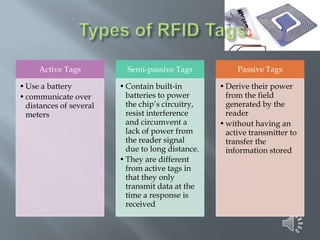
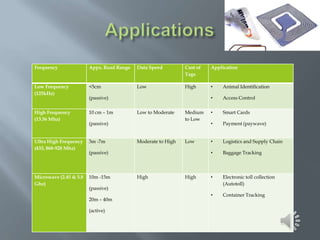
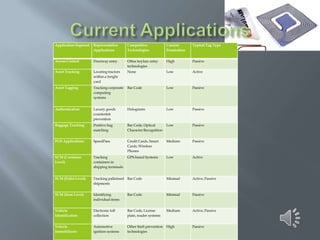
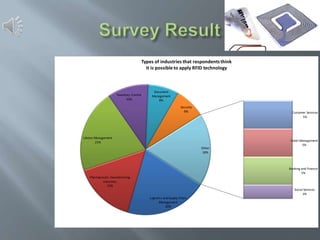
The document discusses RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology. It provides information on the basic components of an RFID system including RFID tags/inlays, readers/antennas, and application software. It describes the three main types of RFID tags - passive, semi-passive, and active - and gives examples of their typical read ranges and uses. The document also presents the results of an RFID survey, showing that respondents thought RFID could be applied most in library management, logistics/supply chain management, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Overall, the document provides an overview of RFID technology and its applications.