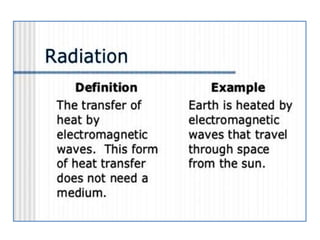
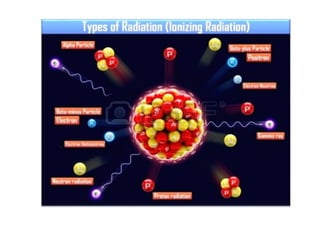
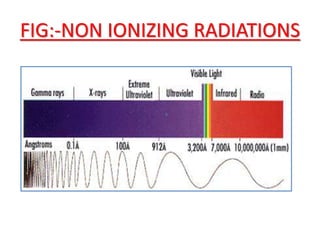
The document discusses the application of different types of radiation in plant science, focusing on their definitions and effects on plant growth and development. It categorizes radiation into ionizing and non-ionizing types, detailing how ultraviolet radiation can negatively impact seed growth, plant cell viability, and reproduction. References are provided for further reading on the topic.