A queue is a first-in, first-out (FIFO) data structure where insertion is done at the rear end and deletion is done at the front end. It can be implemented using either an array or linked list. Basic operations on a queue include enqueue, which inserts an item at the rear, and dequeue, which removes an item from the front. A circular queue addresses the issue of empty spaces in a linear queue by connecting the rear end to the front so the queue can migrate in a circular fashion.

![Page 2 of 7
Steps for inserting an Element in a Queue:a. Initialize both the front and rear as -1, which means that the queue is empty.
b. When the first element will be inserted then the rear and front both will be
incremented by 1. But for the second element onwards only the rear will be
incremented.
c. The value of rear can be maximum up to Max-1, where Max is the maximum
number of elements a queue can hold.
d. If the rear reaches Max-1, then display a message that “The queue is full or Queue
Overflow”.
Algorithm for Insert Operation:If rear=MAX
Print “Queue is full”
Else
rear=rear+1
Queue[rear]=value
END
2. Delete Operation on Queue:In a queue, delete operation takes place at front end. The “Dequeue”operation removes
the item at the “front” of the queue and returns it.
Steps for deleting an Element in a Queue:a. When an element will be deleted from the queue the value of front will be
decremented by 1.
b. The value of front can be minimum up to 0.
c. If the front reaches -1, then display a message that “The queue is empty or Queue
Underflow”.
Prepared By Sumit Kumar Gupta, PGT Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04queue-140115221427-phpapp02/85/Queue-2-320.jpg)
![Page 3 of 7
Algorithm for Delete Operation:If front=rear
Print “Queue is Empty” and Exit from the Program
Else
front=front+1
value=Queue[front]
END
B. LINKED LIST REPRESENTATION OF QUEUE:As we know if we implement the queue in array, sometimes number of memory location
remains unused. To overcome this drawback, it is better to implement queue using linked
list.
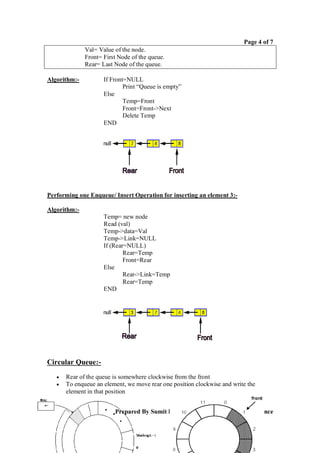
Performing one Dequeue/ Delete Operation:Here
Temp=New node.
Prepared By Sumit Kumar Gupta, PGT Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04queue-140115221427-phpapp02/85/Queue-3-320.jpg)
![Page 5 of 7
To dequeue, we simply move front one position clockwise
Queue migrates in a clockwise direction as we enqueue and dequeue
Emptiness and fullness to be checked carefully.
Apple
Orange
Banana
Front
Guava
Rear
In the above situation queue overflow will occur though the free spaces are also
available since the rear reaches the end. So, queue is full, but still there are two
free cells are available in queue. To avoid this problem, the queue can be arranged
in a circular way called circular queue.
In a circular queue as soon as the rear reaches the Max value, it should be reset to
1. So, if we have to insert Pineapple in the above queue we can insert it into the
first place.
Pineapple
Rear
Apple
Front
Orange
Banana
Guava
Algorithm to Insert an element in a Circular Queue:Note:- Let initially Rear=1 and Front=1.
If (rear+1) Mod Max=Front)
Print “Queue is full”
Else if Rear=Max
Rear=1
Else
Rear=Rear+1
End If
Queue[Rear]=Val
END
Algorithm to Delete an element in a Circular Queue:Prepared By Sumit Kumar Gupta, PGT Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04queue-140115221427-phpapp02/85/Queue-5-320.jpg)
![Page 6 of 7
Note:- Let initially Rear=1 and Front=1.
If Front=Rear
Print “Queue is empty”
Else if Front=Max
Front=1
Else
Front=Front+1
End if
Val=Queue[Front]
END
QUESTION BANK
1. What does ‘front’ signify in a queue?
Ans: Removal of elements from a queue is done through the front terminal.
2. What does ‘rear’ signify in a queue? If in a queue, the ‘rear’ points to the ‘front’,
what is the queue called?
Ans: Insertion of element in a queue is done in the ‘rear’ end. If in a queue, the rear
points to the front, then the queue is considered to be empty.
3. What is the full form of a dequeue?
Ans: It is Double-ended queue.
4. What is the dequeue called that allows insertion at only one end but deletion at
both the ends of the list? What is the dequeue called that allows deletion at only
one end but insertion at both the ends of the list?
Ans:
i. Input restricted dequeue.
ii. Output restricted dequeue.
5. Consider the following circular queue, where CQUEUE is allocated N=6 memory
cells: CQUEUE: AAA, DDD, EEE, FFF, GGG, __________
Describe the queue as the following operation take place:
(a) Insert (CQUEUE, KKK) (b) POP (CQUEUE, ITEM)
(c) Insert (CQUEUE, LLL) (d) Insert (CQUEUE, SSS)
(e) POP (CQUEUE, ITEM) (f) Insert (CQUEUE, TTT)
Ans:
(a) AAA, DDD, EEE, FFF, GGG, KKK
Prepared By Sumit Kumar Gupta, PGT Computer Science](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04queue-140115221427-phpapp02/85/Queue-6-320.jpg)
