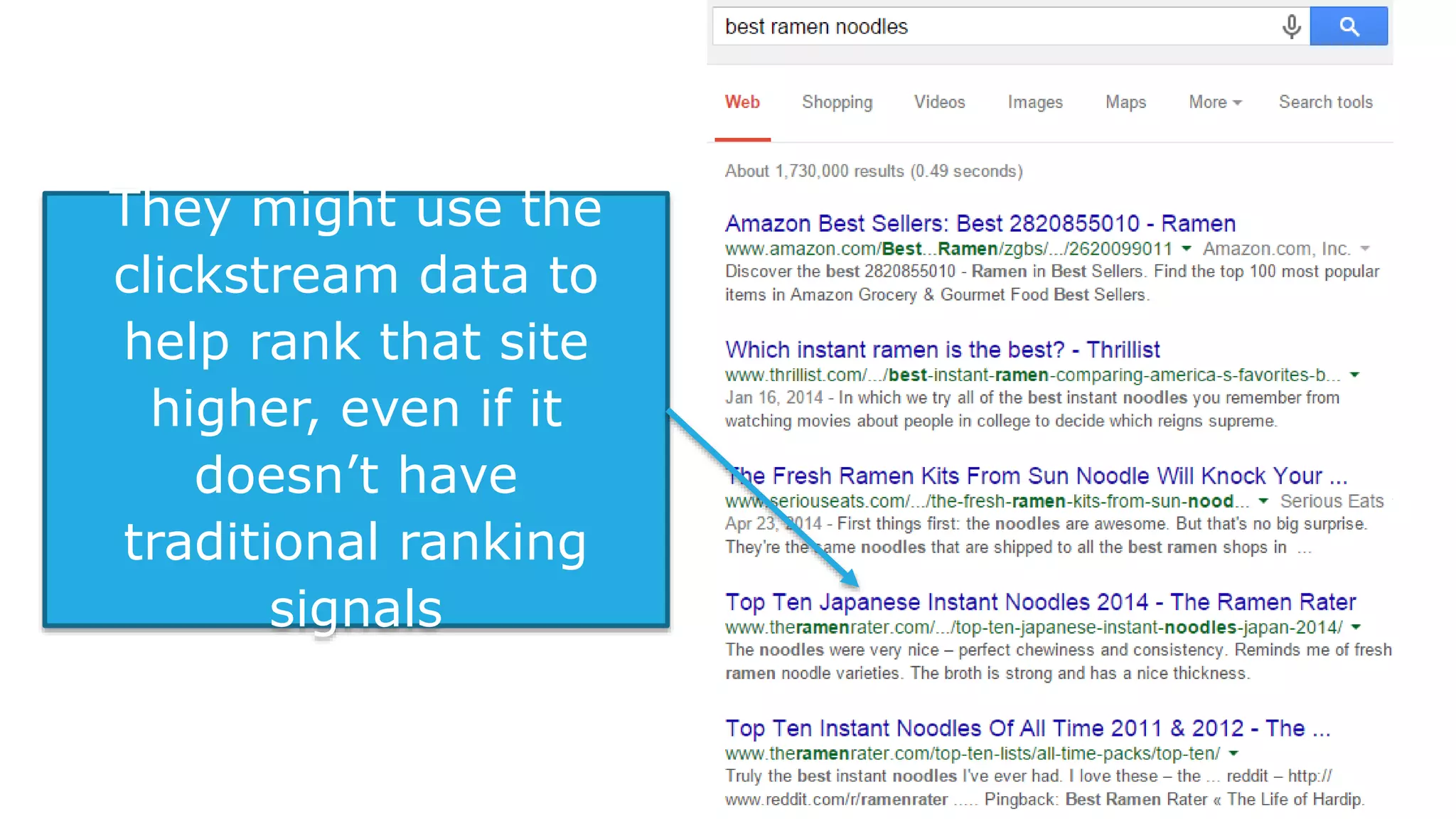
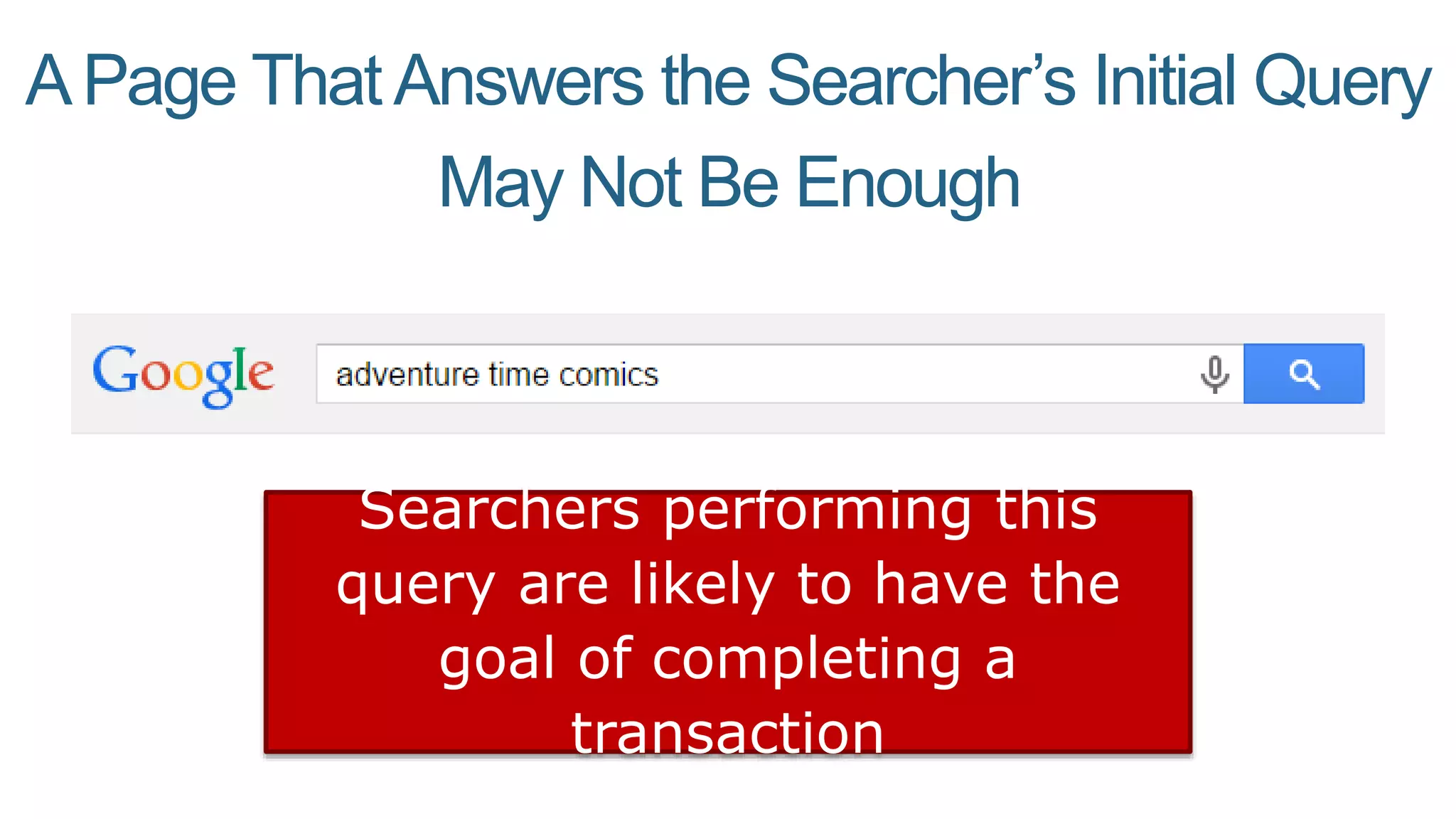
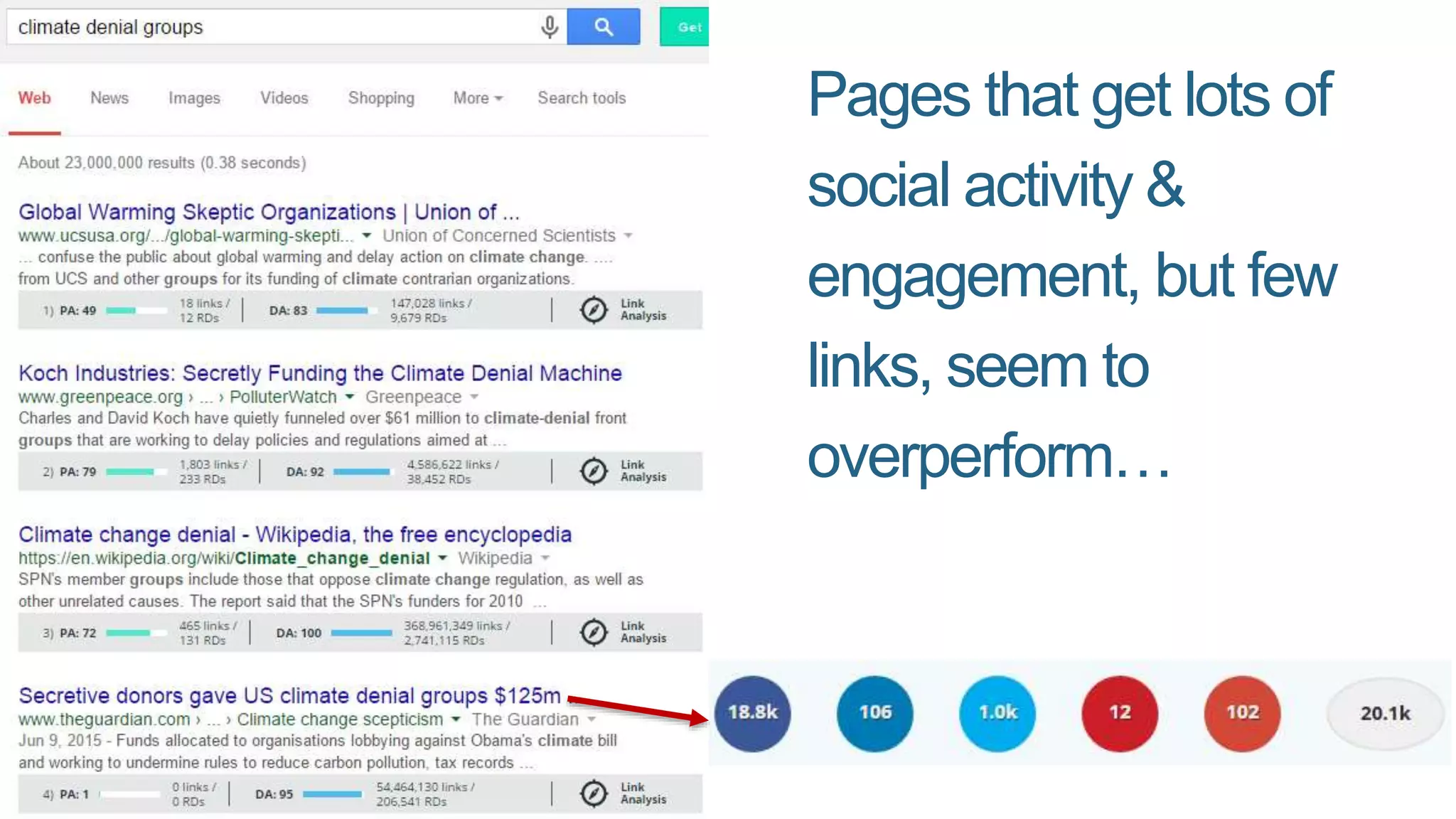
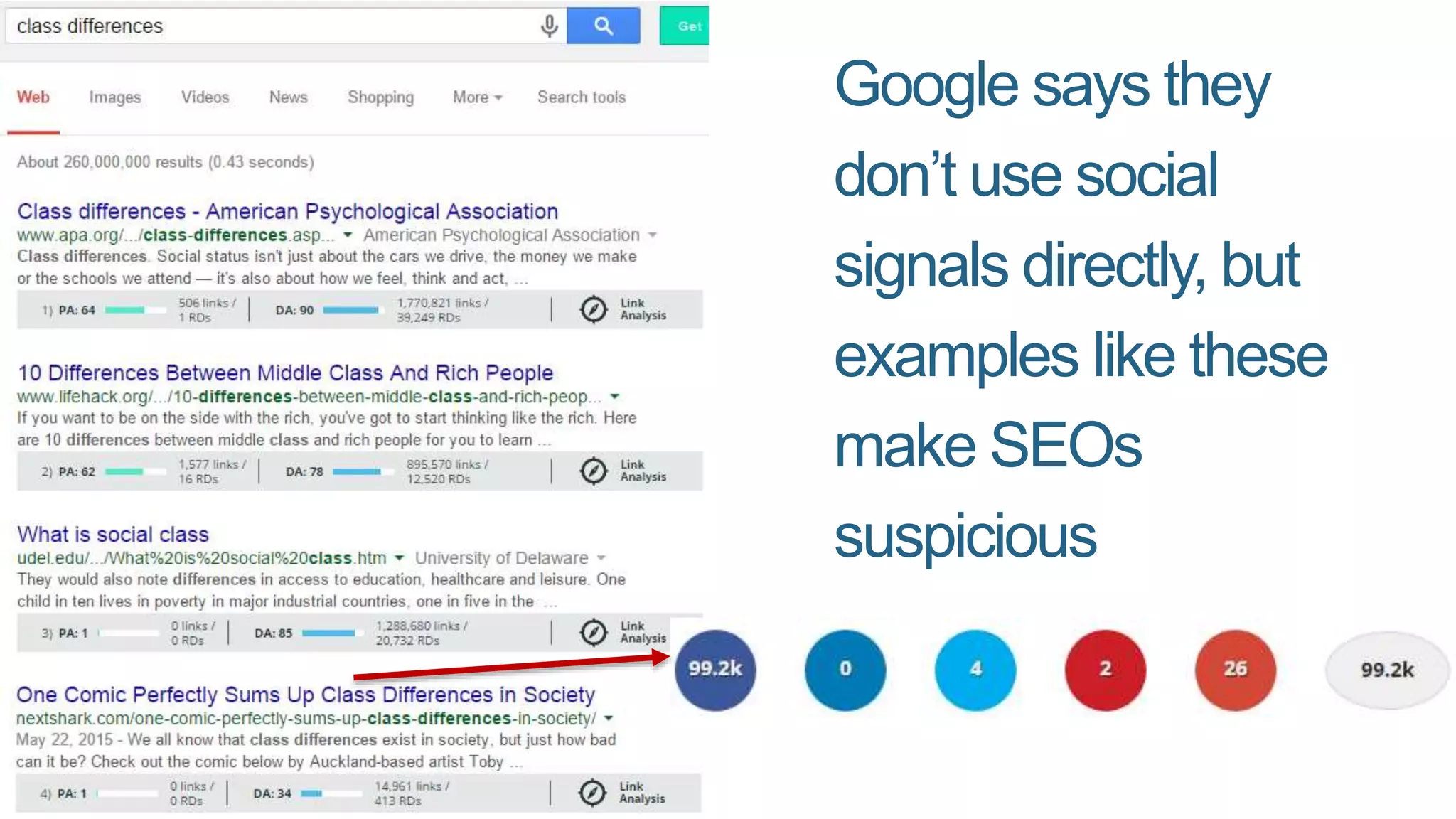
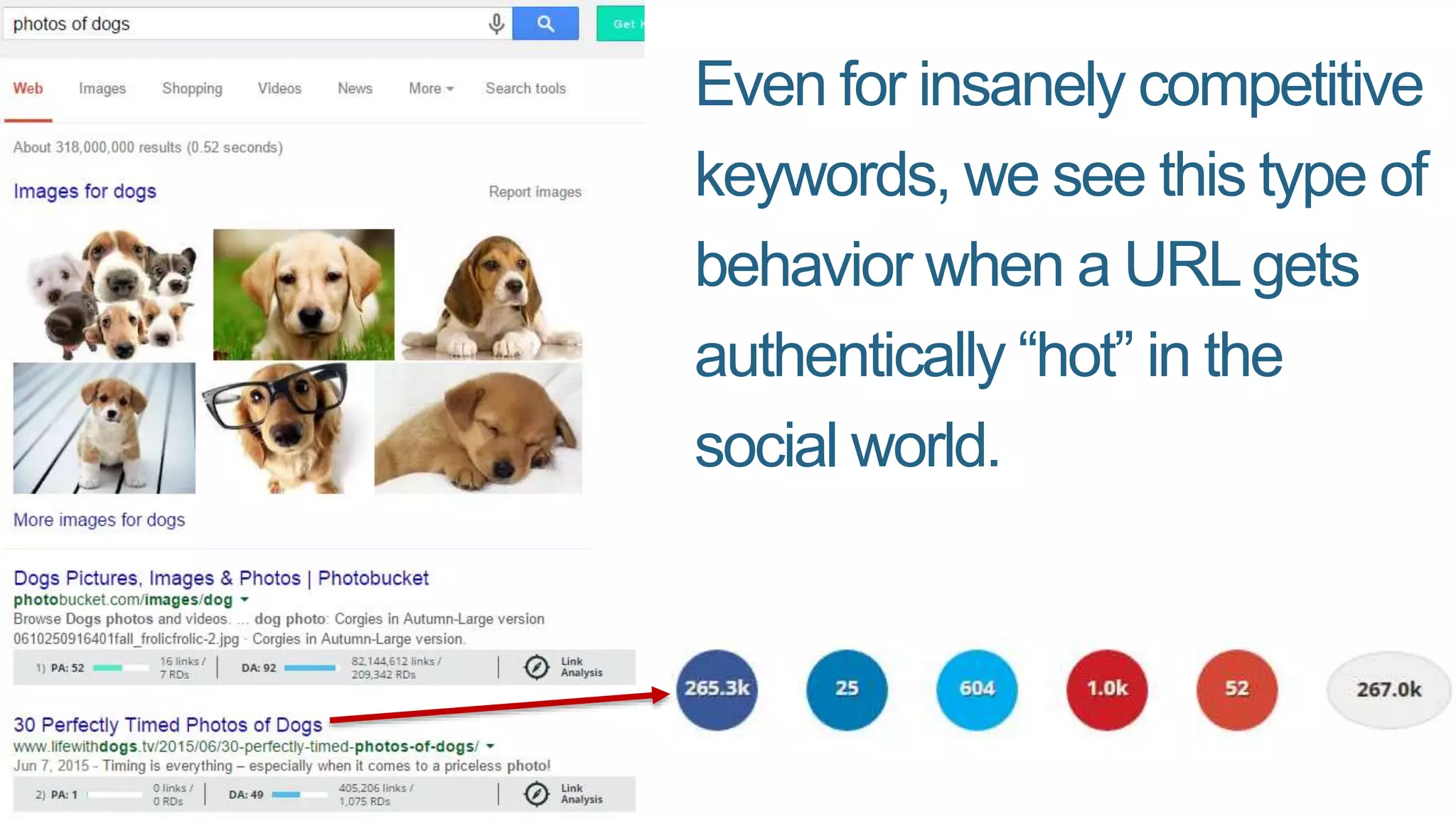
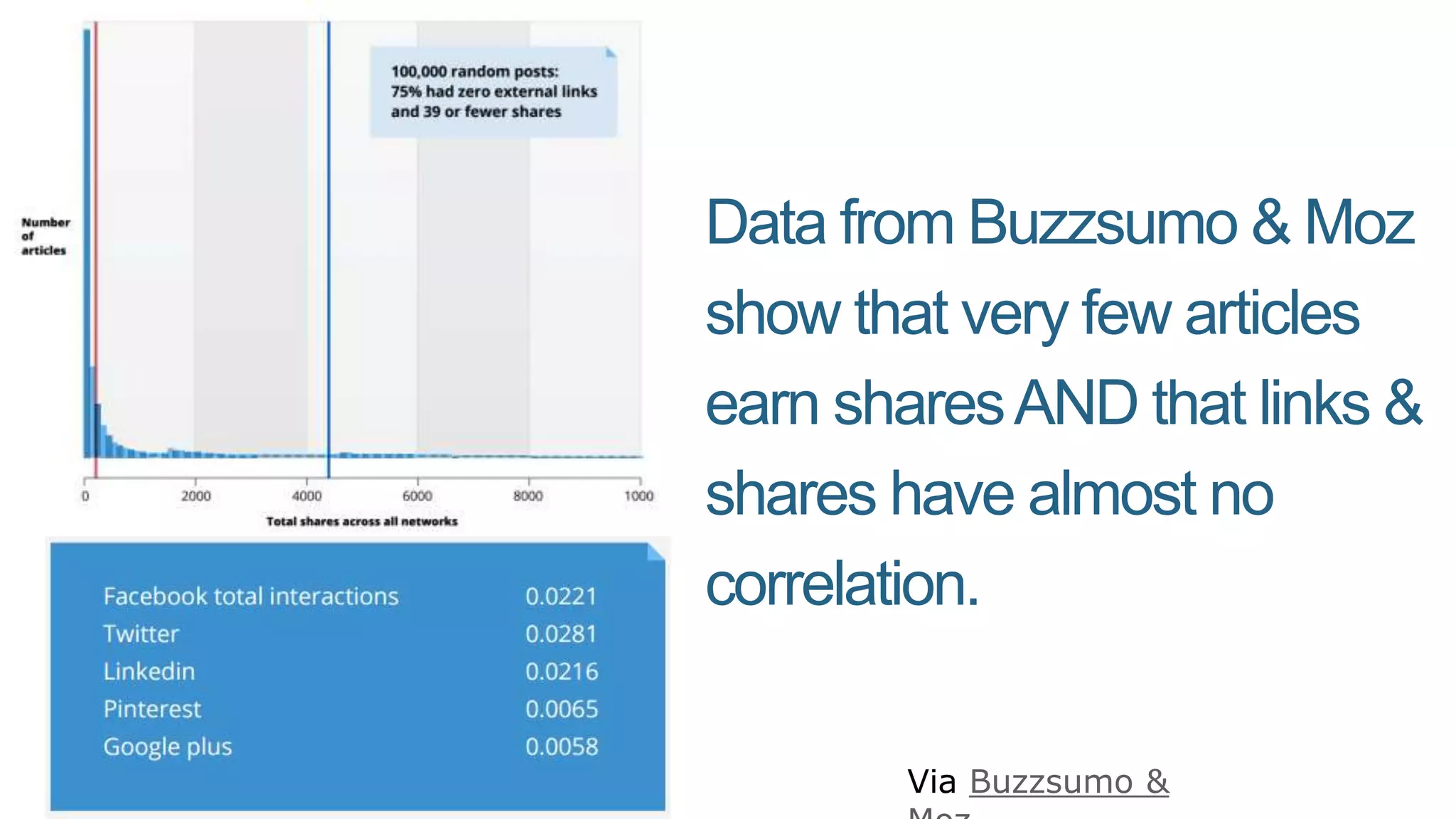
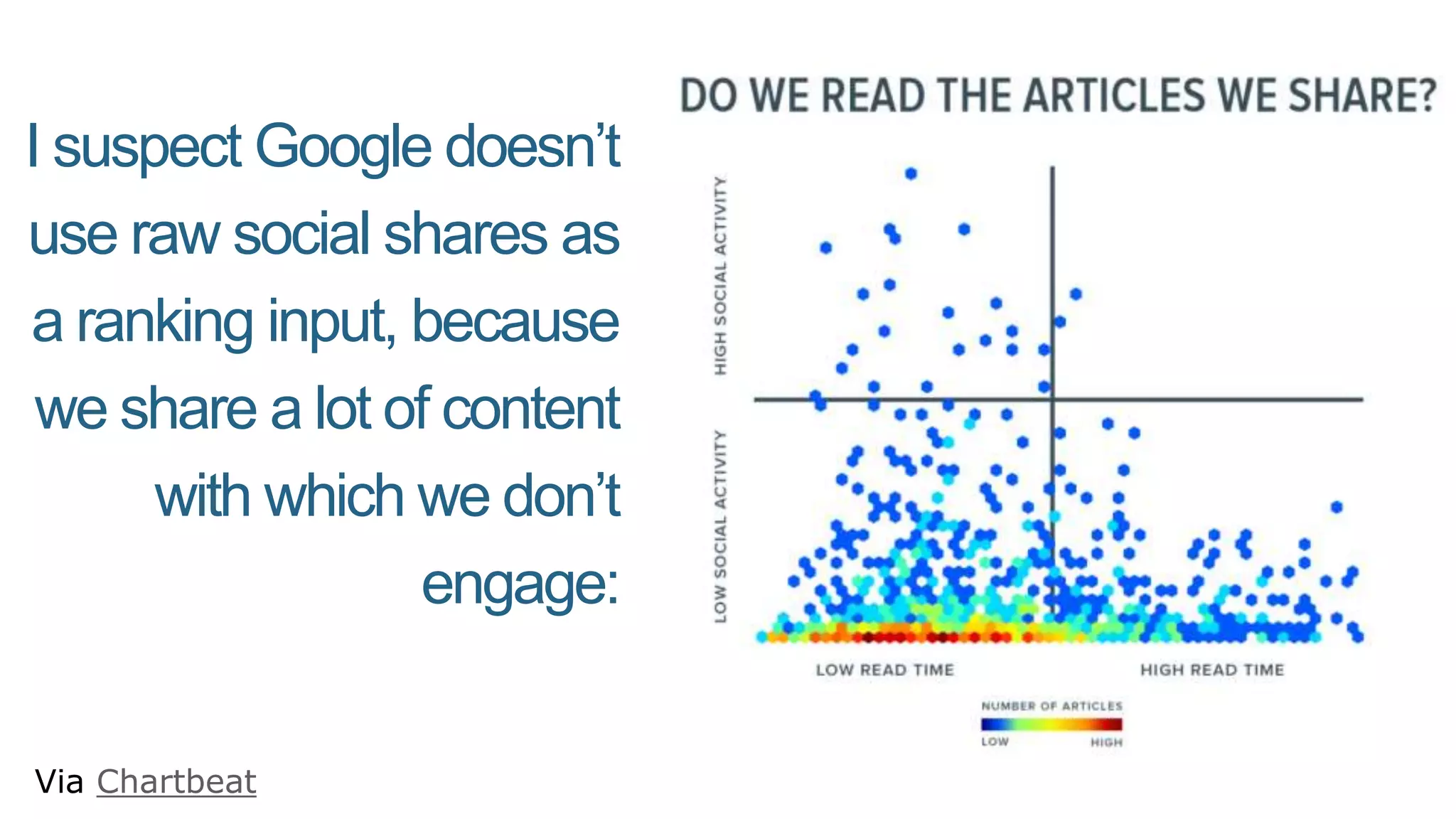
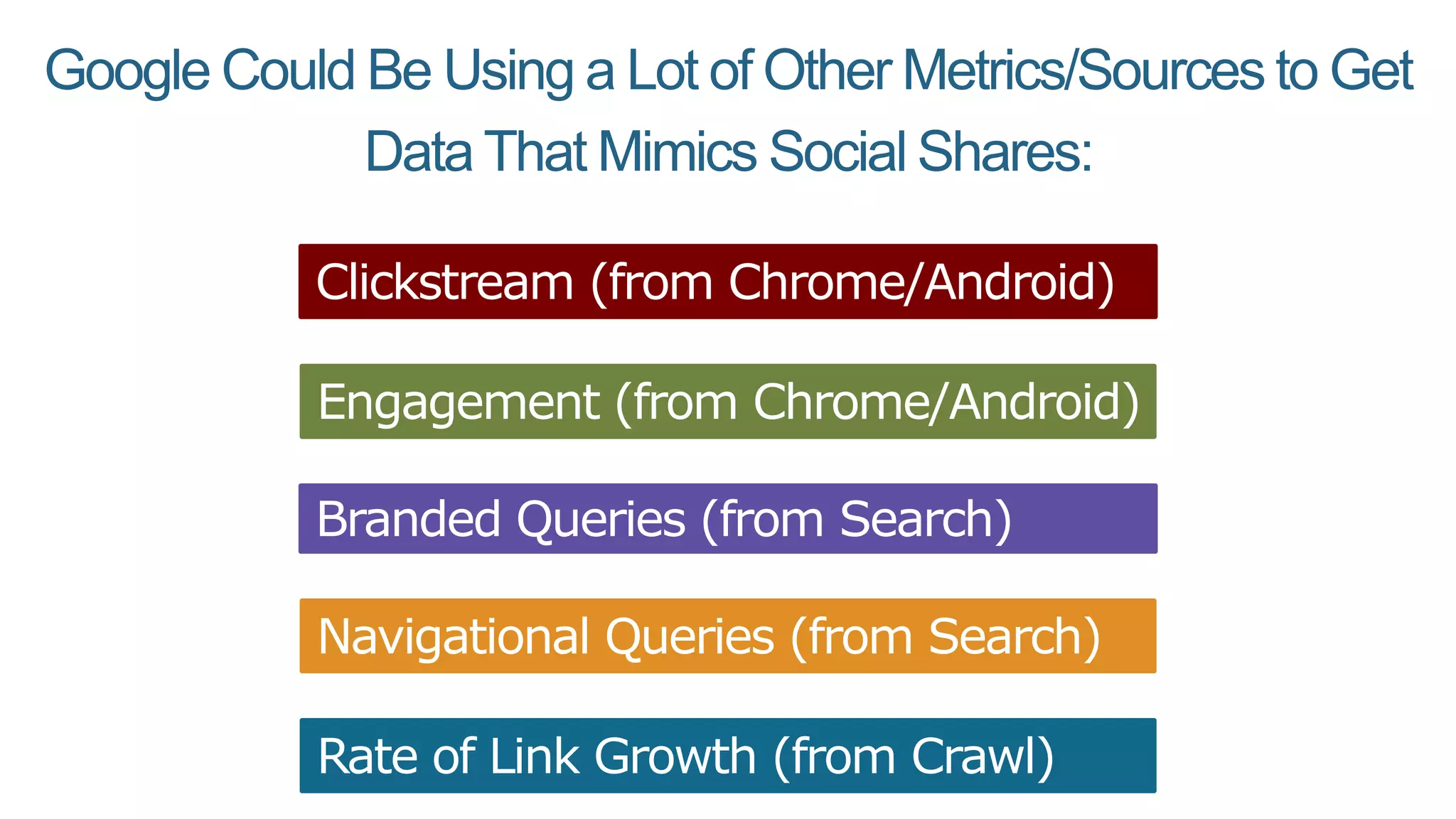
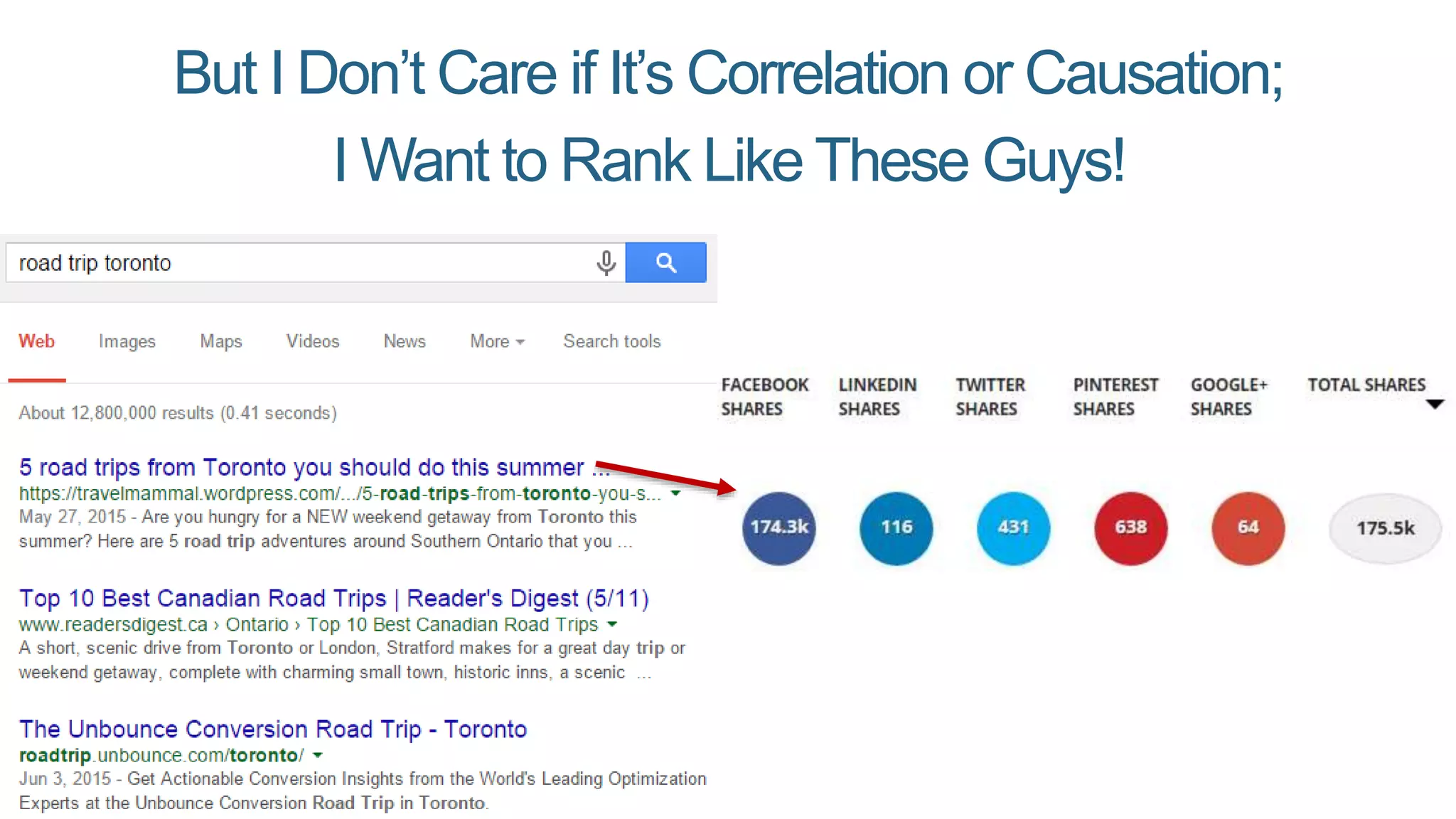
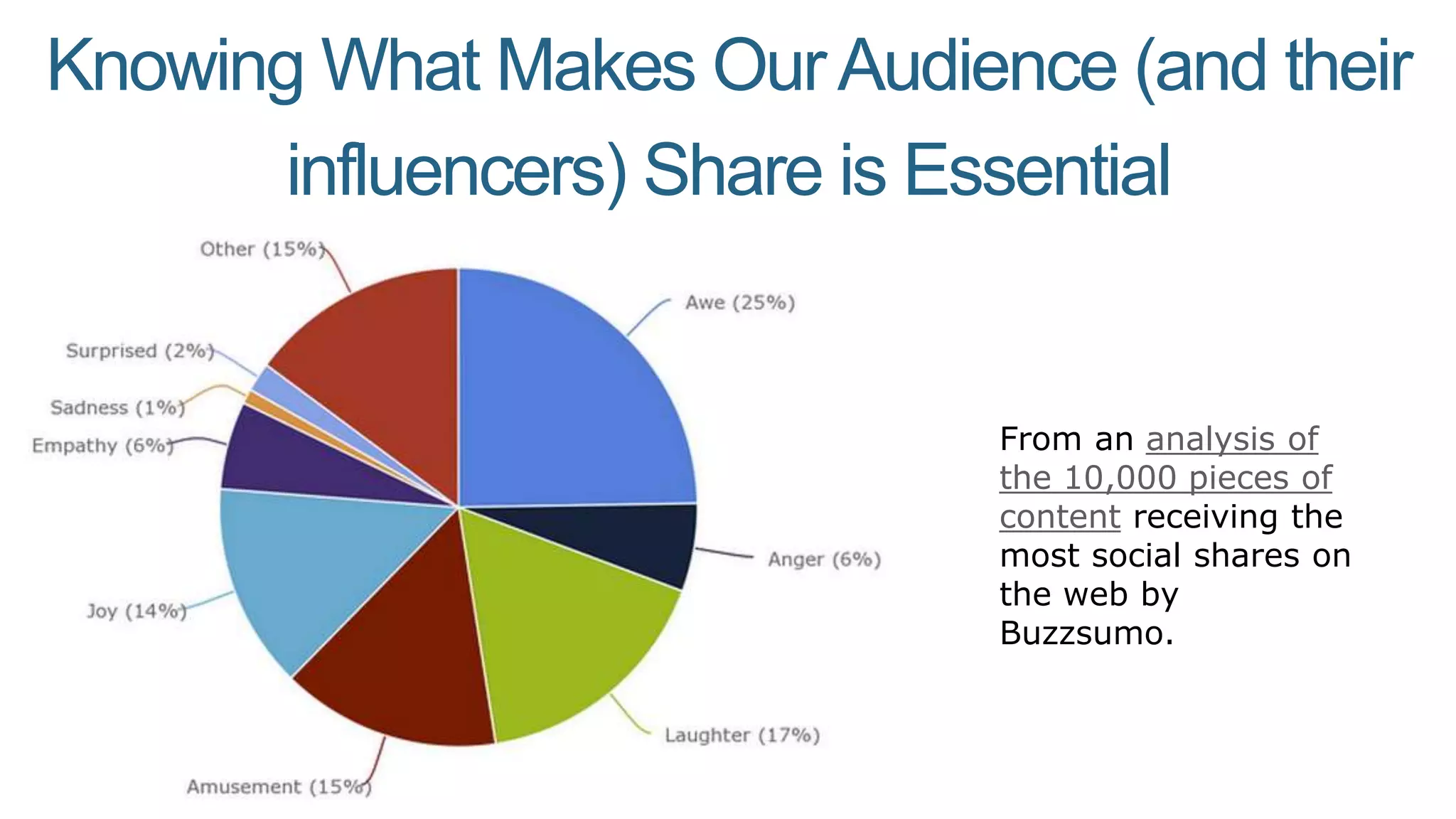
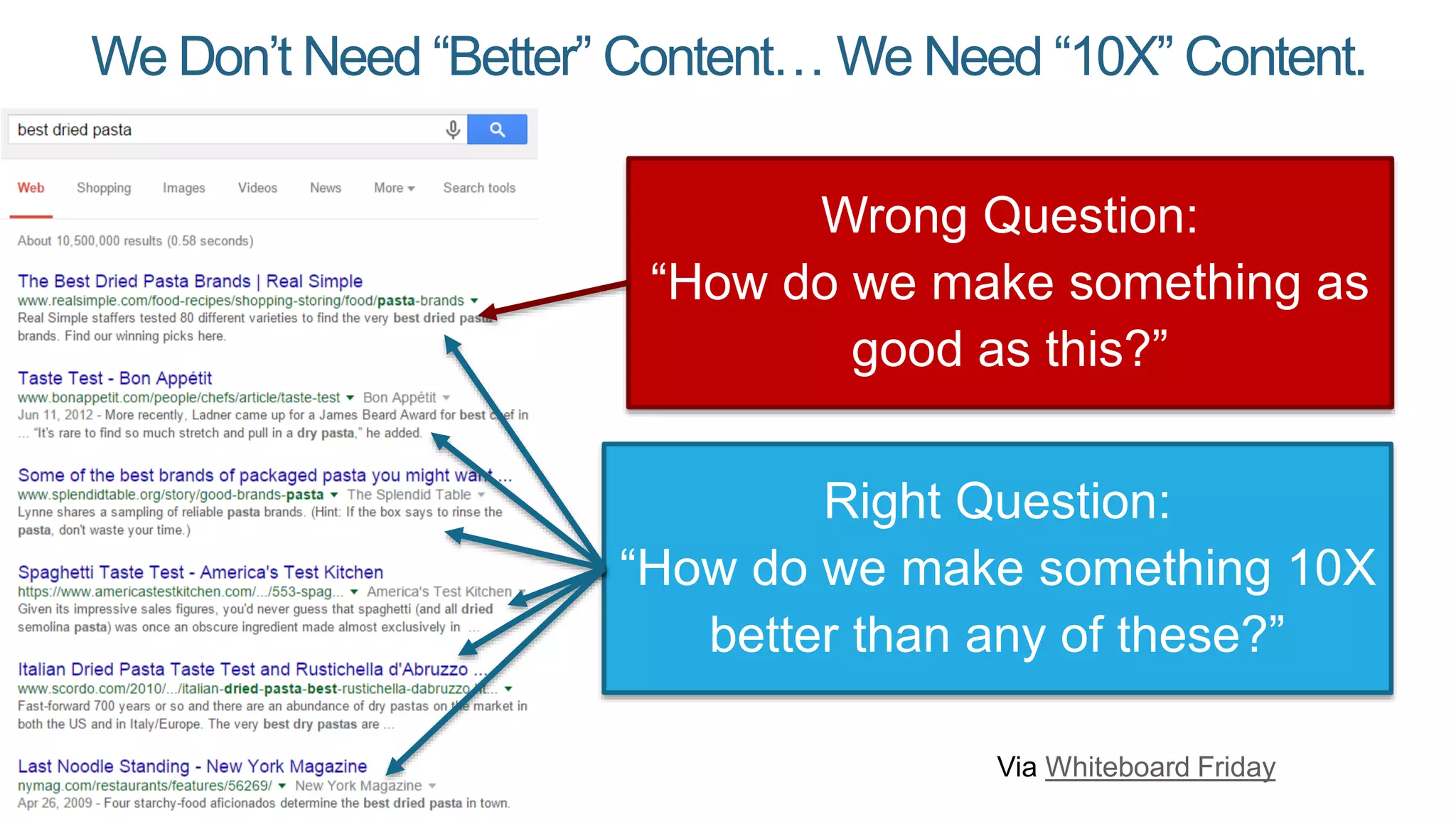
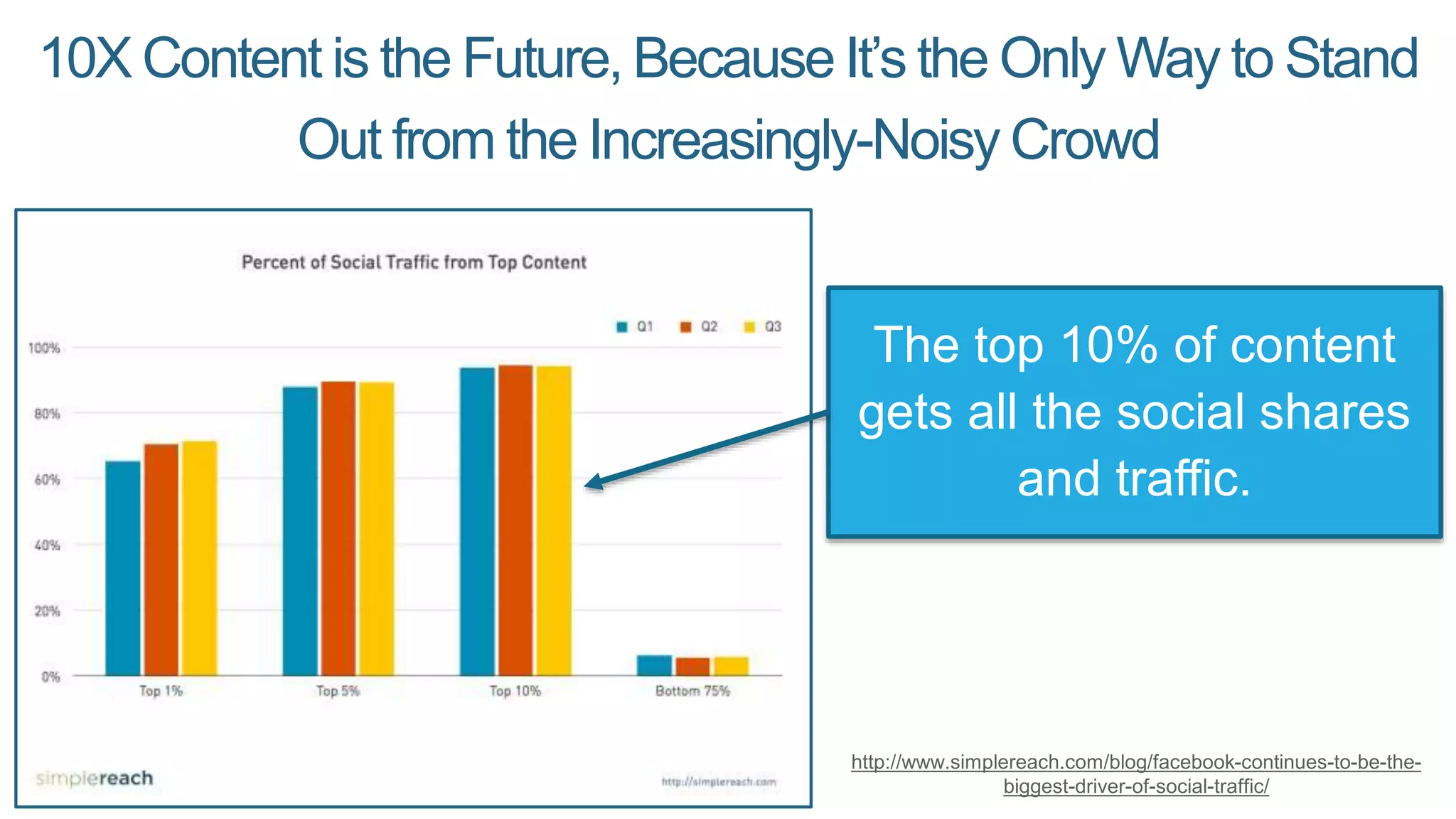
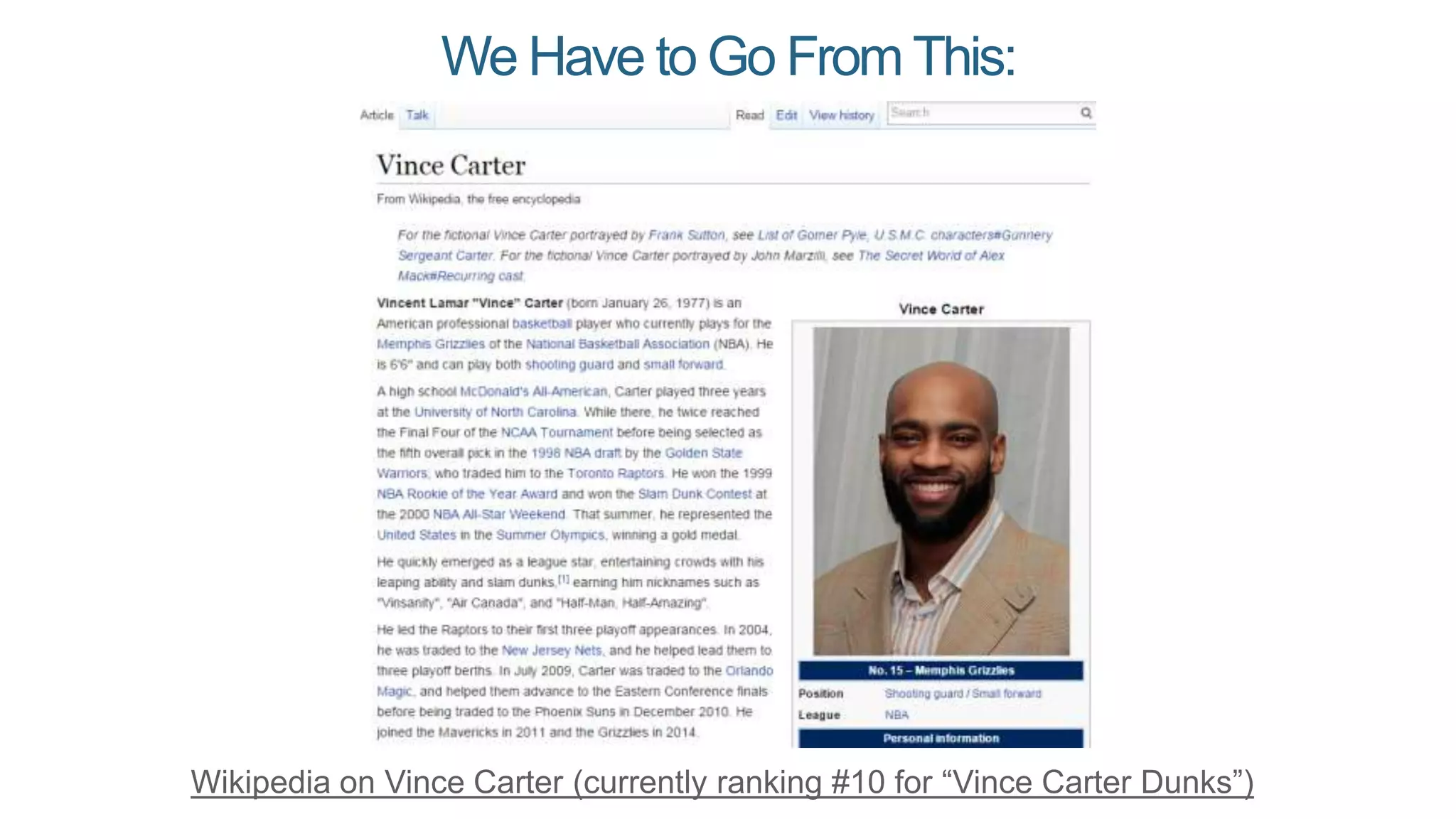
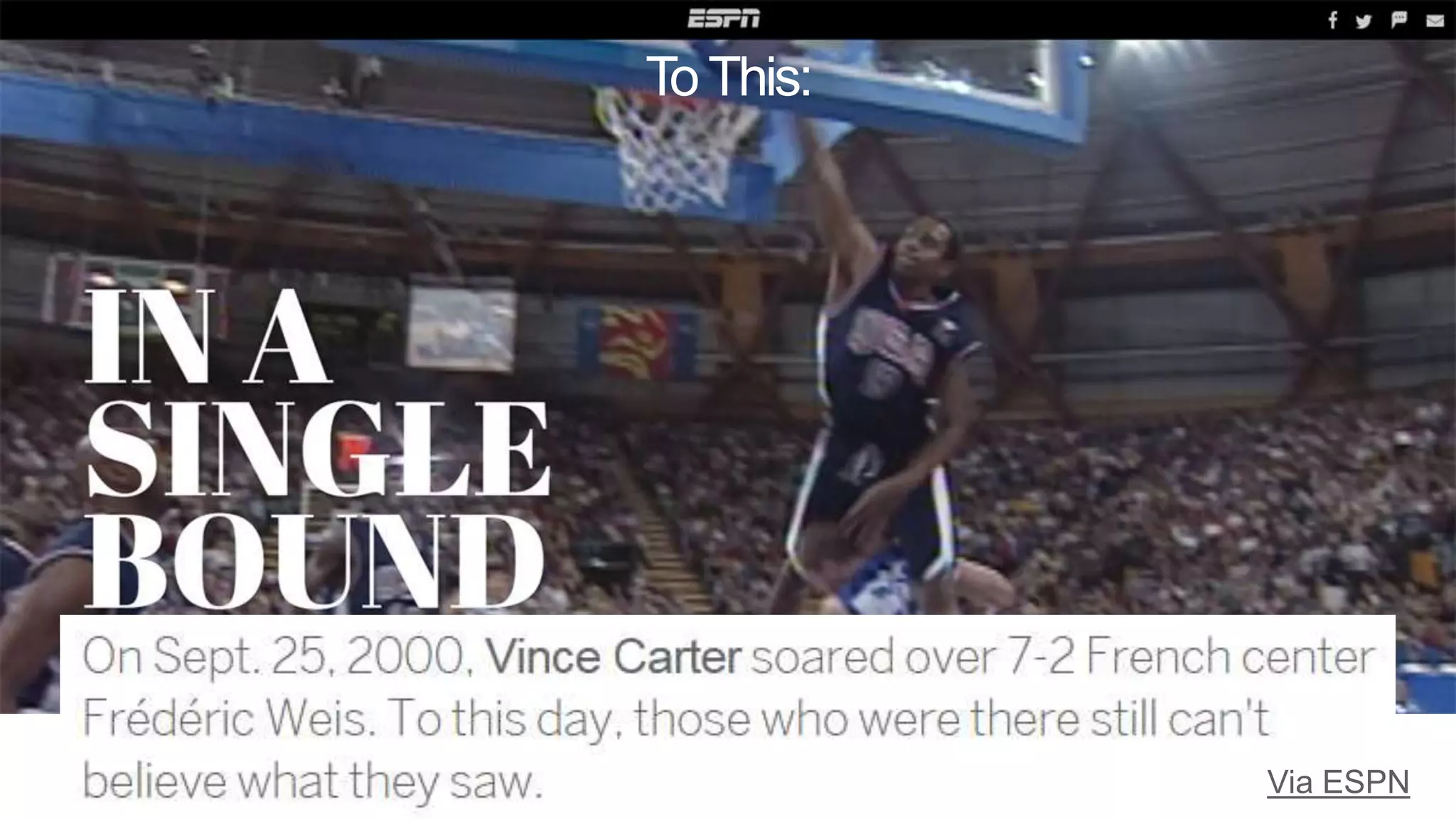
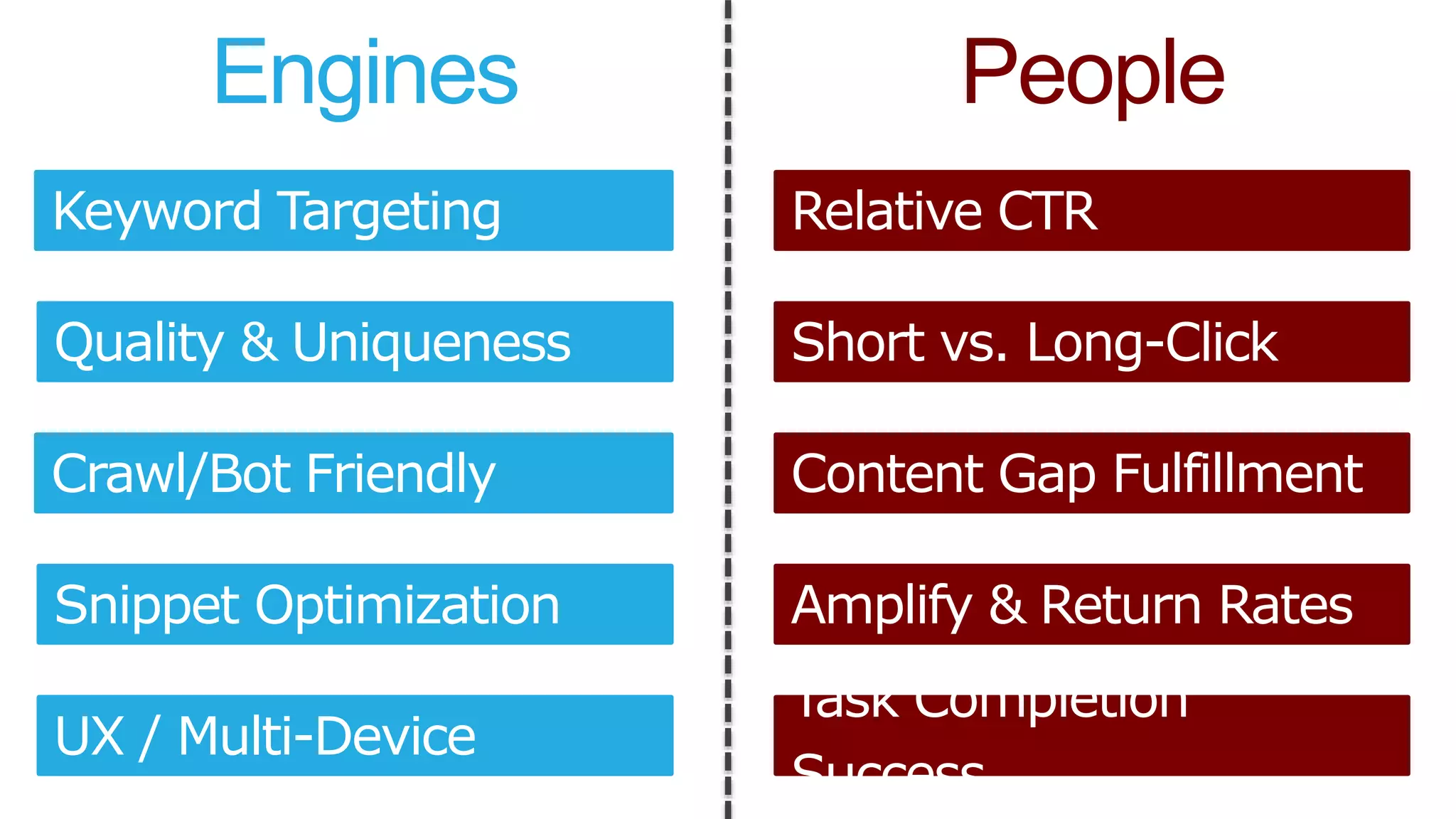
This document summarizes Rand Fishkin's presentation on SEO in a two algorithm world. It discusses how Google's search algorithm has evolved from primarily considering links to now using machine learning and user signals like click-through rates and engagement. It recommends that SEO professionals optimize for both algorithms by focusing on factors like filling content gaps, driving task completion, and creating content that earns loyalty and amplification rather than just links. The future of SEO involves balancing traditional on-site optimization with a new approach focused on searcher outputs and engagement.