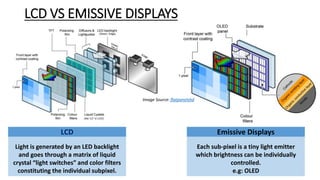
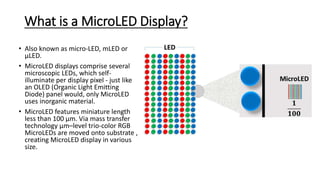
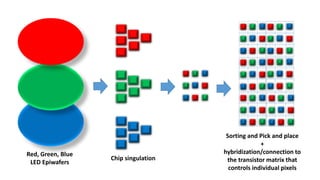
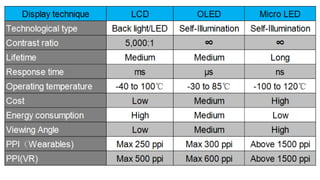
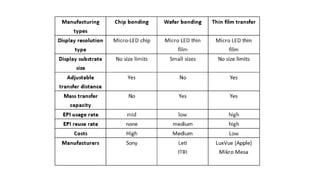
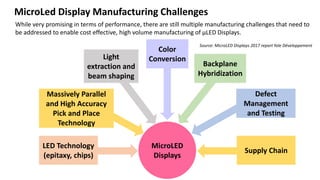
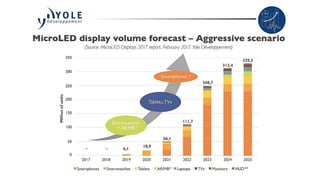
MicroLED displays comprise arrays of microscopic LEDs that self-illuminate individual pixels, similar to OLED but using inorganic material. They offer advantages over LCD and OLED like high dynamic range, wide color gamut, and long lifetime. However, manufacturing microLEDs at a small scale remains challenging and expensive for mass production. Key challenges include parallel pick and place of microLED chips, light extraction, and defect management during the manufacturing process. If the challenges can be addressed, microLED has potential applications in devices like smartwatches, VR/AR headsets, automotive displays, and future generation TVs and smartphones.