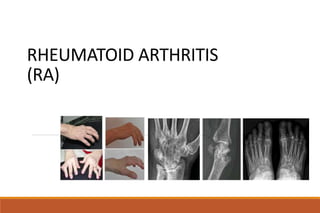
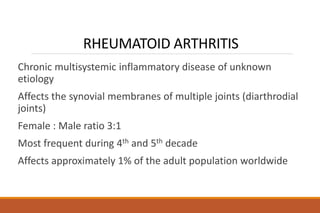
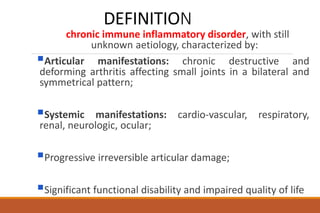
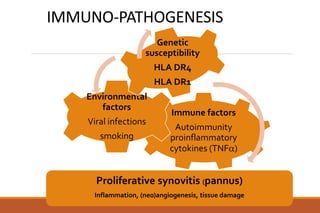
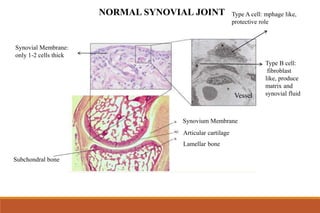
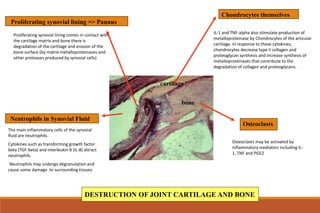
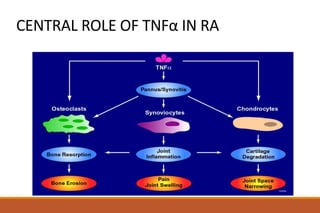
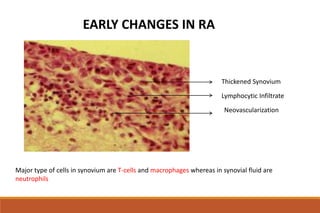
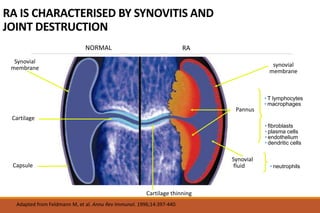
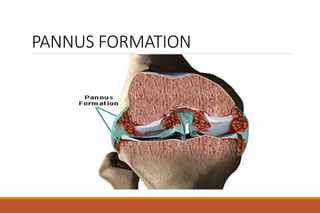
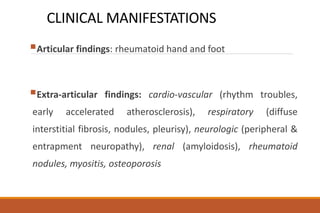
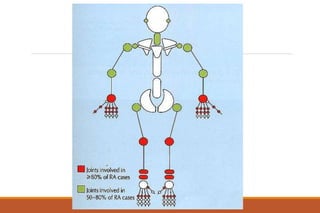
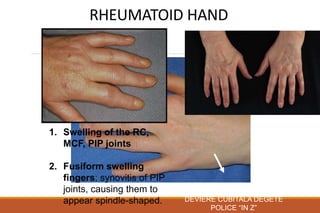
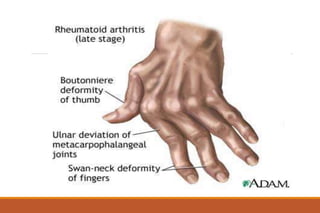
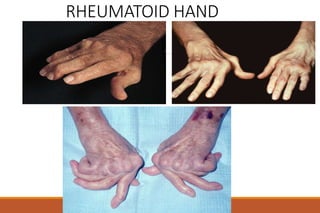
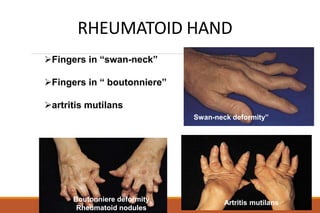
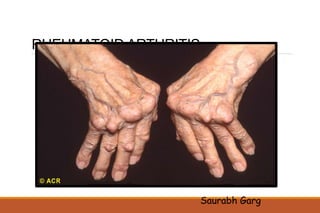
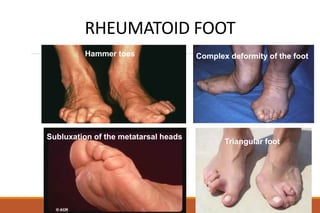
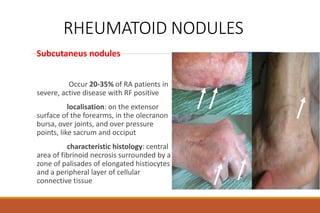
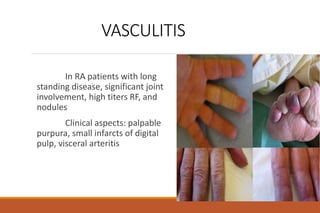
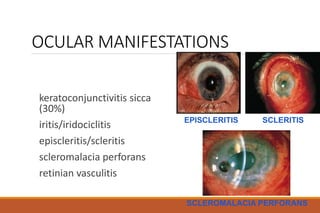
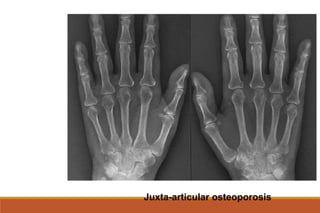
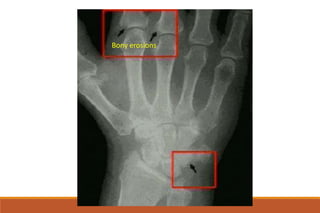
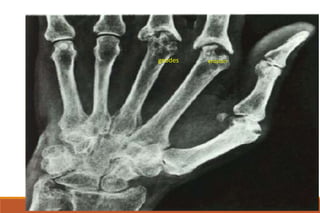
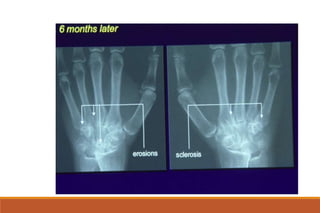
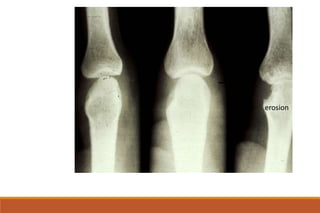
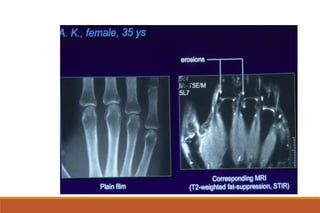
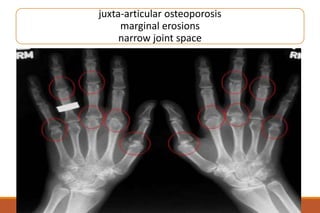
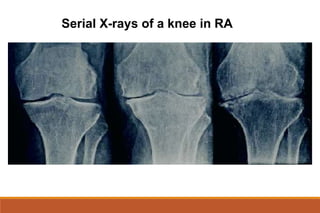
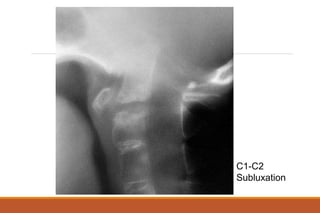
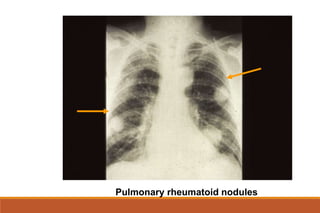
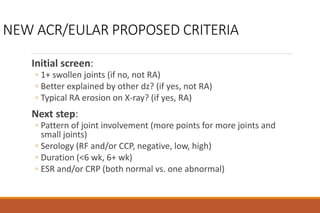
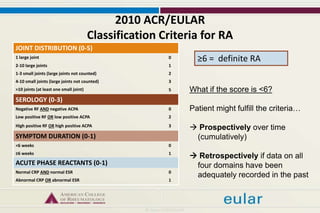
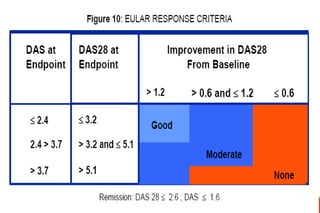
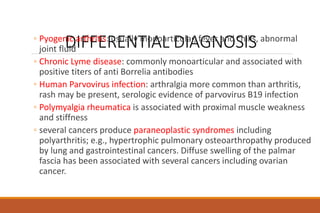
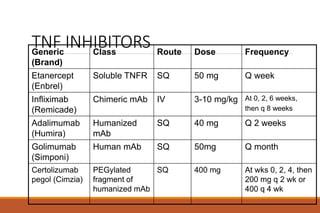
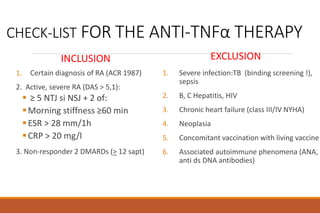
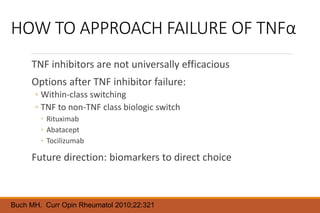
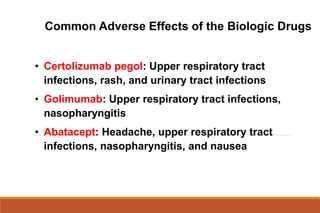
This document provides an overview of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), including its definition, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, investigations, assessment, monitoring, and management. RA is a chronic inflammatory disease that commonly affects the small joints in a symmetrical pattern. It is characterized by proliferative synovitis driven by autoimmune and inflammatory processes. Clinical features may include joint stiffness, swelling, and pain as well as systemic symptoms. Investigations include labs showing inflammation, rheumatoid factor or CCP antibodies, and characteristic findings on x-ray such as erosions. The goal of management is remission and minimal disease activity using treatments like DMARDs and biologics tailored to disease severity and prognosis.