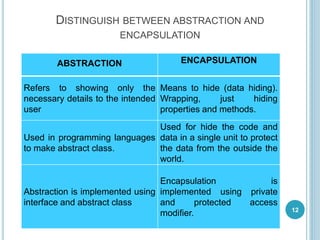
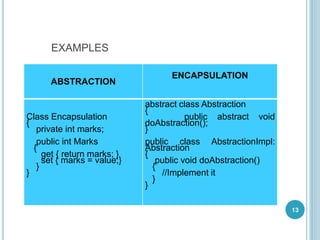
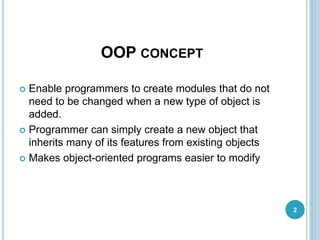
This document provides an introduction to object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts. It discusses the history and advantages of OOP, including enabling code reuse through inheritance and encapsulation. Key OOP concepts like classes, objects, encapsulation, abstraction, inheritance, polymorphism are defined. Classes are blueprints that define common attributes and behaviors of objects. Objects are instances of classes. Encapsulation binds code and data together, hiding implementation details. Inheritance allows classes to inherit behaviors from superclasses. Polymorphism allows the same interface to exhibit different behaviors depending on data types used.

![HISTORY OF OOP
Many people believe that OOP is a product of the
1980s (Bjarne Stroustrup).
Actually, SIMULA 1 (1962) and Simula 67 (1967)
[earliest object-oriented languages]
The work on the Simula languages (Ole-John Dahl
and Kristen Nygaard) at the Norwegian Computing
Center in Oslo, Norway.
Most of the advantages of OOP available in the
earlier Simula languages, it wasn't until C++
became entrenched in the 1990s that OOP began
to flourish.
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/babsatu-140703233001-phpapp01-240127025836-863dde32/85/babsatu-140703233001-phpapp666666601-pdf-3-320.jpg)